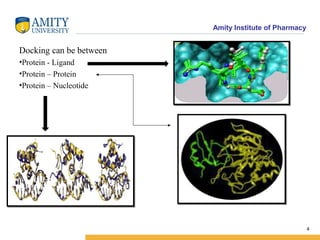
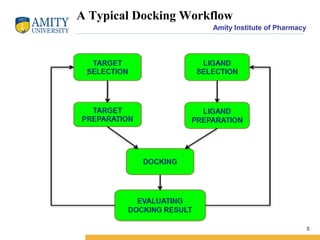
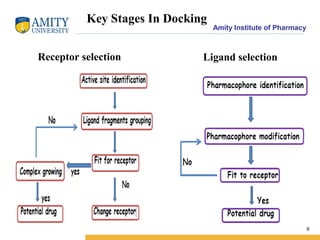
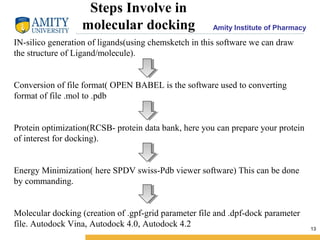
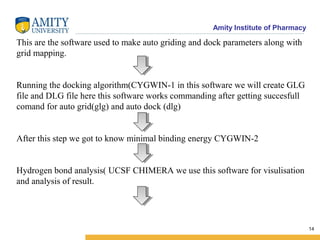
Molecular docking is a method for predicting how two molecules, such as a ligand and its protein target, will interact and fit together in three dimensions. Docking has become an important tool in drug discovery for identifying potential binding conformations between drug candidates and protein targets. The key steps in a typical docking workflow involve selecting the receptor and ligand molecules, then using software to computationally predict the orientation of binding and evaluate the fit through scoring functions. Popular molecular docking software packages include AutoDock, GOLD, and Glide. Applications of docking include virtual screening in drug discovery and lead optimization.