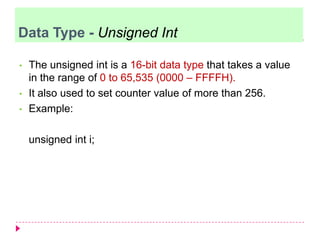
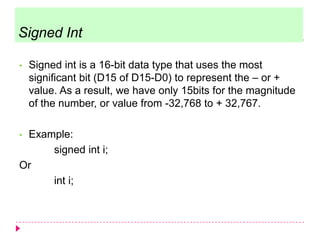
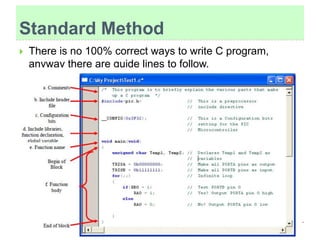
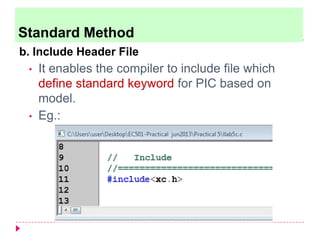
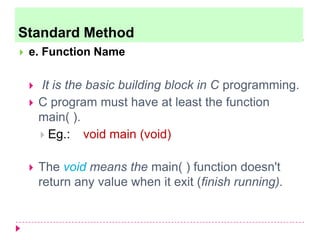
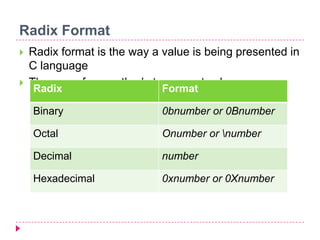
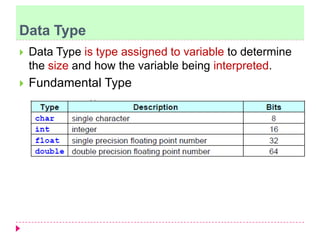
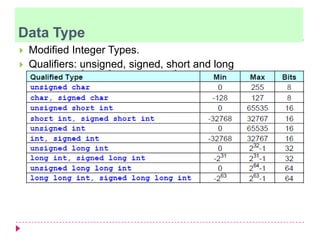
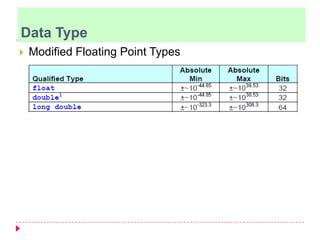
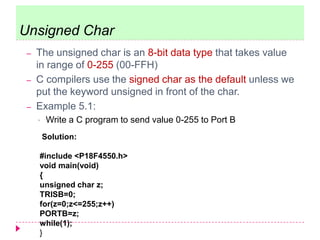
The document discusses C programming for PIC microcontrollers. It covers the reasons for using C over assembly, the standard structure of a C program including comments, header files, configuration bits, functions, and function bodies. It also discusses various C data types like unsigned char, signed char, unsigned int, signed int, and others; and provides examples of using these data types in programs.










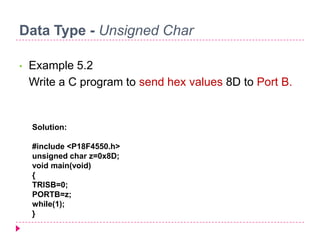

![Data Type - Signed Char
• Example 5-4
Write a C18 program to send values of -4 to
+4 to Port B.
Solution:
#include <P18F4550.h>
void main(void)
{
char mynum[ ]={+1,-1,+2,-2,+3,-3,+4,-4};
signed char z;
TRISB=0; //make Port B an output
for (z=0;z<8;z++)
{
PORTB=mynum[z];
}
while(1); //stay here forever](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter5-part1-140329135318-phpapp01/85/Embedded-system-Chapter-5-part-1-23-320.jpg)