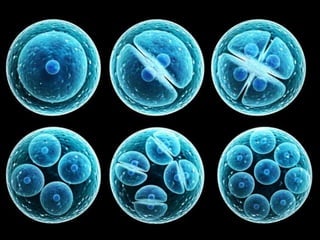
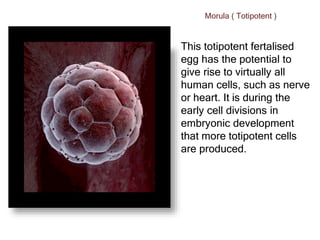
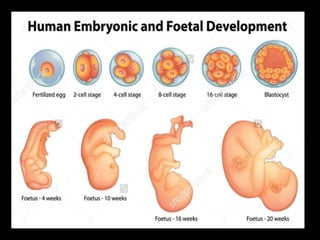
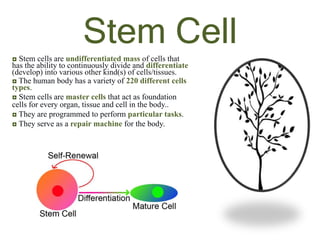
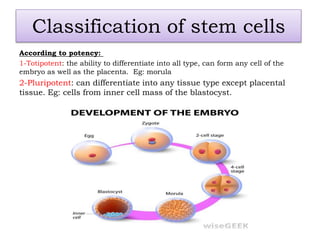
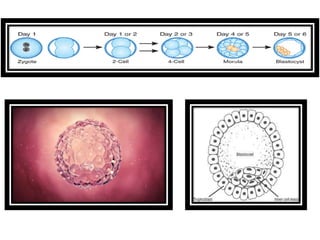
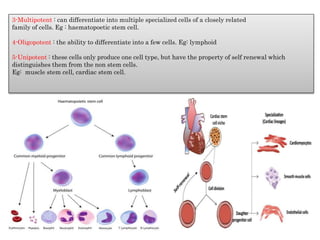
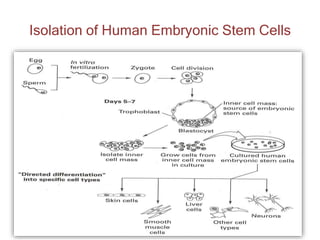
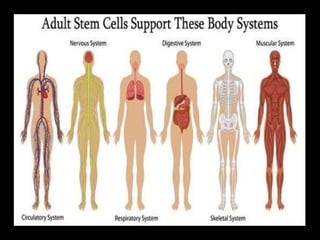
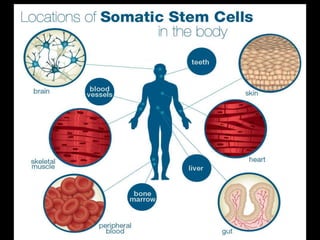
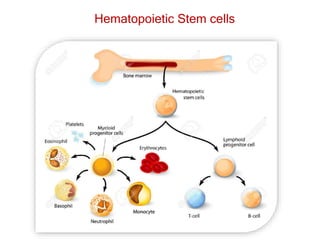
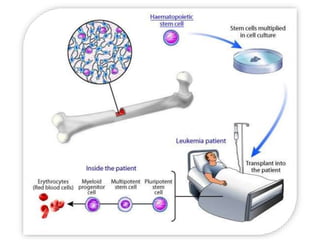
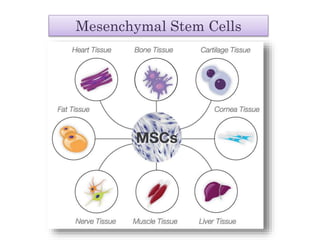
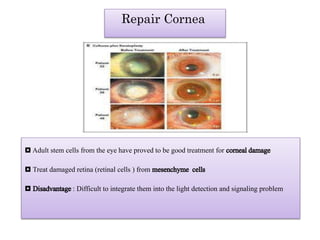
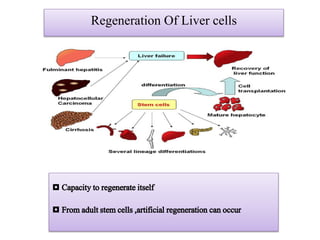
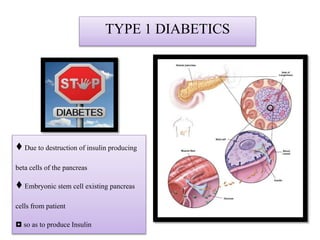
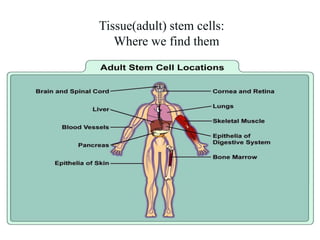
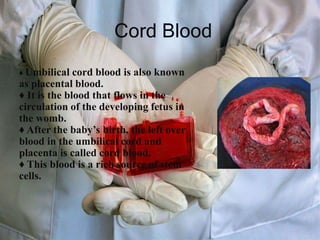
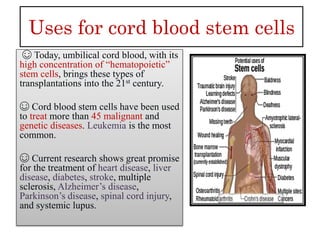
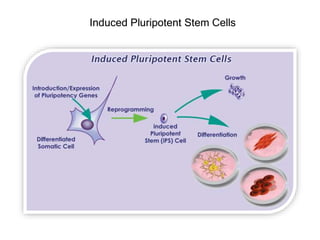
The document discusses stem cells, the basic unit of life that can divide and differentiate into various cell types, and classifies them based on potency and origin. It covers different types of stem cells including totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent, and unipotent, along with their sources such as embryonic, fetal, and adult stem cells. The potential applications of stem cells in medical treatments and therapies, along with ethical considerations, are also highlighted.