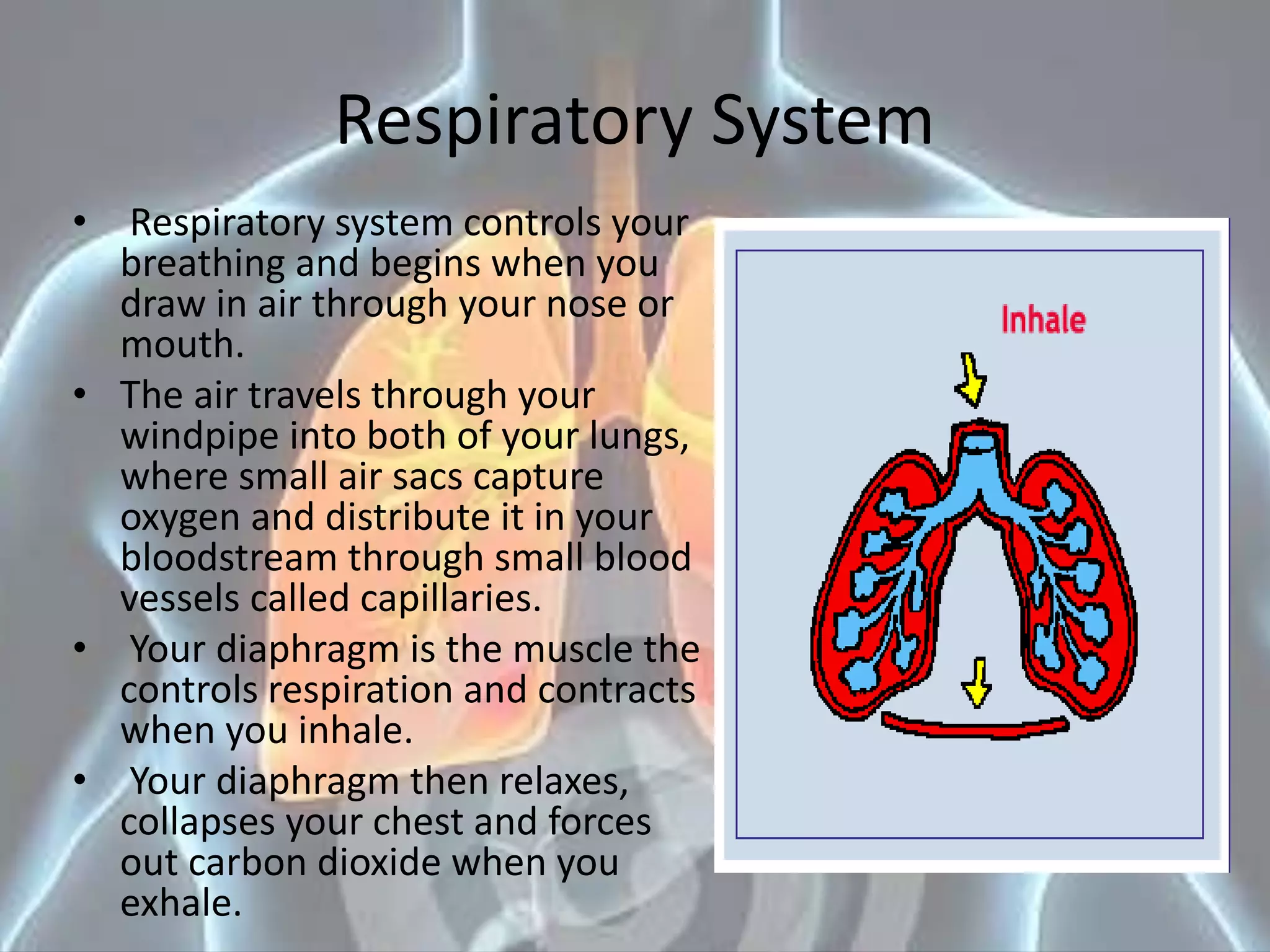
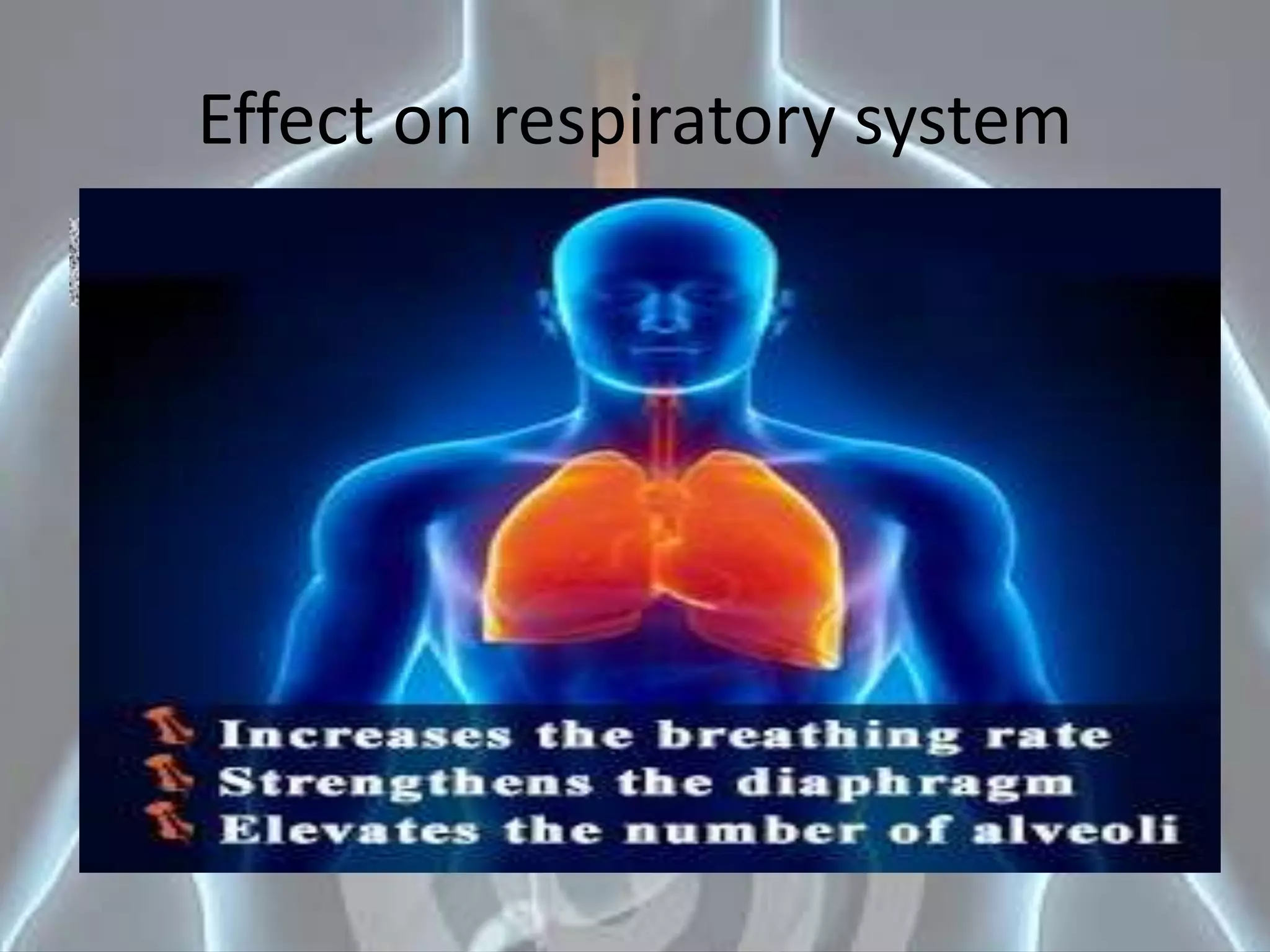
Exercise has both short-term and long-term effects on the respiratory system. In the short-term, exercise increases respiratory rate, tidal volume, and the rate of gas exchange. In the long-term, it strengthens respiratory muscles, increases respiratory volume, improves lung efficiency, and makes gas exchange more efficient. Regular exercise helps the lungs work harder to increase oxygen intake and remove carbon dioxide, ultimately improving pulmonary function.