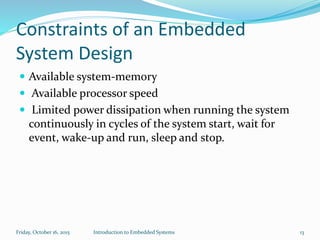
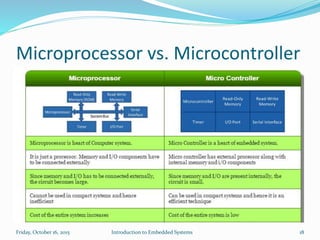
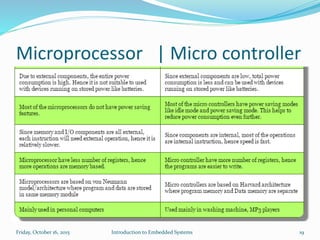
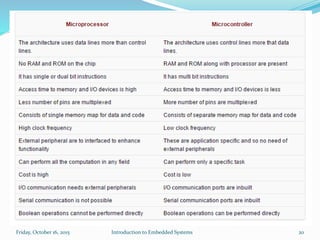
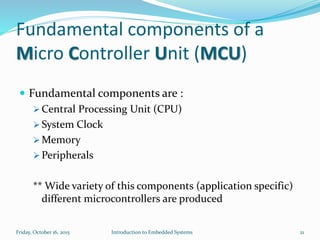
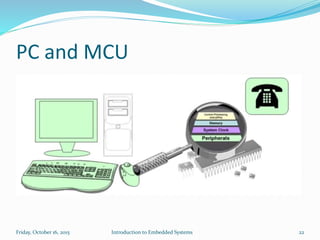
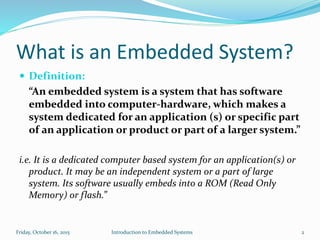
An embedded system is a dedicated computer system that performs specific tasks, and is embedded as part of a complete device including hardware and software. Examples include watches, washing machines, cell phones and more. Embedded systems have limited memory and processing capabilities compared to general purpose computers. They also have dedicated functions and real-time constraints. Microcontrollers are commonly used in embedded systems and contain a CPU, memory and programmable input/output peripherals on a single chip. Real-time operating systems help schedule tasks to meet timing constraints in embedded systems.


![Let’s consider a Computer
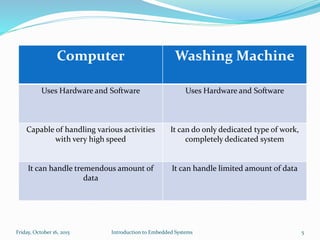
A computer is a system that has the following or more
components.
A microprocessor
A large memory comprising the following two kinds:
(a) Primary memory (semiconductor memories - RAM, ROM
and fast accessible caches)
(b) Secondary memory [(magnetic memory located in hard
disks, diskettes (Floppy Disk) and cartridge tapes, optical
memory in CD-ROM or memory stick (removable
flash memory card in mobile computer)] using which
different user programs can load into the primary memory
and can be run.
Sunday, November 8, 2015 Introduction to Embedded Systems 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-151016120011-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-Embedded-Systems-6-320.jpg)



![Sophisticated Embedded System
Characteristics
(1) Dedicated functions
(2) Dedicated complex algorithms
(3) Dedicated (GUIs) and other user interfaces for the
application
(4) Real time operations— Defines the ways in which the
system works, reacts to the events and interrupts,
schedules the system functioning in real time and executes
by following a plan to control the latencies and to meet the
deadlines. [Latency — Waiting interval between the
instance at which a need to run the codes arises for task (or
interrupt service routine) following an event and instance
of start executing the codes]
Sunday, November 8, 2015 Introduction to Embedded Systems 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1-151016120011-lva1-app6892/85/Introduction-to-Embedded-Systems-11-320.jpg)