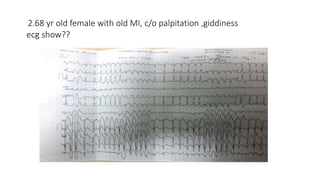
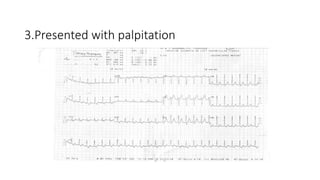
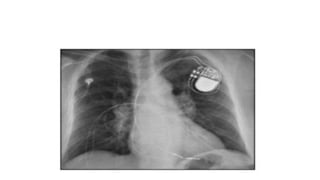
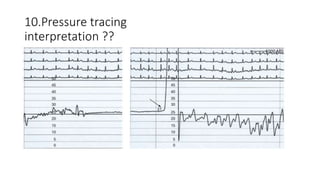
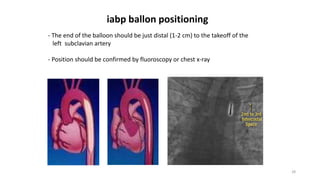
The document provides information about various cardiac conditions that can be identified on ECGs, echocardiograms, chest x-rays and other cardiac tests. It describes the findings and diagnoses for 12 different clinical cases, including polymorphic atrial tachycardia, preexcited atrial fibrillation, AV nodal reentrant tachycardia, Brugada syndrome, R-on-T phenomenon, hypokalemia, catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia, atrial lead dislodgment, atrial flutter, pulmonary and aortic pressures in ventricular septal defect, and intra-aortic balloon pump positioning.