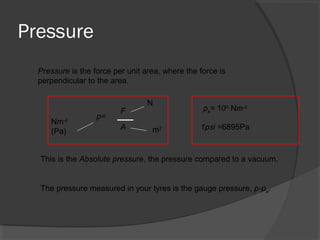
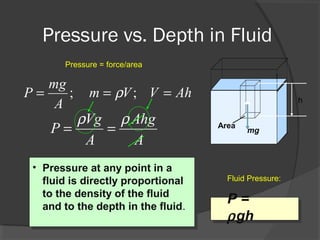
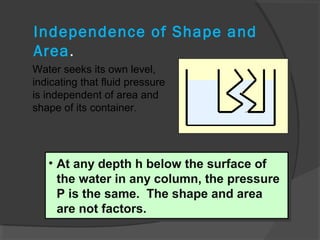
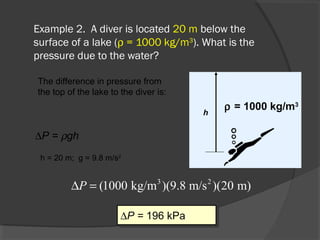
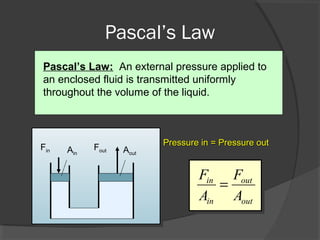
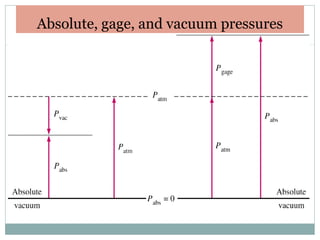
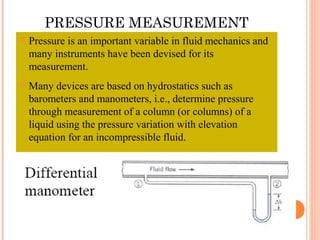
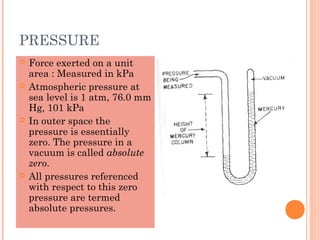
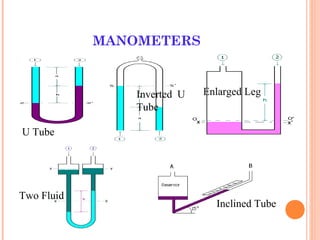
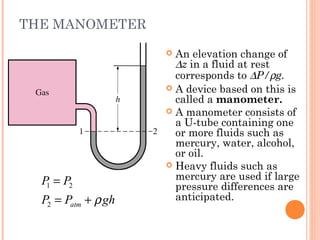
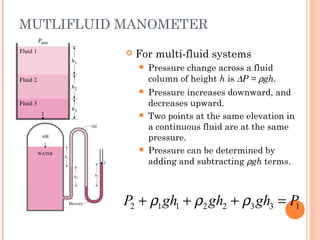
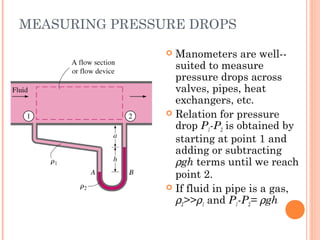
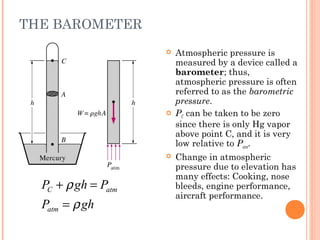
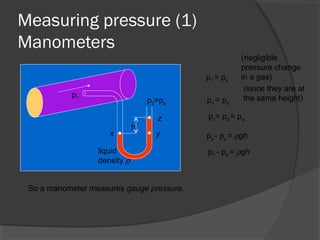
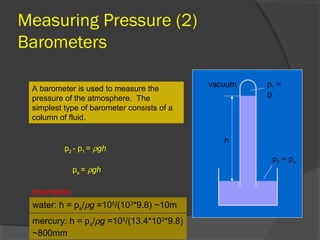
This document discusses fluid pressure and various ways to measure it. It defines pressure as a force per unit area and explains that pressure increases linearly with depth in a static fluid. It also describes how manometers and barometers work to measure pressure differences and atmospheric pressure respectively using the hydrostatic pressure equation. Manometers use columns of liquid like mercury or water, while barometers use a mercury column to directly measure atmospheric pressure at sea level.