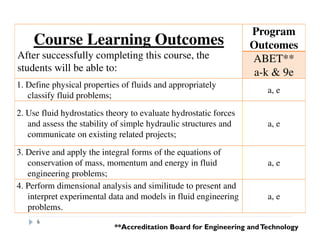
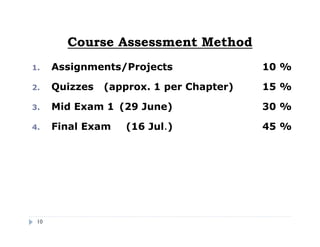
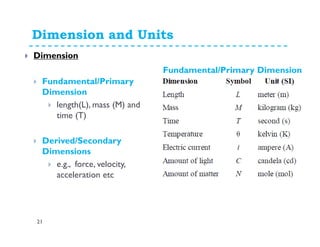
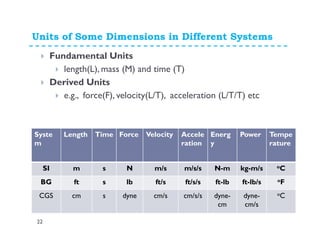
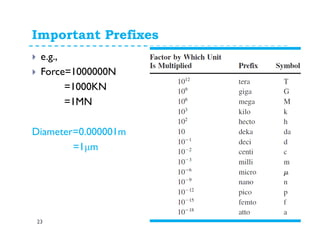
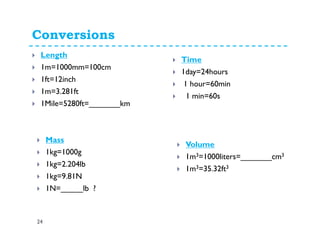
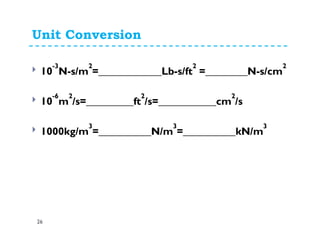
This document provides an introduction and overview of a fluid mechanics course taught by Dr. Mohsin Siddique. It outlines the course details including goals, topics, textbook, and assessment methods. The course aims to provide an understanding of fluid statics and dynamics concepts. Key topics covered include fluid properties, fluid statics, fluid flow measurements, dimensional analysis, and fluid flow in pipes and open channels. Students will be evaluated through assignments, quizzes, a midterm exam, and a final exam. The course intends to develop skills relevant to various engineering fields involving fluid mechanics.