1. During exercise, the body undergoes adjustments to supply nutrients and oxygen to active tissues and prevent overheating.
2. There are two types of exercise - dynamic exercise involves muscle movement while static exercise does not.
3. Exercise can be aerobic, using oxygen for energy over long periods, or anaerobic, using glycogen without oxygen for short bursts.
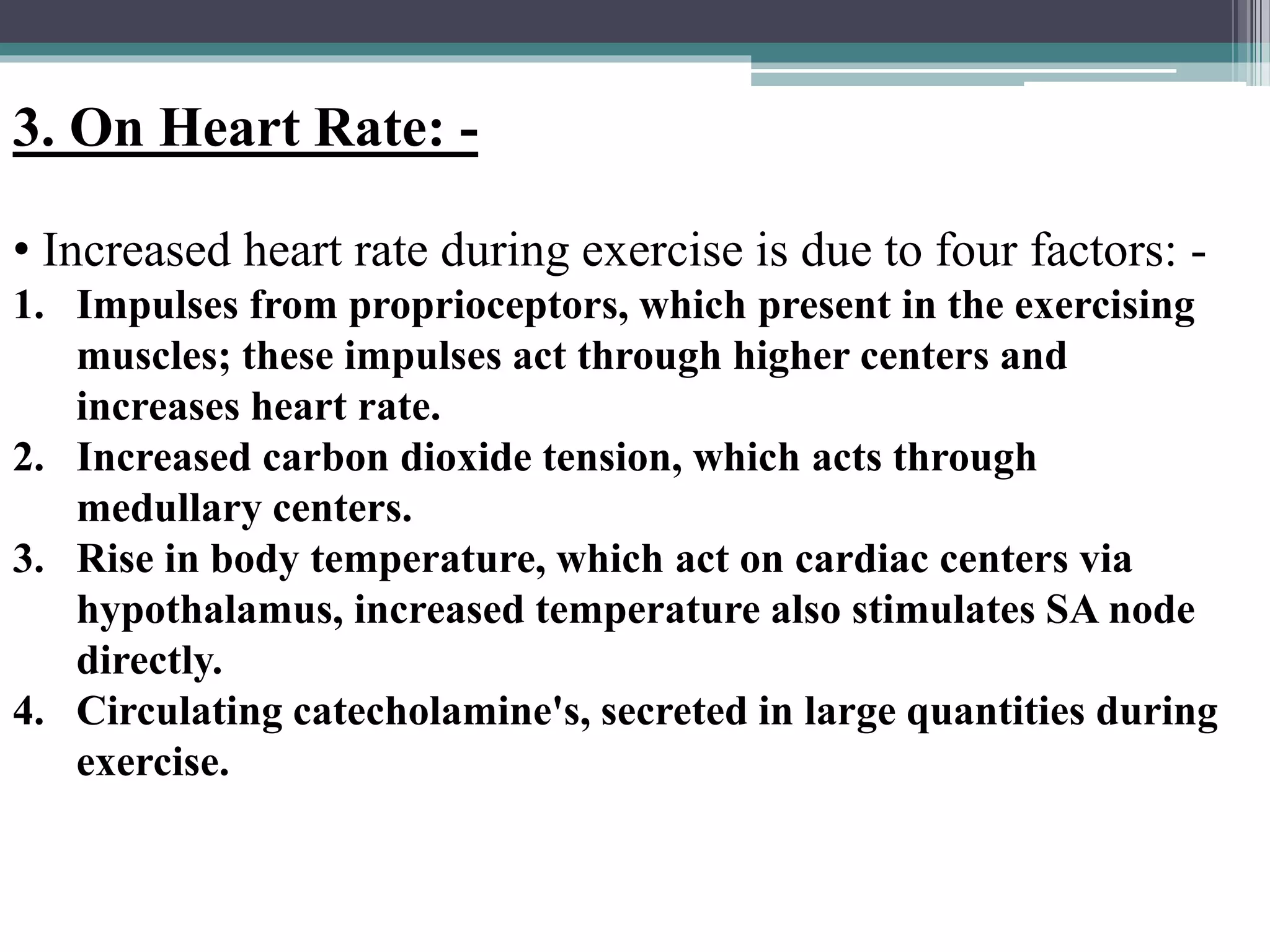
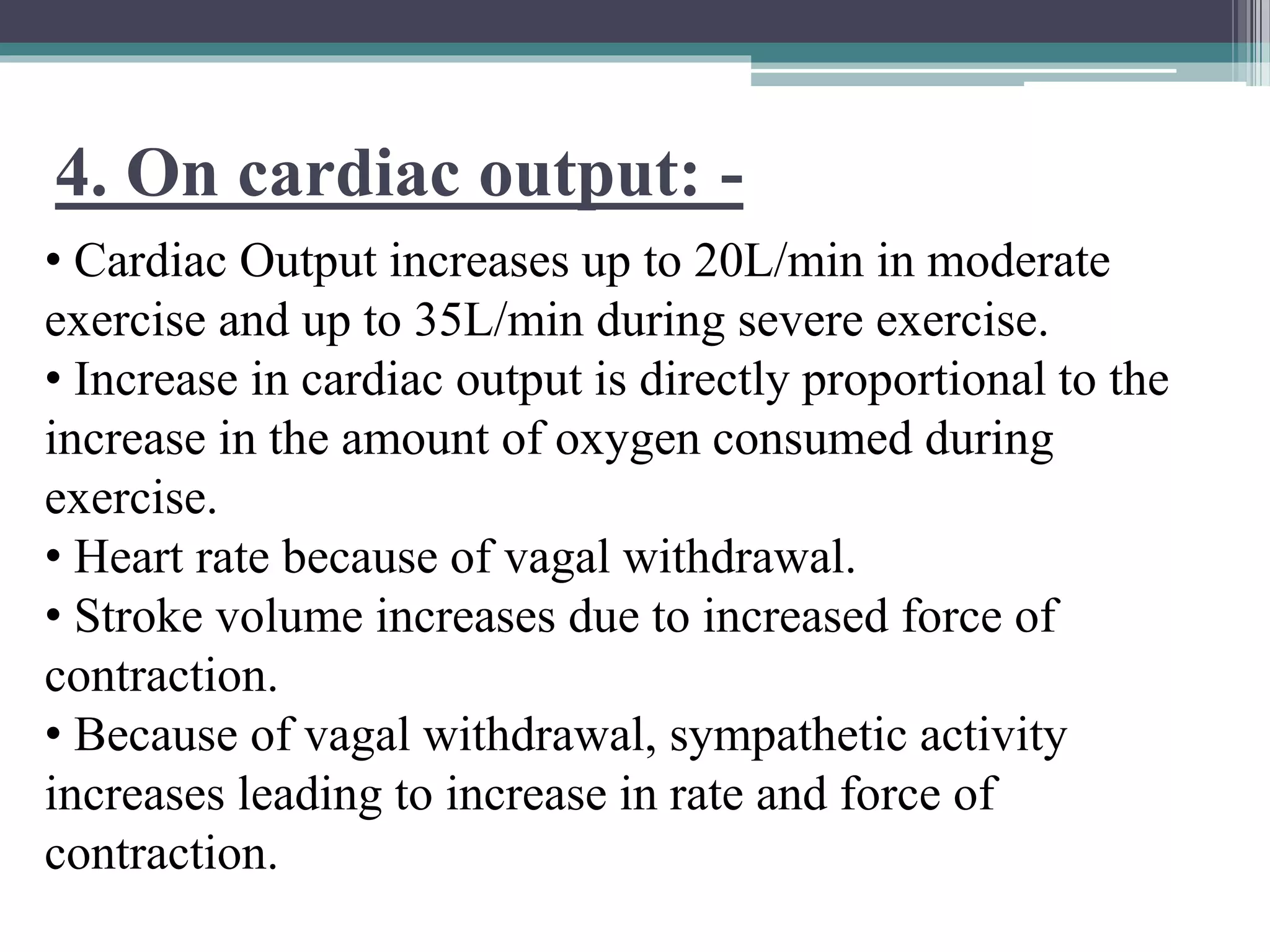
4. The cardiovascular system responds to exercise through increased heart rate, cardiac output, and blood flow to muscles to meet energy demands, while blood pressure rises with intense exercise but falls below resting after as metabolites accumulate.