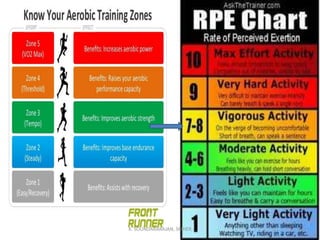
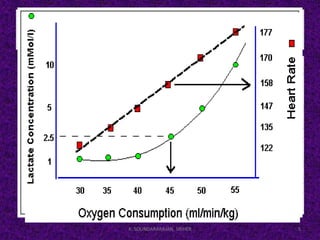
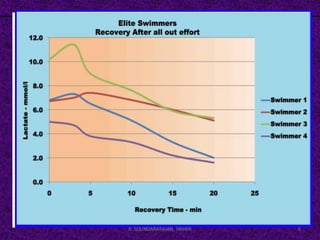
This document discusses the anaerobic threshold and factors that influence threshold training. The anaerobic threshold is defined as the point at which lactic acid starts to accumulate in the muscles, around 85-90% of maximum heart rate. Anaerobic threshold testing involves gradually increasing effort over a 20-30 minute run, swim, or bike while monitoring heart rate to identify the threshold point where heart rate levels off. Factors like VO2 max, muscle fiber type, and lactate removal ability influence an individual's threshold. The threshold can be measured during a 30 minute long distance run using heart rate monitoring equipment.