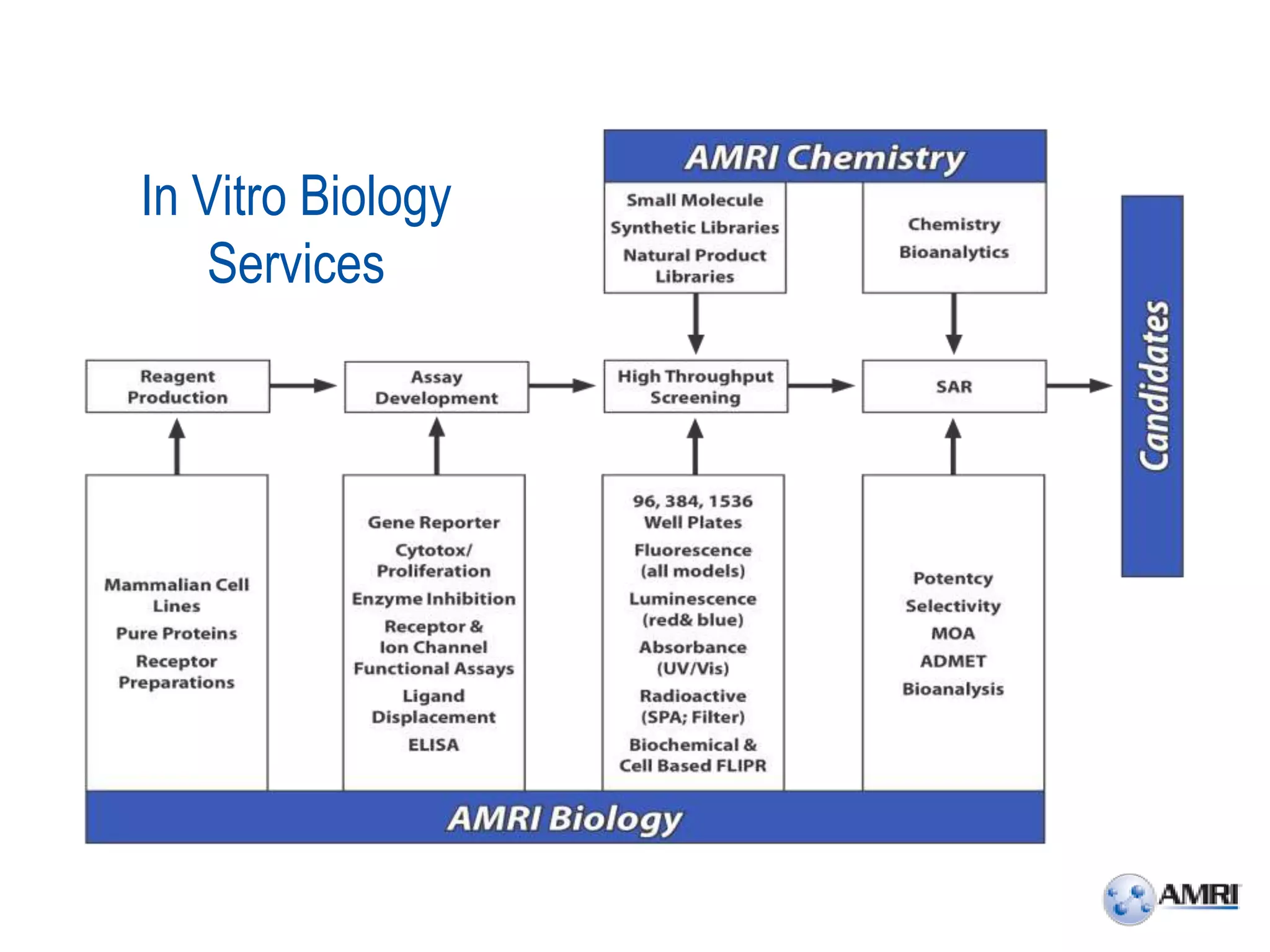
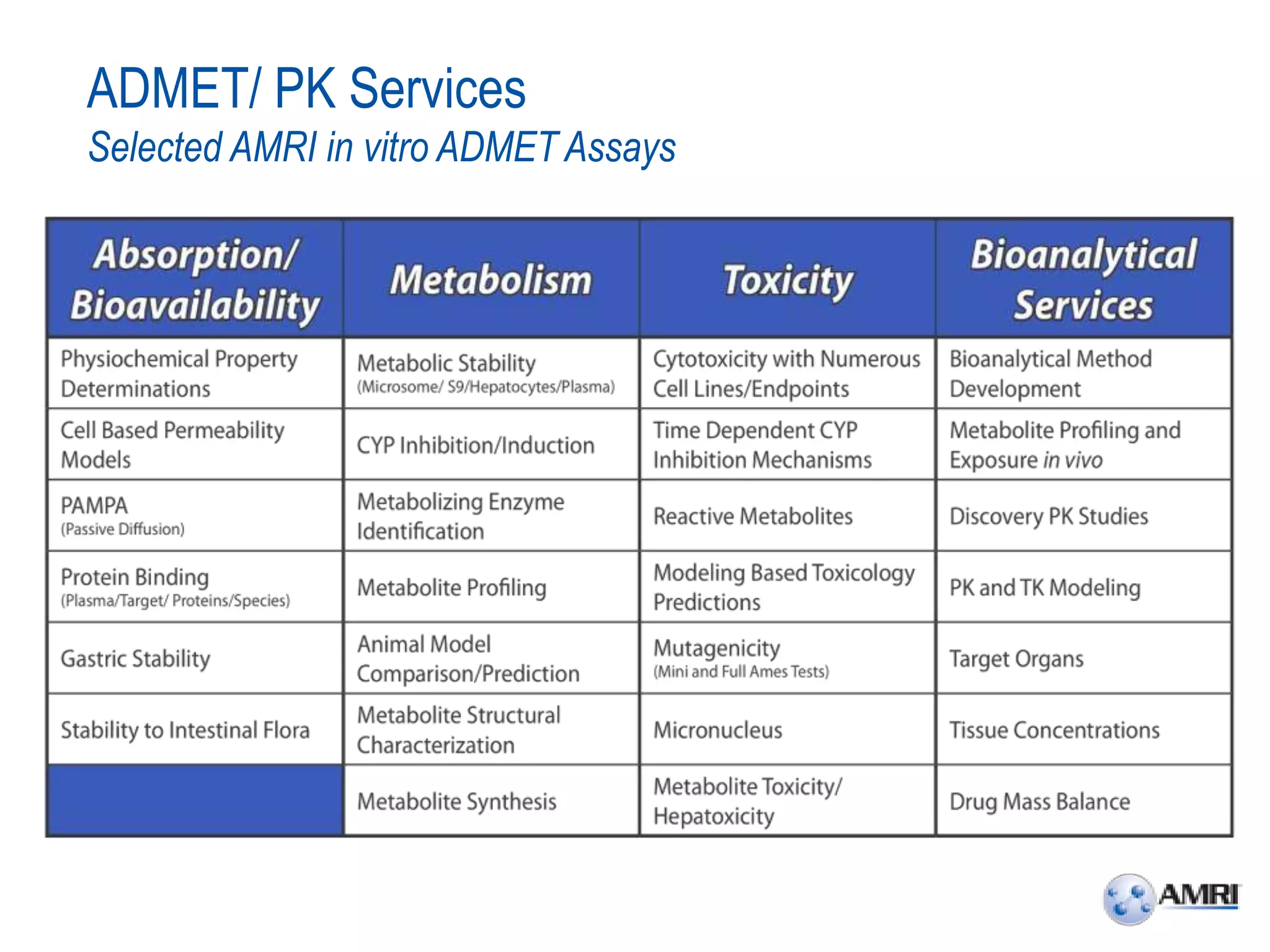
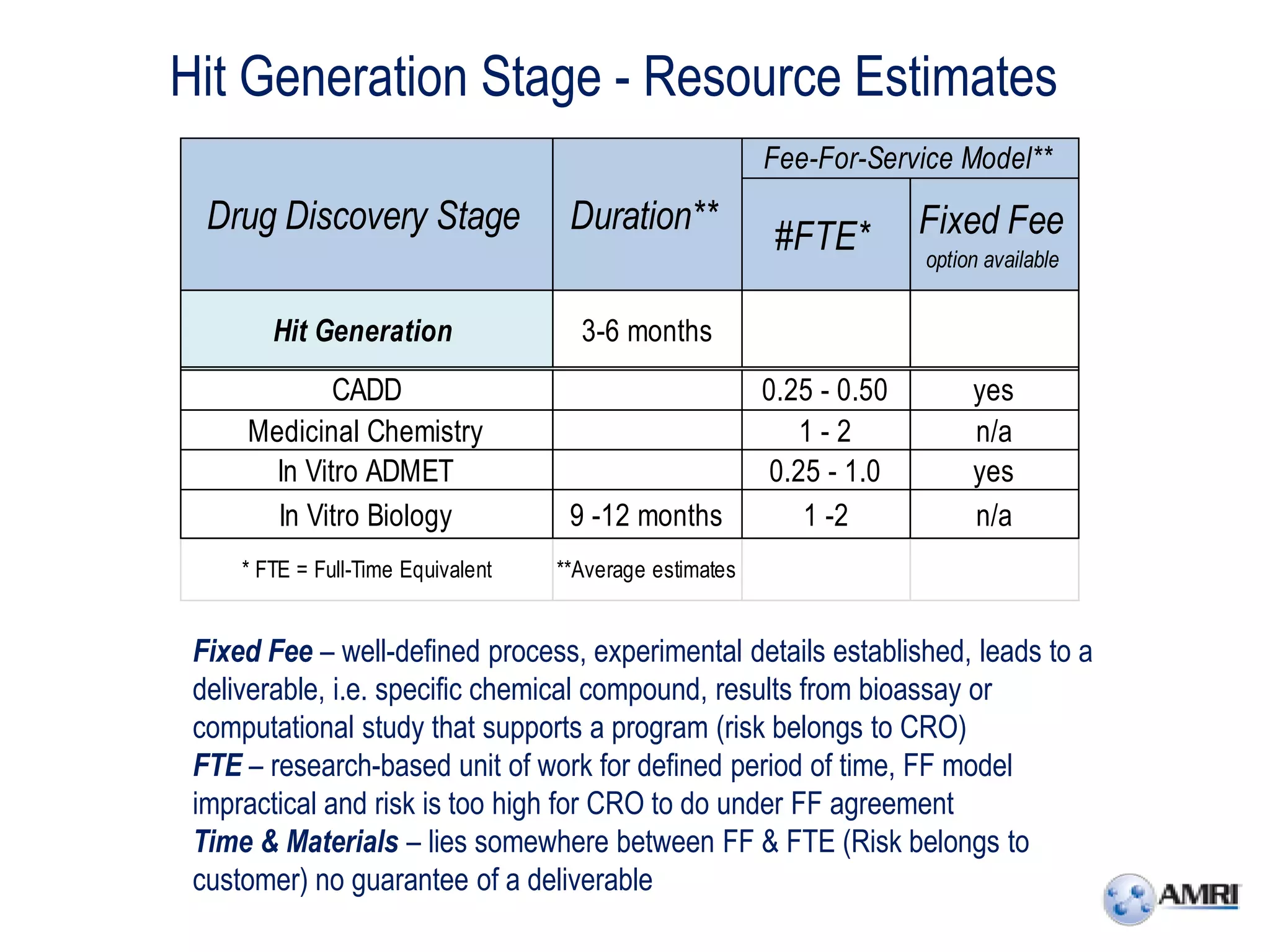
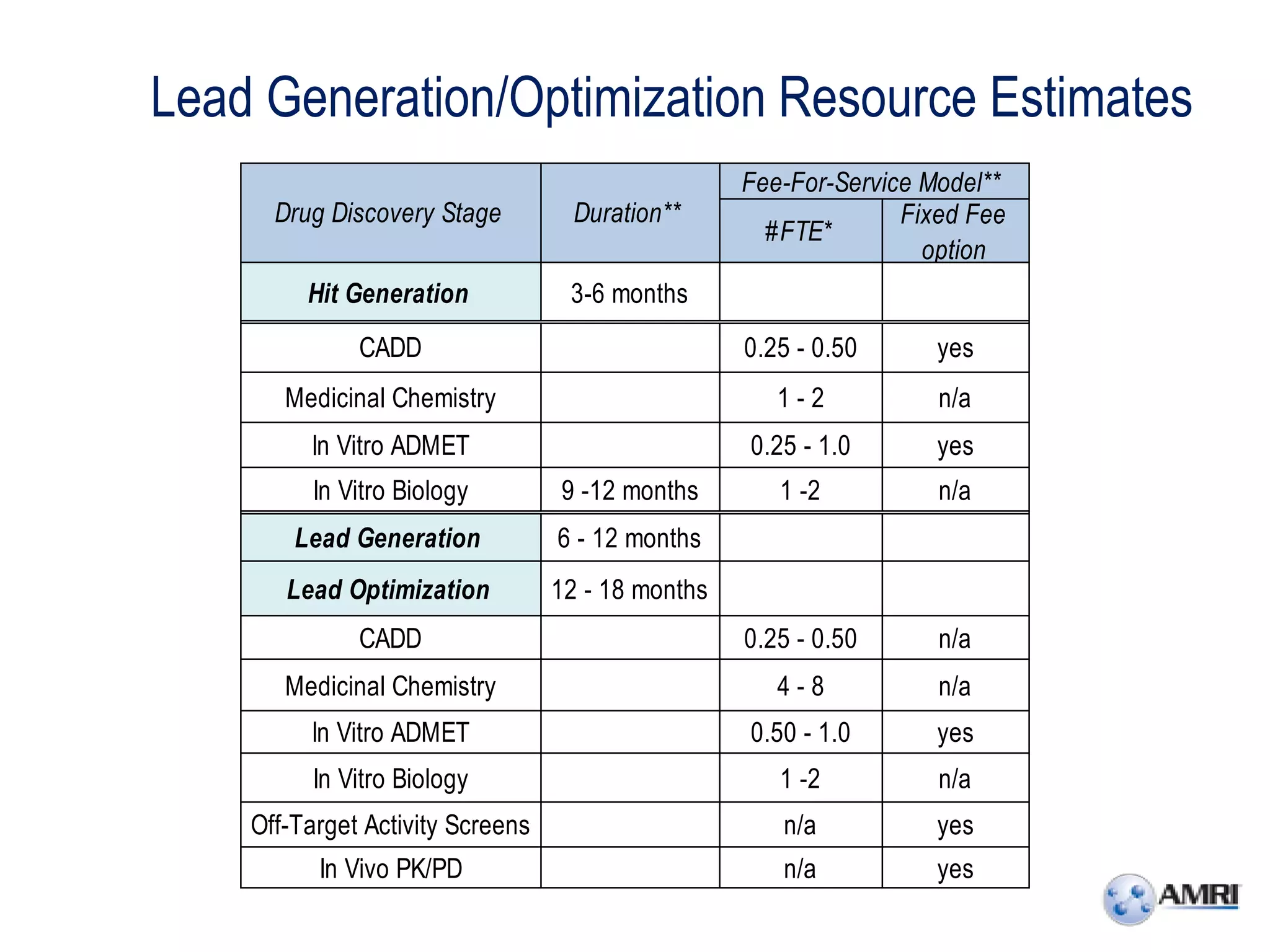
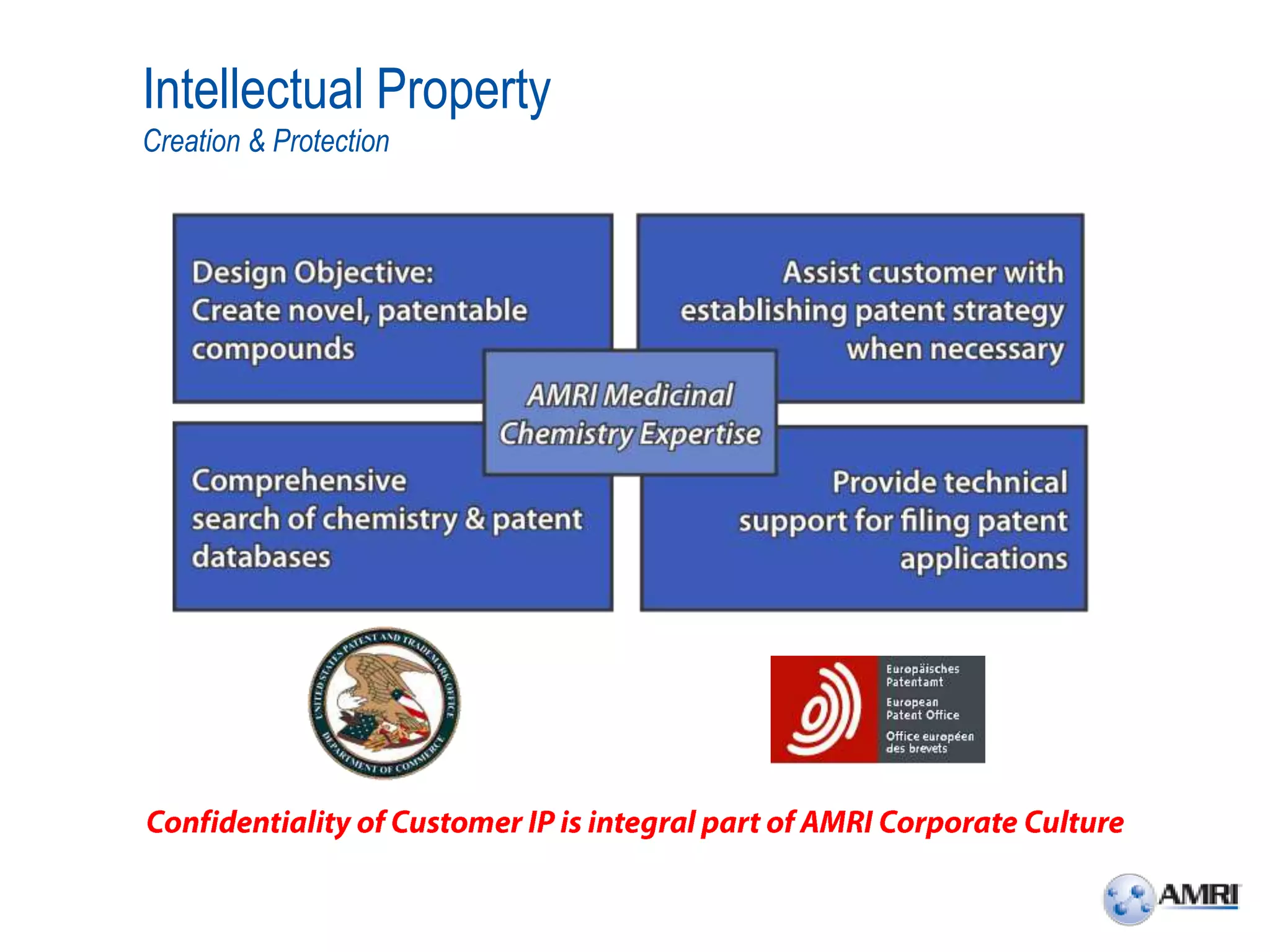
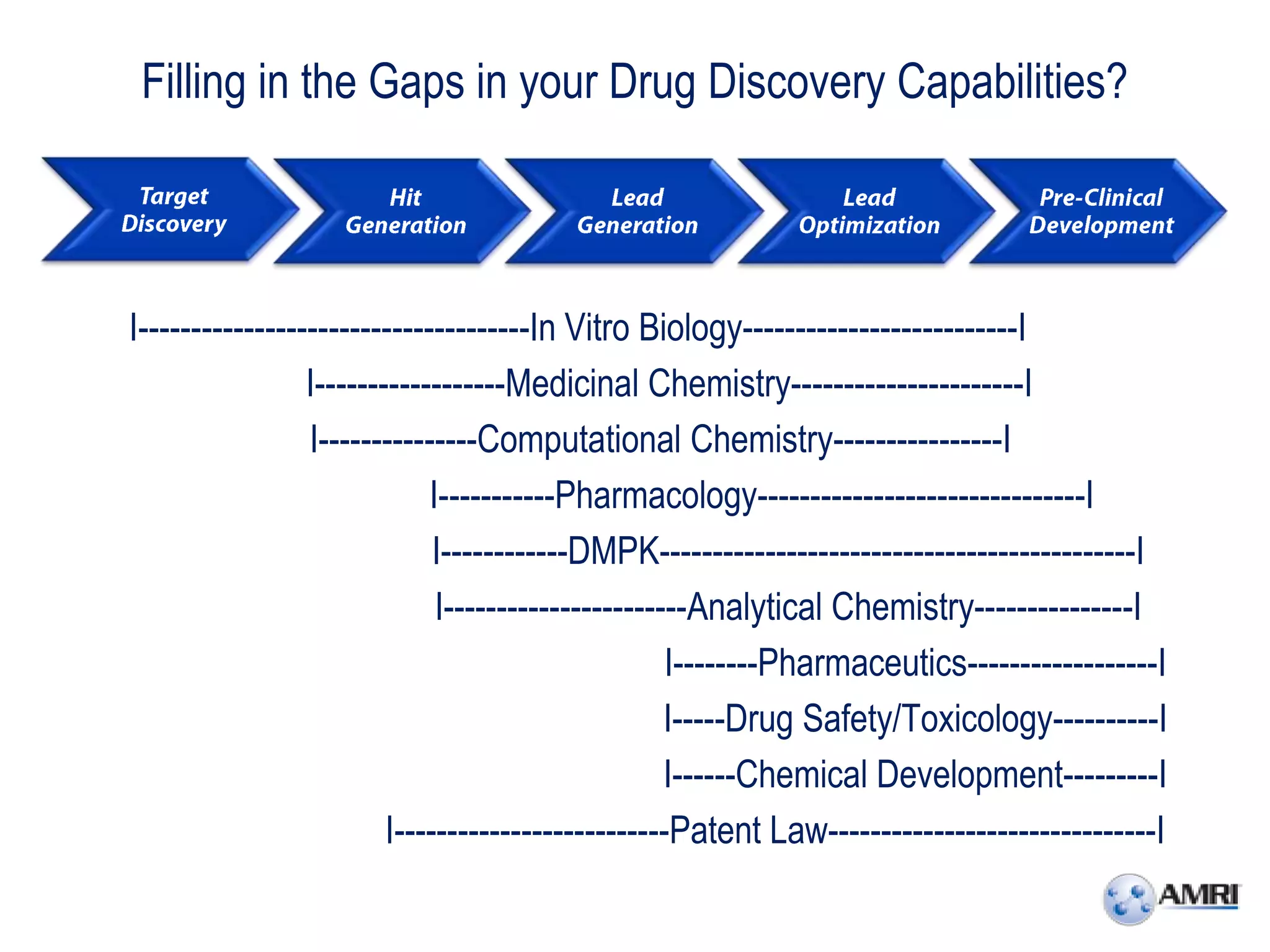
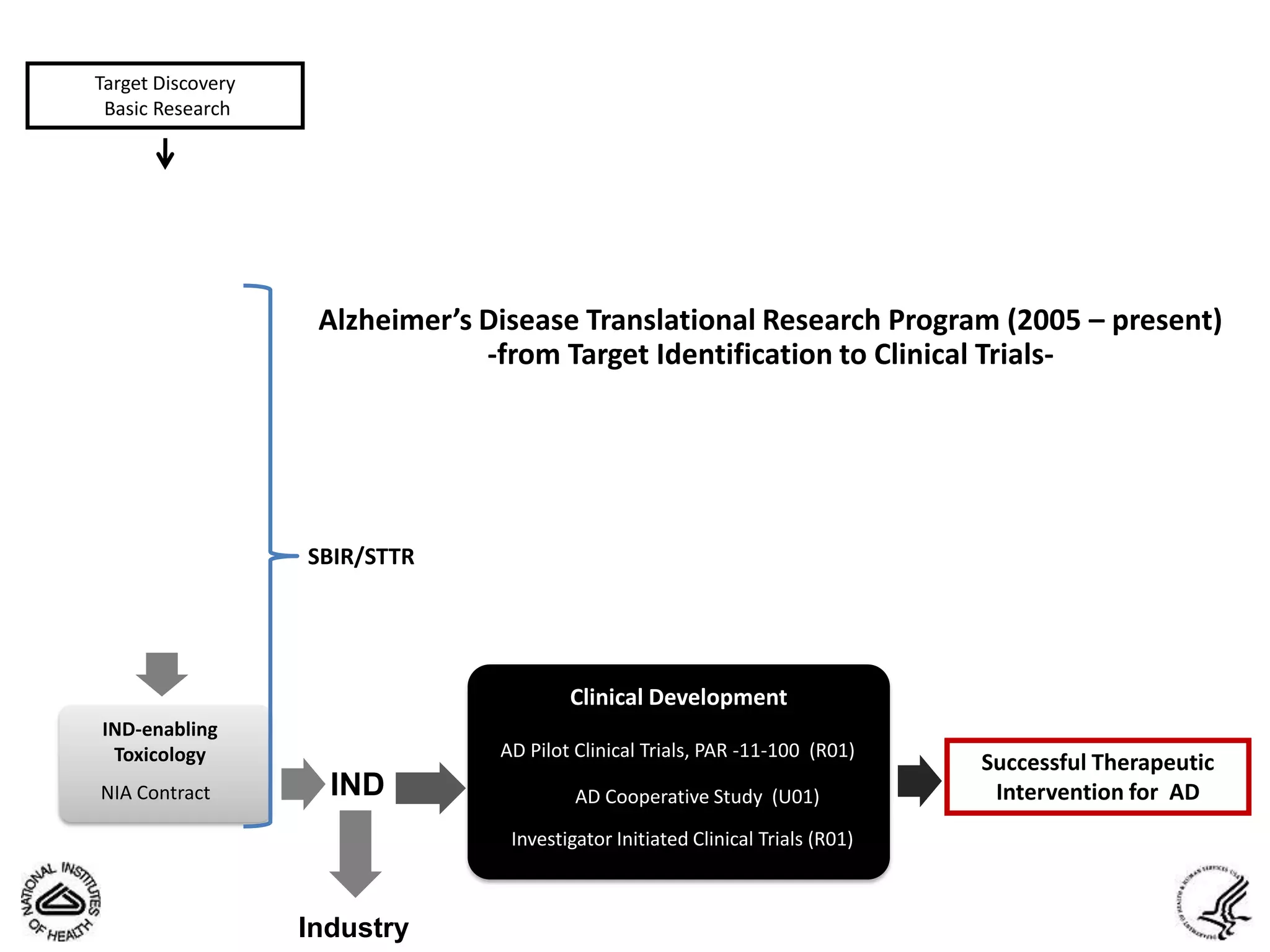
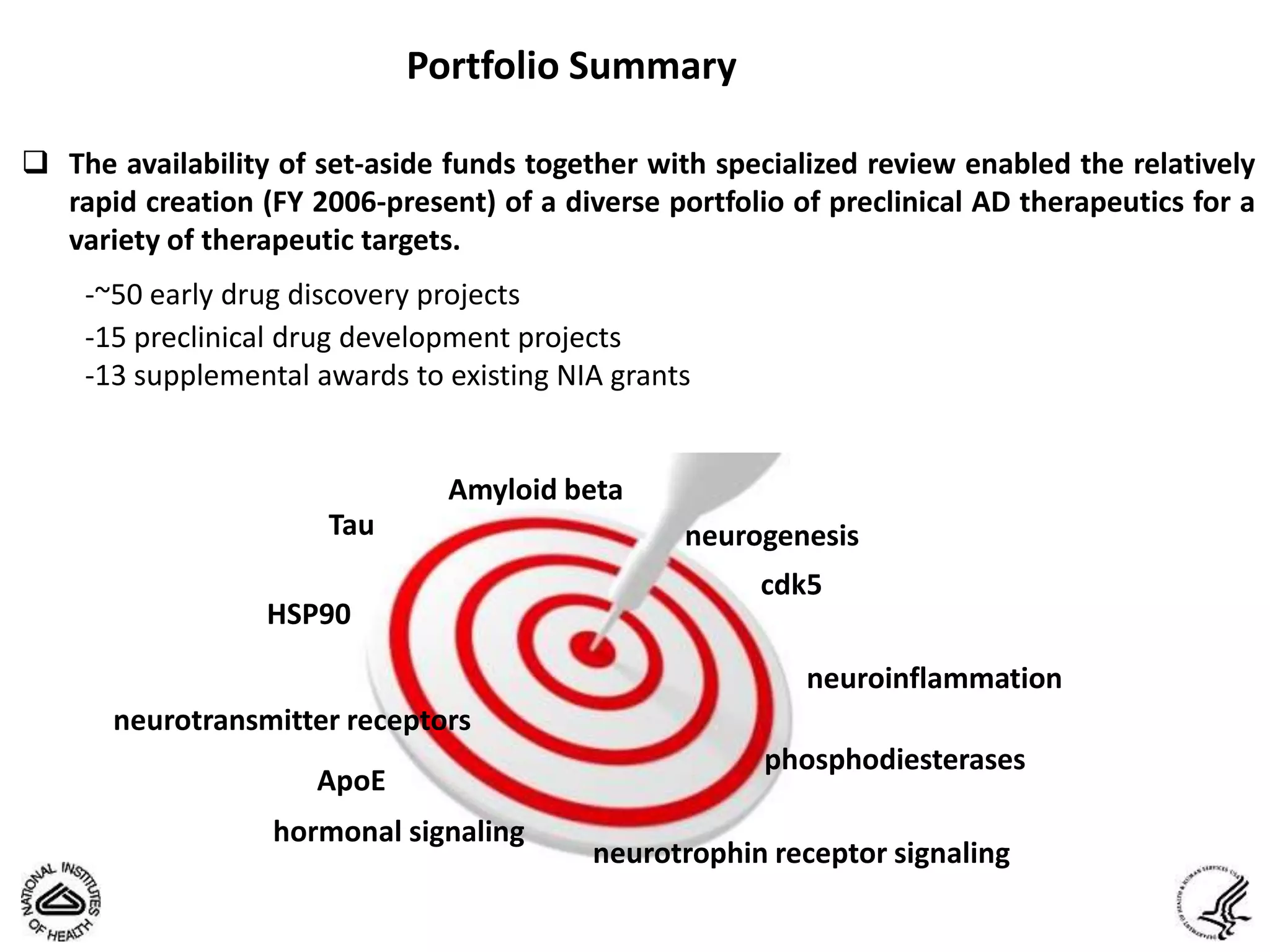
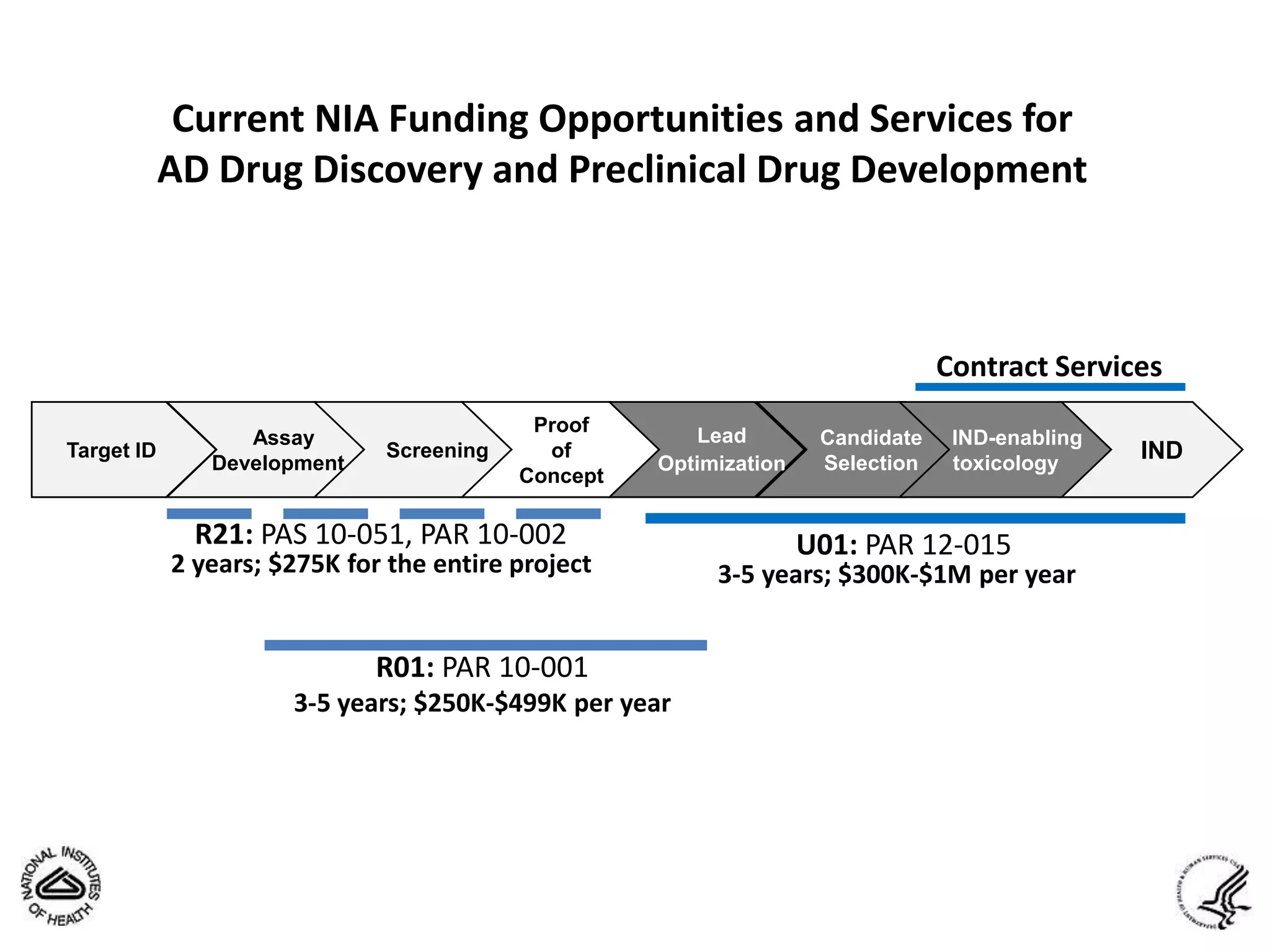
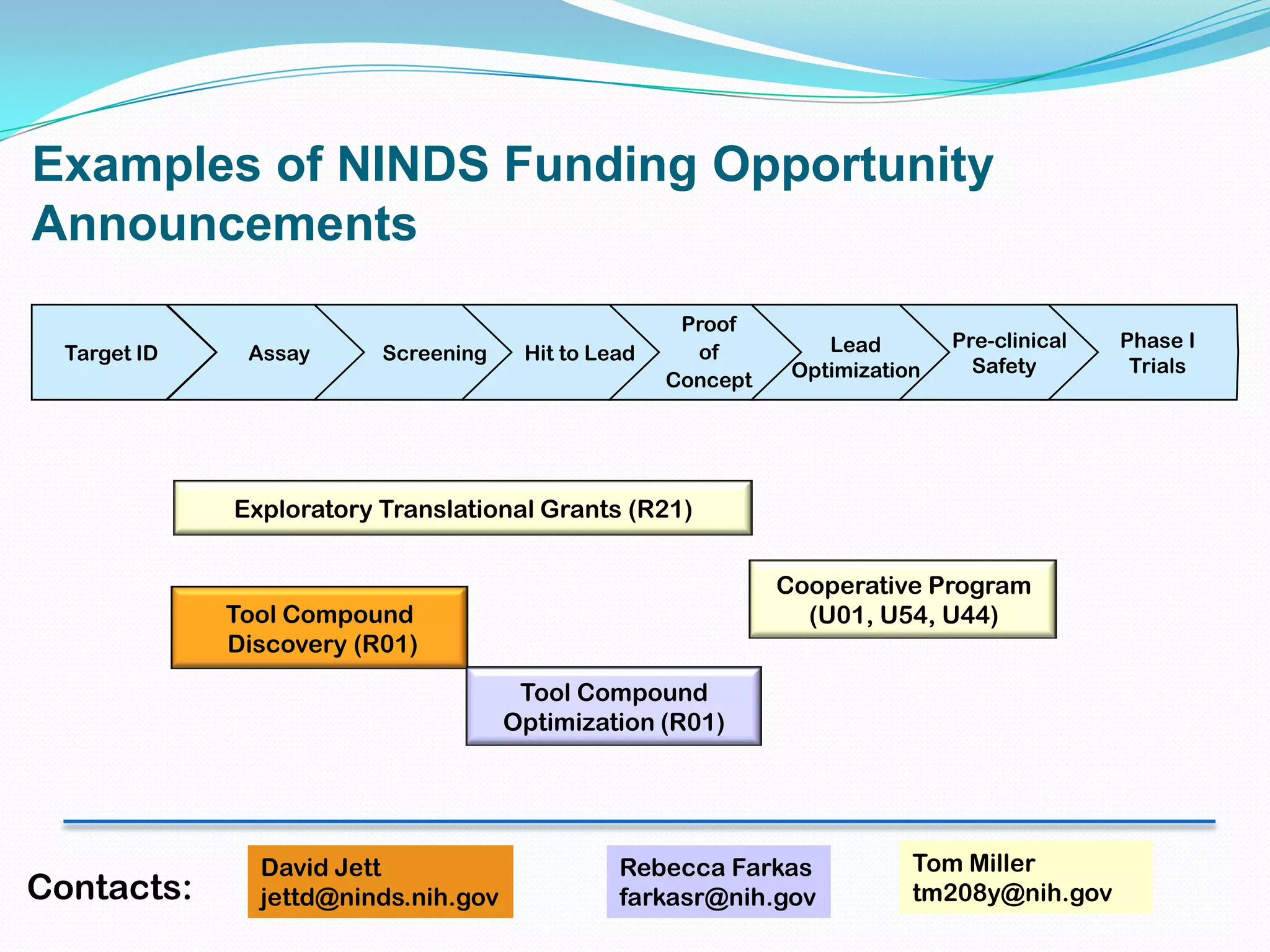
This document summarizes in vitro biology and drug discovery services offered by a contract research organization. It discusses computer-aided drug design, structure-based drug design, cheminformatics, virtual screening, and homology modeling services. It also describes medicinal chemistry, ADMET/pharmacokinetic services, and chemistry services including hit identification, lead optimization, and preclinical/clinical development. Resource estimates and funding models for various stages of drug discovery are provided. The document discusses moving projects from in vitro to in vivo testing and considerations for outsourcing various capabilities.