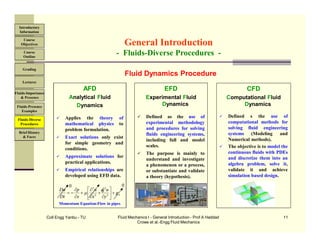
The document outlines the course 'Fluid Mechanics I (ME 371)' for junior engineering students, highlighting its objectives, prerequisites, textbook, and grading structure. It details the course content, including fluid properties, fluid statics, and dynamics, while emphasizing the importance of fluids in various applications like weather, medicine, and engineering. The course includes theoretical lectures and laboratory sessions to enhance understanding through practical experiments.