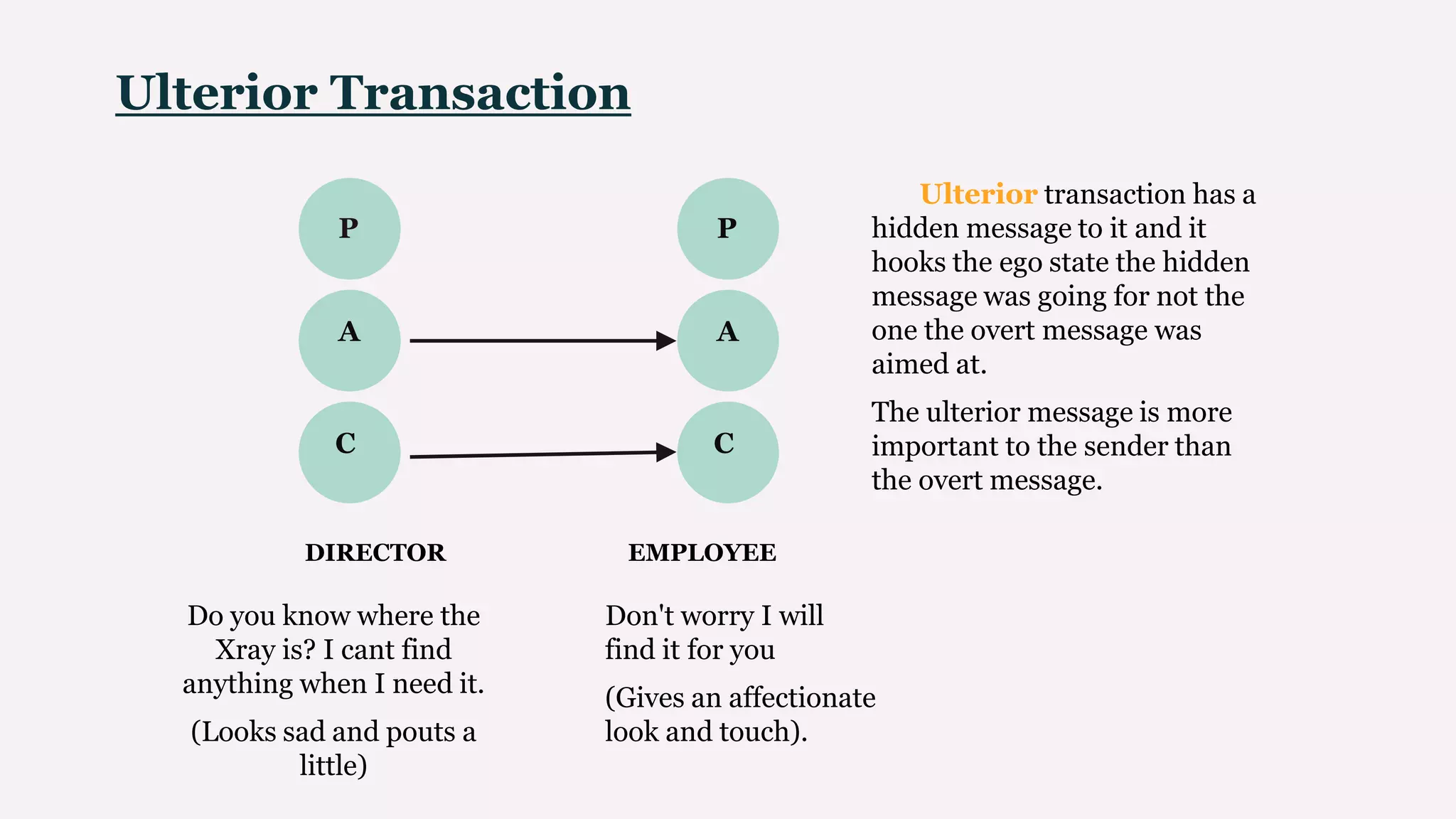
Transactional Analysis (TA) is a personality theory developed by Eric Berne that explores psychological structuring, communication, and interpersonal relationships, emphasizing that individuals have the capacity for change and deserve acceptance. It introduces key concepts like ego states (Parent, Adult, Child), life positions, transactional interactions, and the psychological games people engage in to meet their need for recognition or 'strokes.' TA is applied in psychotherapy to foster personal growth, improve communication, and aid in self-awareness and responsibility.