This document provides an introduction to embedded systems and microcontrollers. It defines an embedded system as a computer system designed to perform a specific task and is contained within a larger system. Microcontrollers are described as the "brain" or central processing unit of an embedded system. Key points include:
- Microcontrollers integrate a processor, memory and input/output ports on a single chip, making embedded systems more compact and energy efficient than those using general purpose microprocessors.
- Embedded systems have a diverse range of applications from consumer electronics to industrial equipment to automobiles. Nearly every electronic device today contains one or more embedded systems.
- Microcontrollers are cheaper and better suited than microprocessors for many embedded applications as they require

![08072013
EMBEDDED SYSTEM EXAMPLES
Embedded systems are used in all aspects of
modern life and there are many examples of
their use, including:
1. Telecommunications systems
2. Consumer electronics
3. Transportation systems
EMBEDDED SYSTEM EXAMPLES
..cont…
Physically, embedded systems range from
portable devices such as digital watches
and MP3 players, to large stationary
installations like traffic lights, factory
controllers, or the systems controlling
nuclear power plants.
4. Medical equipment
5. Etc
EMBEDDED SYSTEM EXAMPLES
Line Follower
Robot
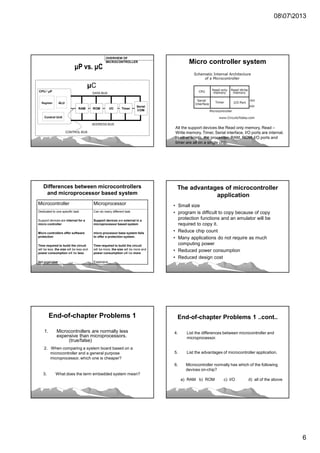
• Microcontroller is great…how about our
computer (microprocessor)?
Next slide describe the difference between
uP and uC
Washing Machine
uP
For more
detail, please
refer book
page 25
uC
Air-Bag
Applications
Areas
Application Areas
• TV
• stereo
• remote control
• phone / mobile phone
• refrigerator
• microwave
• washing machine
• electric tooth brush
• oven / rice or bread cooker
• watch
• alarm clock
• electronic musical instruments
• electronic toys (stuffed animals,handheld toys, pinballs, etc.)
• medical home equipment (e.g. blood
pressure, thermometer)
•…
• [PDAs?? More like standard computer system]
Consumer Products
2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securedownload-131023225509-phpapp01/85/Embedded-system-Chapter-1-2-320.jpg)
![08072013
Application Areas
• Medical Systems
– pace maker, patient monitoring systems, injection systems,
intensive care units, …
• Office Equipment
– printer, copier, fax, …
• Tools
– multimeter, oscilloscope, line tester, GPS, …
• Banking
– ATMs, statement printers, …
• Transportation
– (Planes/Trains/[Automobiles] and Boats)
• radar, traffic lights, signalling systems, …
Application Areas
• Automobiles
– engine management, trip computer, cruise
control, immobilizer, car alarm,
– airbag, ABS, ESP, …
• Building Systems
– elevator, heater, air conditioning, lighting, key
card entries, locks, alarm systems, …
• Agriculture
– feeding systems, milking systems, …
• Space
– satellite systems, …
Application Areas
• Facts:
– 1997: The average U.S. household has over 10
embedded computers (source: www.it.dtu.dk/~jan)
Automobiles
• 1998: 90% Embedded Systems vs. 10%
Computers
– (source: Frautschi, www.caliberlearning.com)
• 2001: The Volvo S80 has 18 embedded
controllers and 2 busses (source: Volvo)
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/securedownload-131023225509-phpapp01/85/Embedded-system-Chapter-1-3-320.jpg)