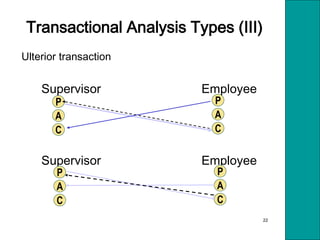
The document outlines essential interpersonal skills and competencies necessary for effective communication and conflict resolution, emphasizing self-awareness, motivation, and communication methods. It presents transactional analysis as a framework for understanding interpersonal dynamics, highlighting the significance of ego states (parent, adult, child) and types of transactions (complementary, crossed, ulterior) in interactions. Strategies for building positive relationships, handling criticism, and effective negotiation tactics are also discussed.