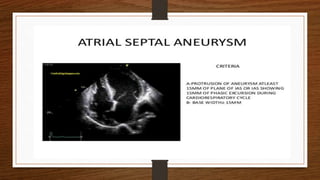
Atrial septal defect (ASD) closure can be performed surgically or percutaneously. Percutaneous closure is preferred for secundum ASDs that meet criteria such as defect size less than 38mm and adequate rim tissue. Echocardiography guides device placement and confirms closure. Complications include device embolization, arrhythmias, and erosion. Most studies report high success rates with percutaneous closure and shorter hospital stays than surgery. Surgical closure is preferred for sinus venosus, primum, or coronary sinus defects.









































![EFFECT OF DEFECT CLOSURE ON
RISK OF ATRIAL ARRHYTHMIAS
• Atrial arrhythmias, primarily atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter, occur in approximately 20 percent of adult patients with an ASD and are often
the presenting symptom.
• The risk of these arrhythmias increases with patient age (especially over age 40) and with higher pulmonary artery pressures .
• In a report of 211 adults, for example, the incidence of AF or atrial flutter prior to surgery was 1 percent for those aged 18 to 40, 30 percent
for those aged 40 to 60, and 80 percent in those over the age of 60.
• Observational data suggest that ASD closure may reduce but does not eliminate the risk of atrial tachyarrhythmias.
• The effect of surgical or percutaneous defect closure on the prevalence of atrial arrhythmias was evaluated by a systematic review, including
26 studies in which a total of 1841 patients (with median or mean age at least 18 years prior to intervention) underwent surgical closure and
945 patients underwent percutaneous closure .
• Meta-analysis demonstrated a reduction in the prevalence of atrial tachyarrhythmias after ASD closure (odds ratio [OR] = 0.66, 95% CI 0.57-
0.77).
• This effect was found after both surgical closure (OR = 0.72, 95% CI 0.60-0.87) and percutaneous closure (OR = 0.49, 95% CI 0.32-0.76). A
significant decline in atrial tachyarrhythmias was seen both at <30 days and midterm (30 days to five years) follow-up.
• Limitations of the analysis include differences in methods for monitoring arrhythmias before and after closure in most of the studies.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asddeviceclosure-210519103447/85/Asd-device-closure-44-320.jpg)

