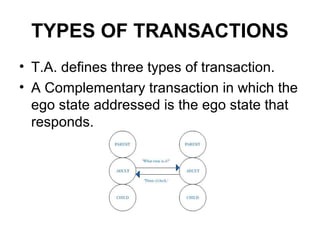
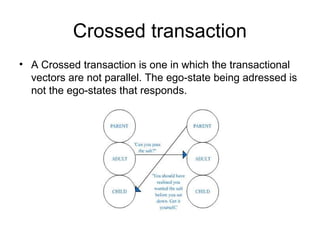
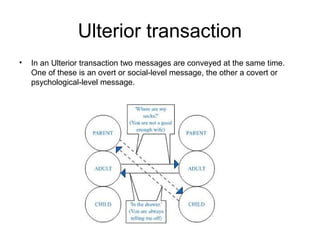
Transactional analysis (TA) is a theory of psychology that analyzes human behavior and communication through interactions called "transactions". TA posits that people operate through three ego states - Parent, Adult, and Child. Understanding these ego states and the different types of transactions (complementary, crossed, ulterior) between them provides insights to improve interpersonal communication and relationships. TA was developed by Eric Berne in the 1950s and remains a widely used approach in modern psychology.