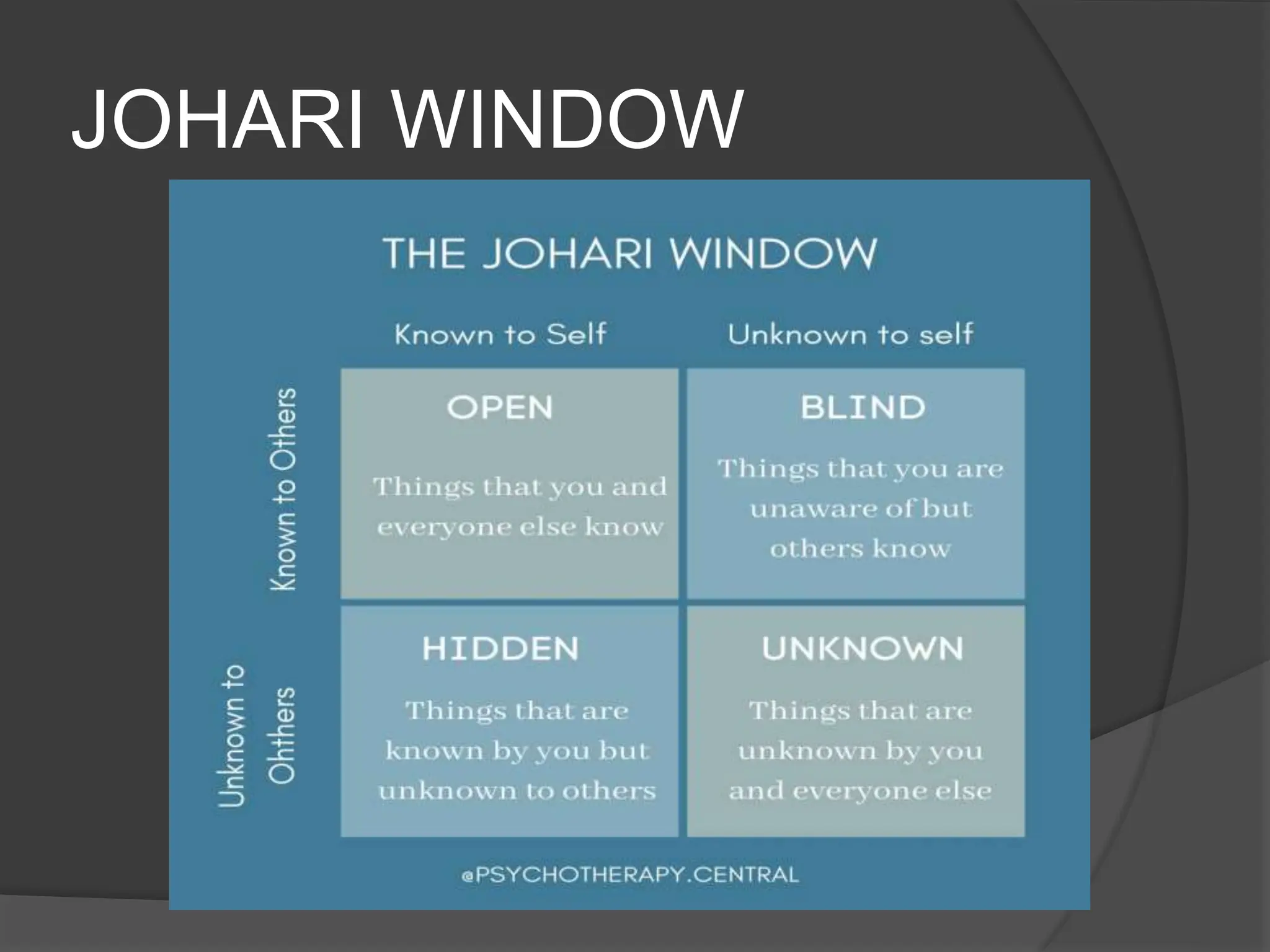
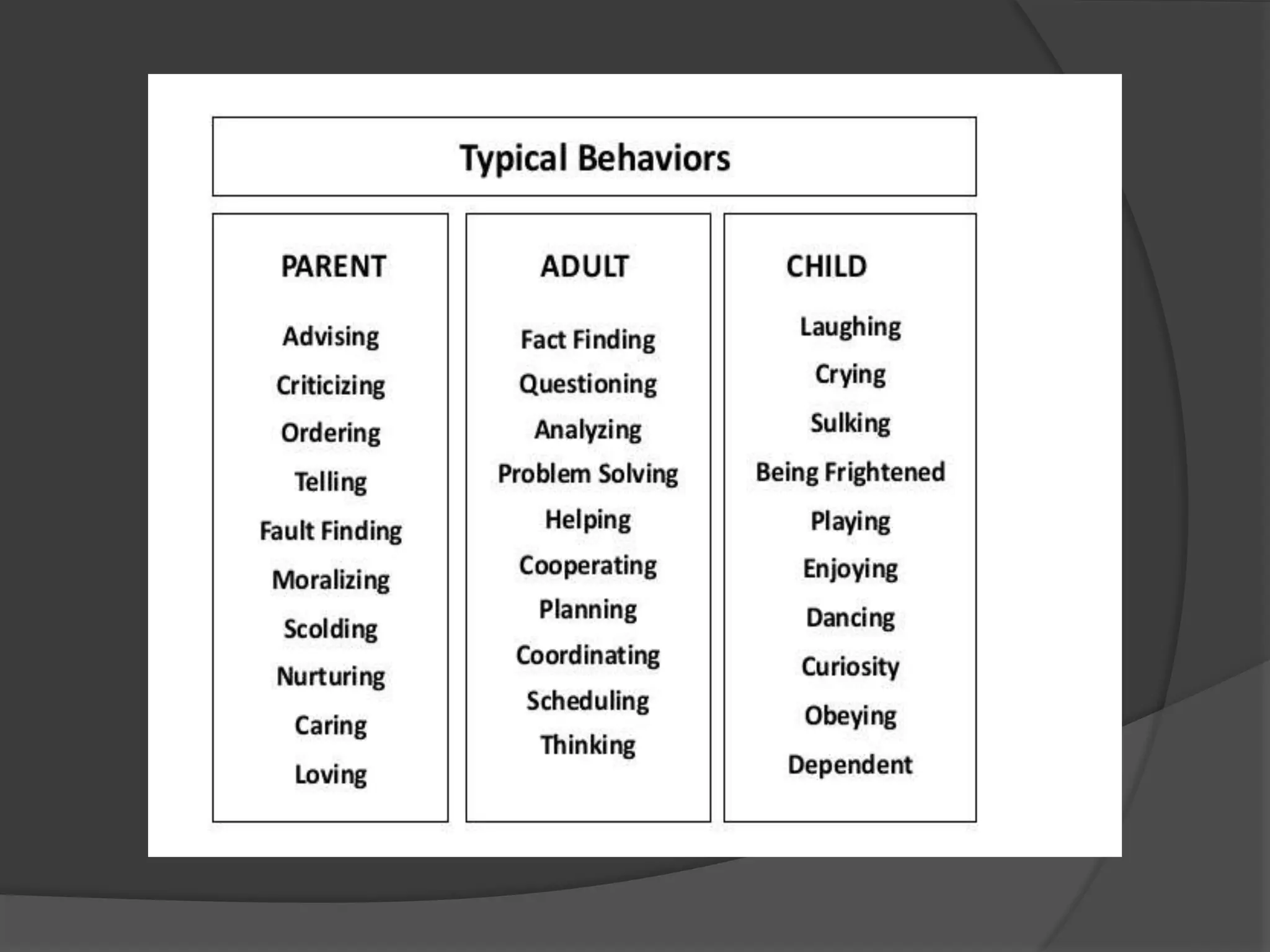
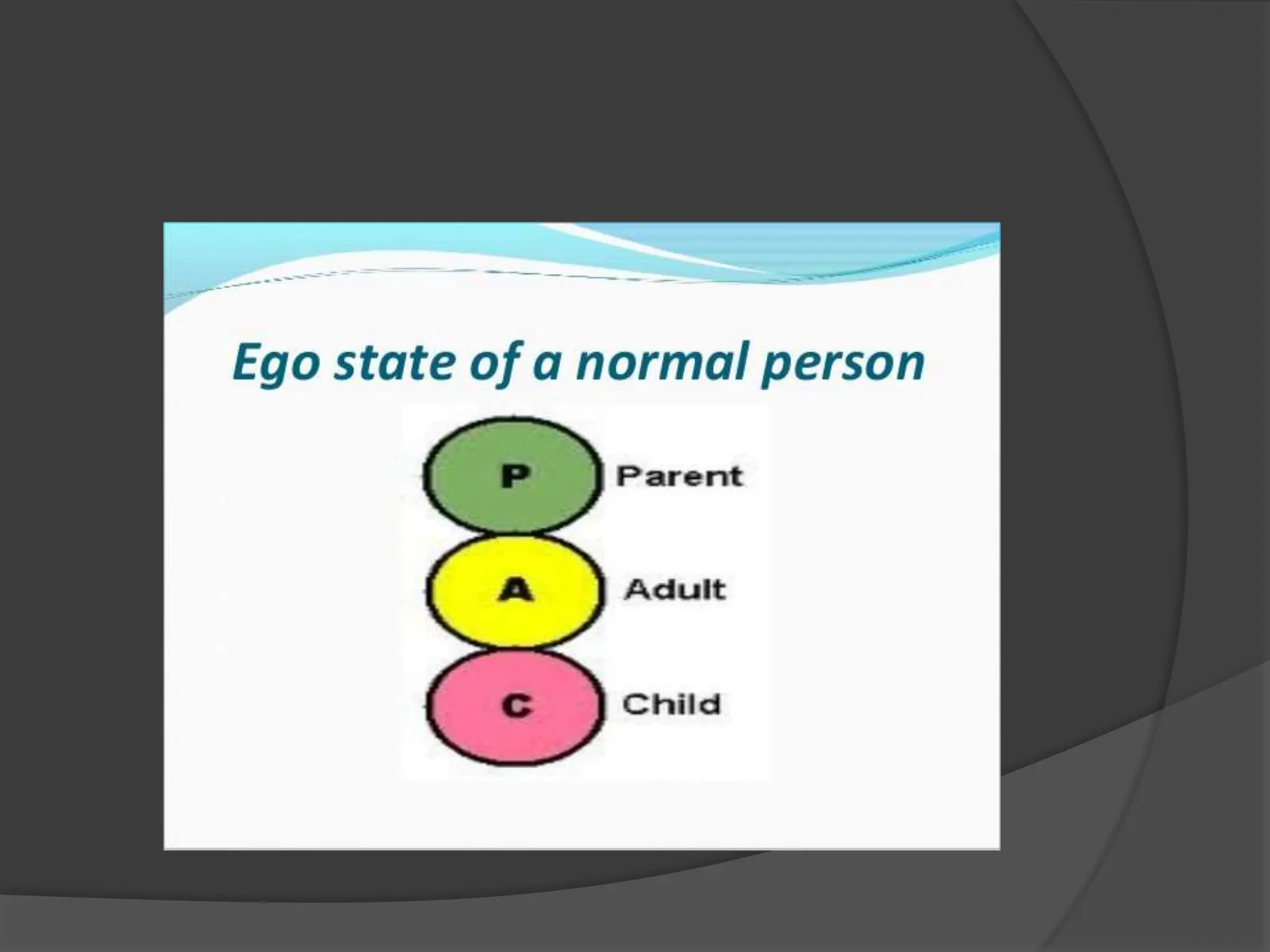
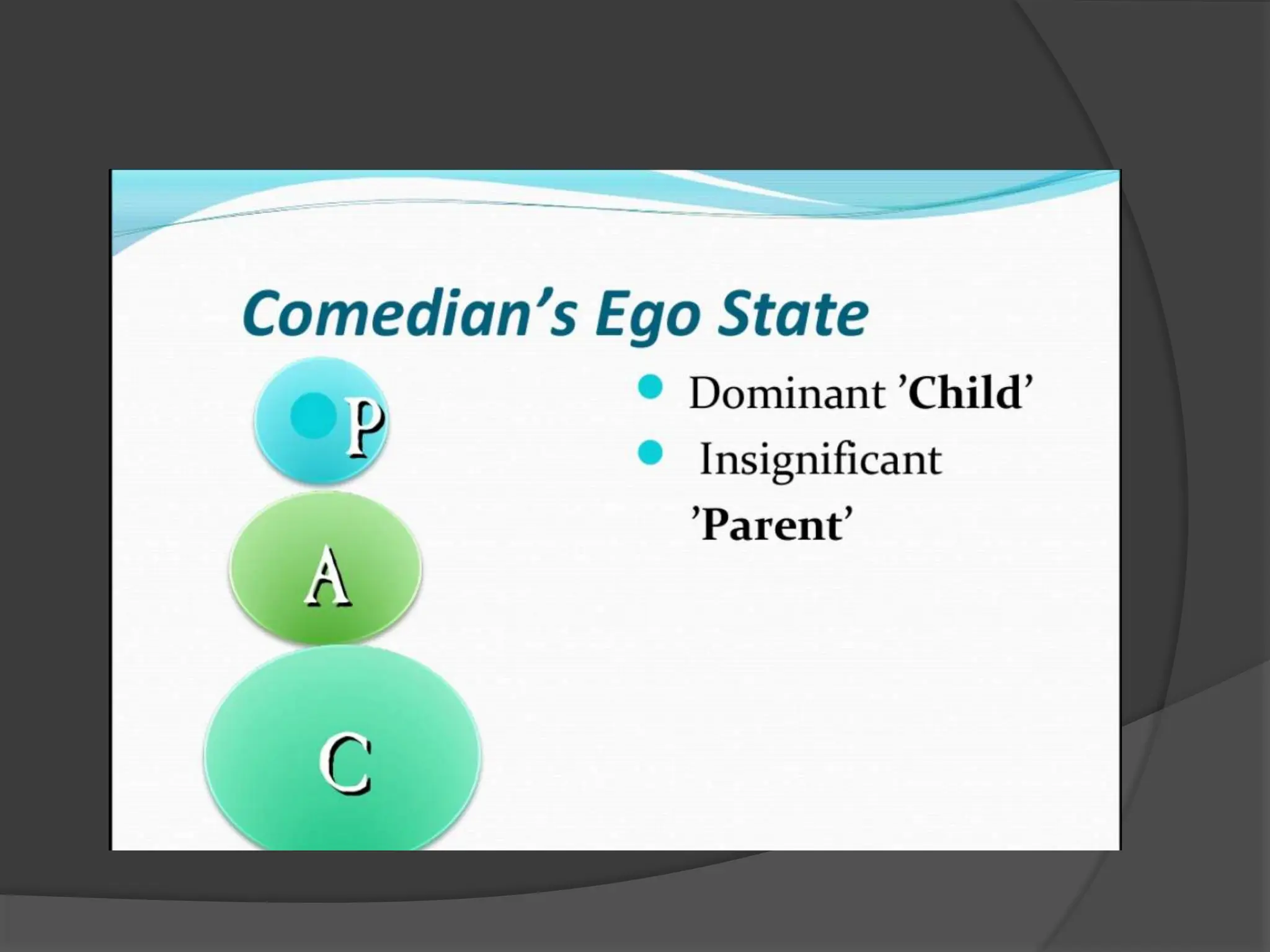
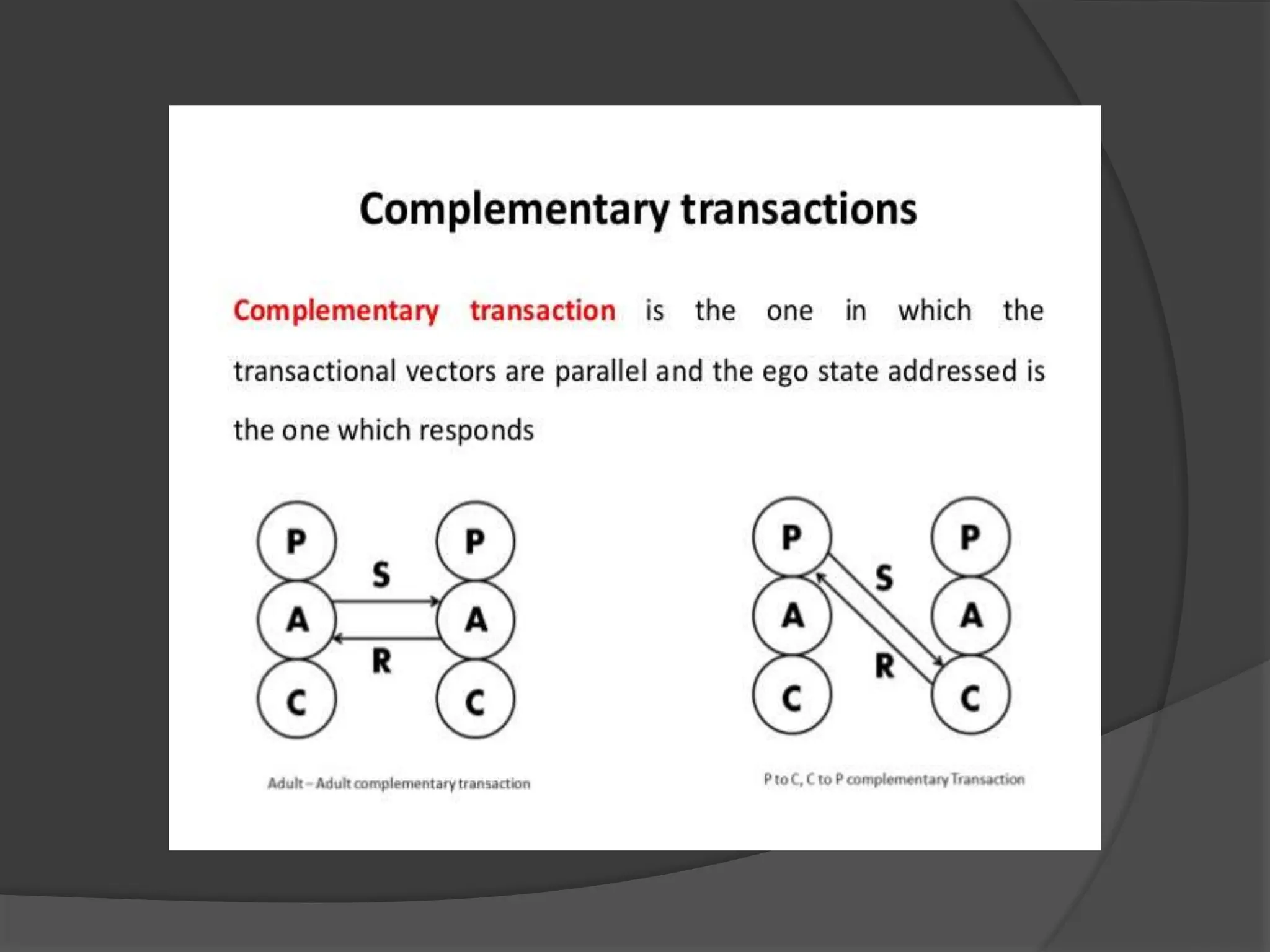
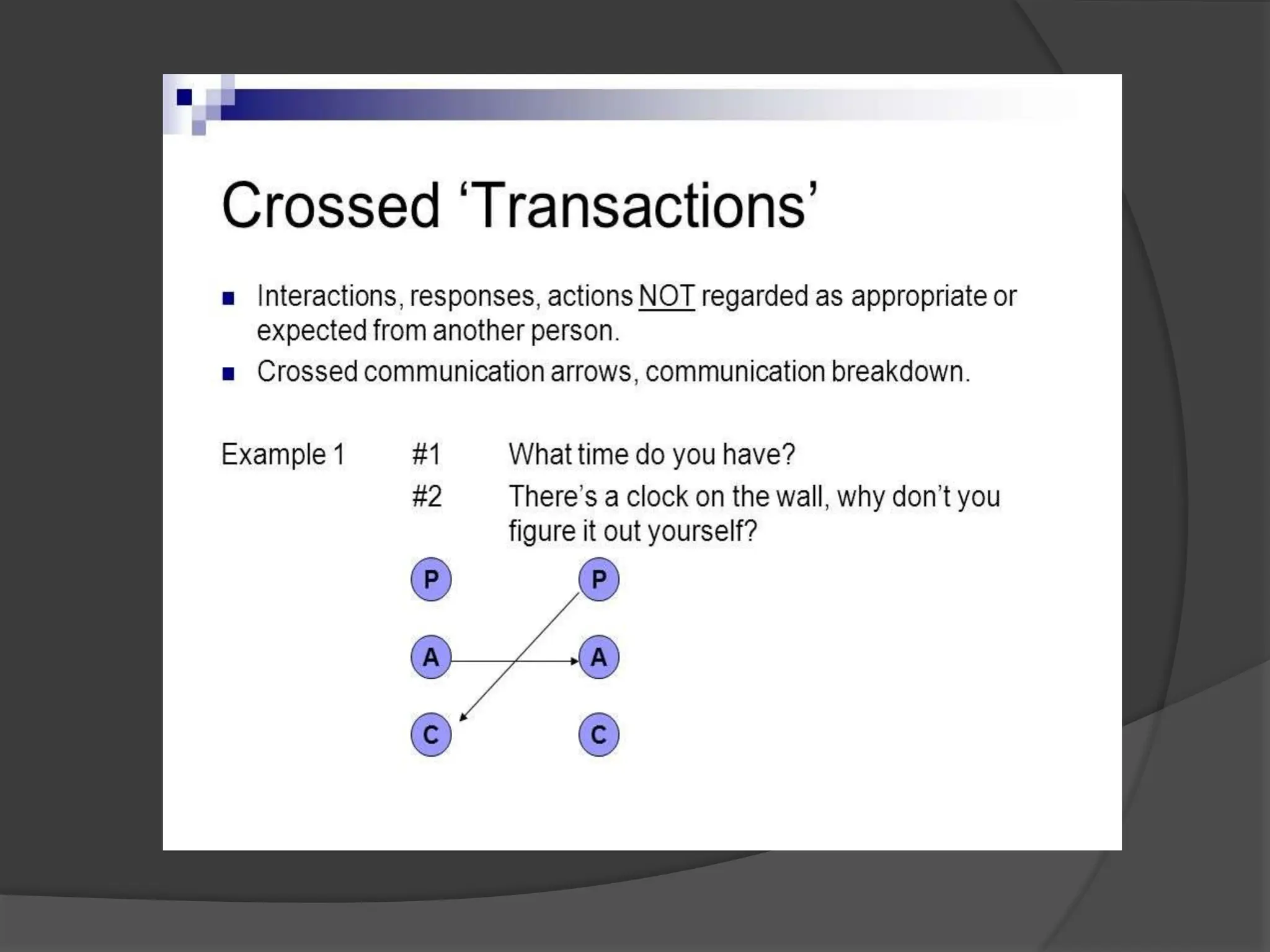
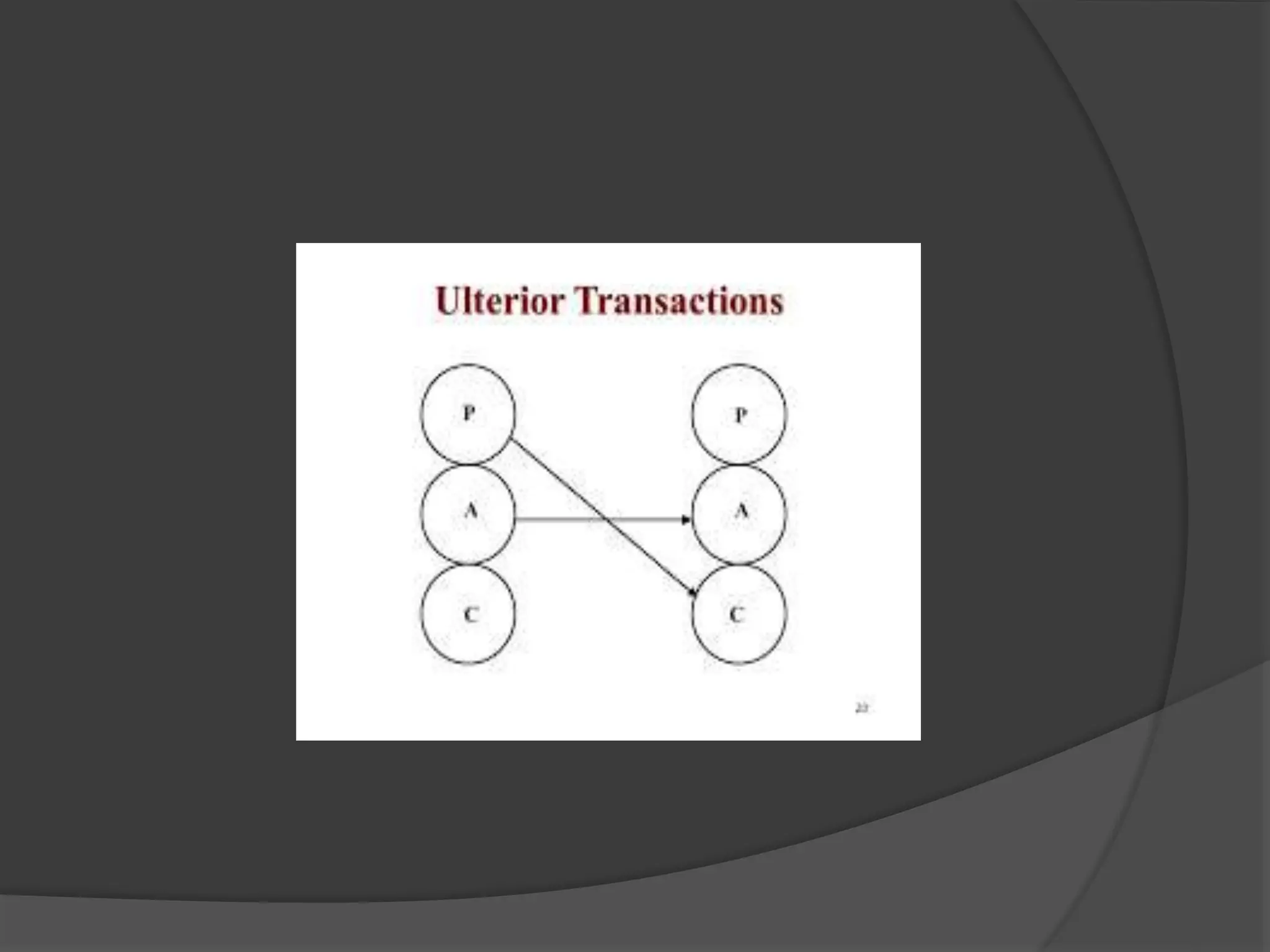
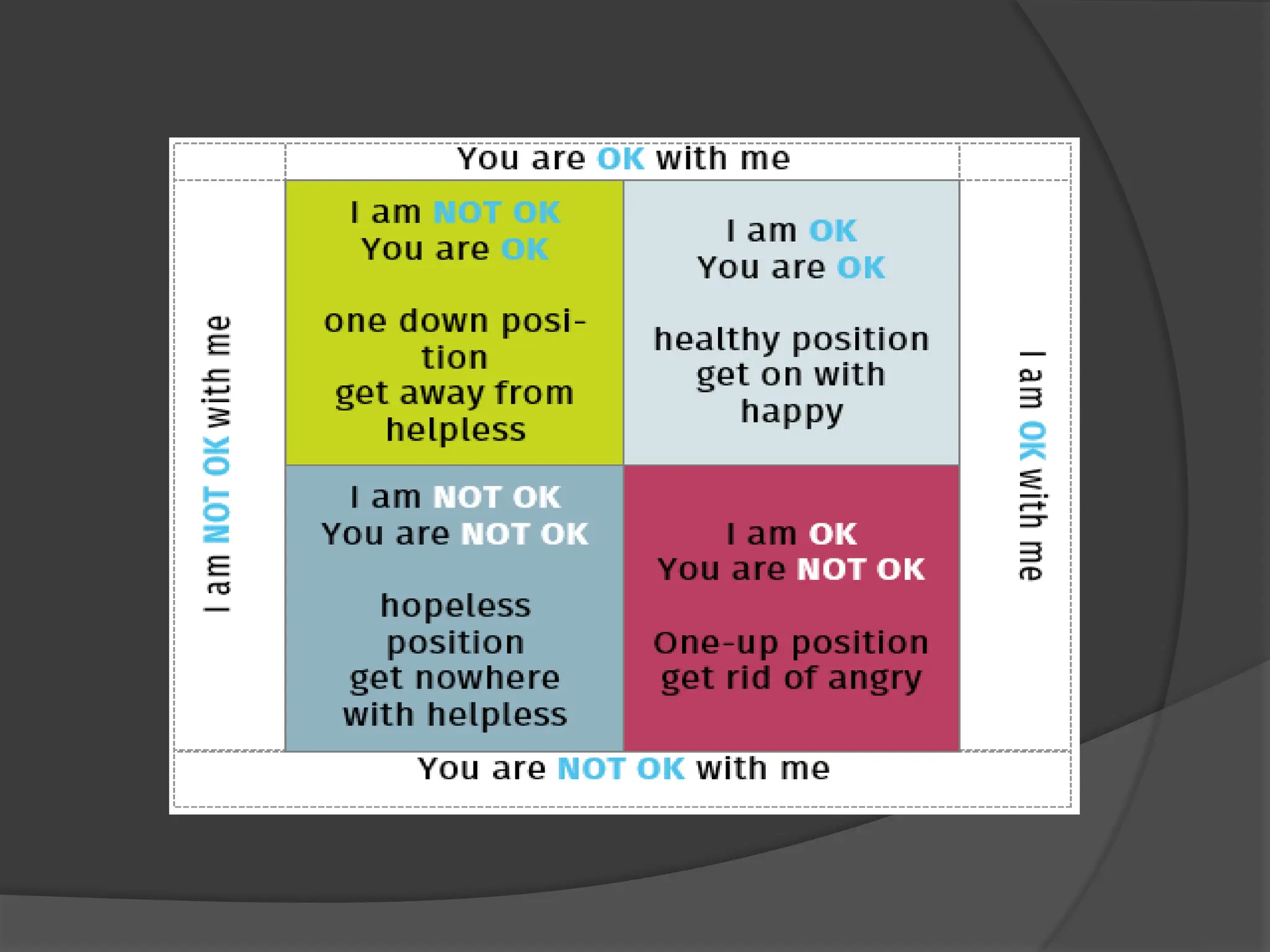
The document discusses transactional analysis, which is a technique used to understand interpersonal relationships and behavior. It involves analyzing ego states (parent, adult, child), transactions between people, scripts that guide behavior, and games people play. Transactional analysis aims to improve communication, understand motivations, and promote healthy relationships through awareness of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in interactions.