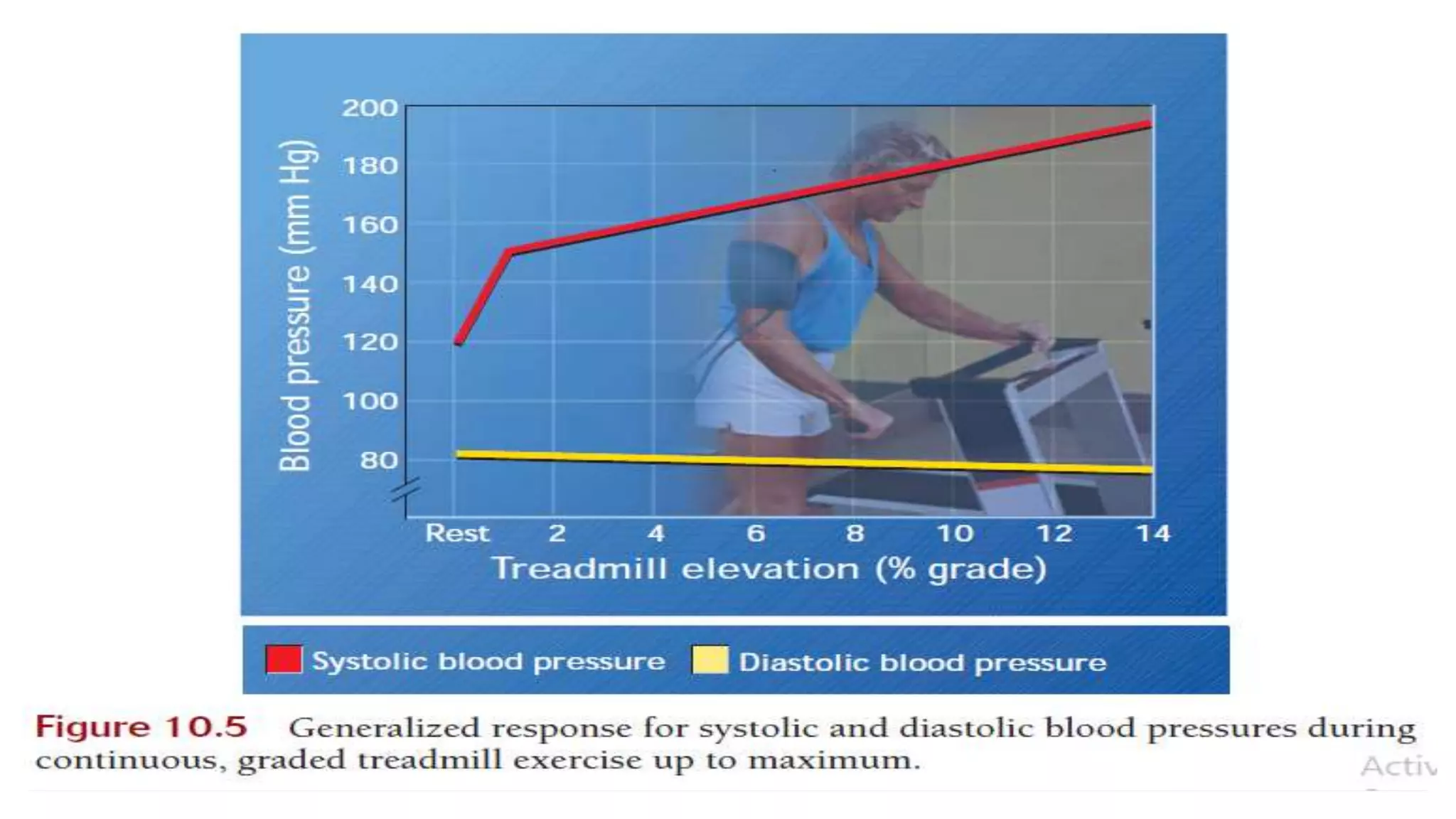
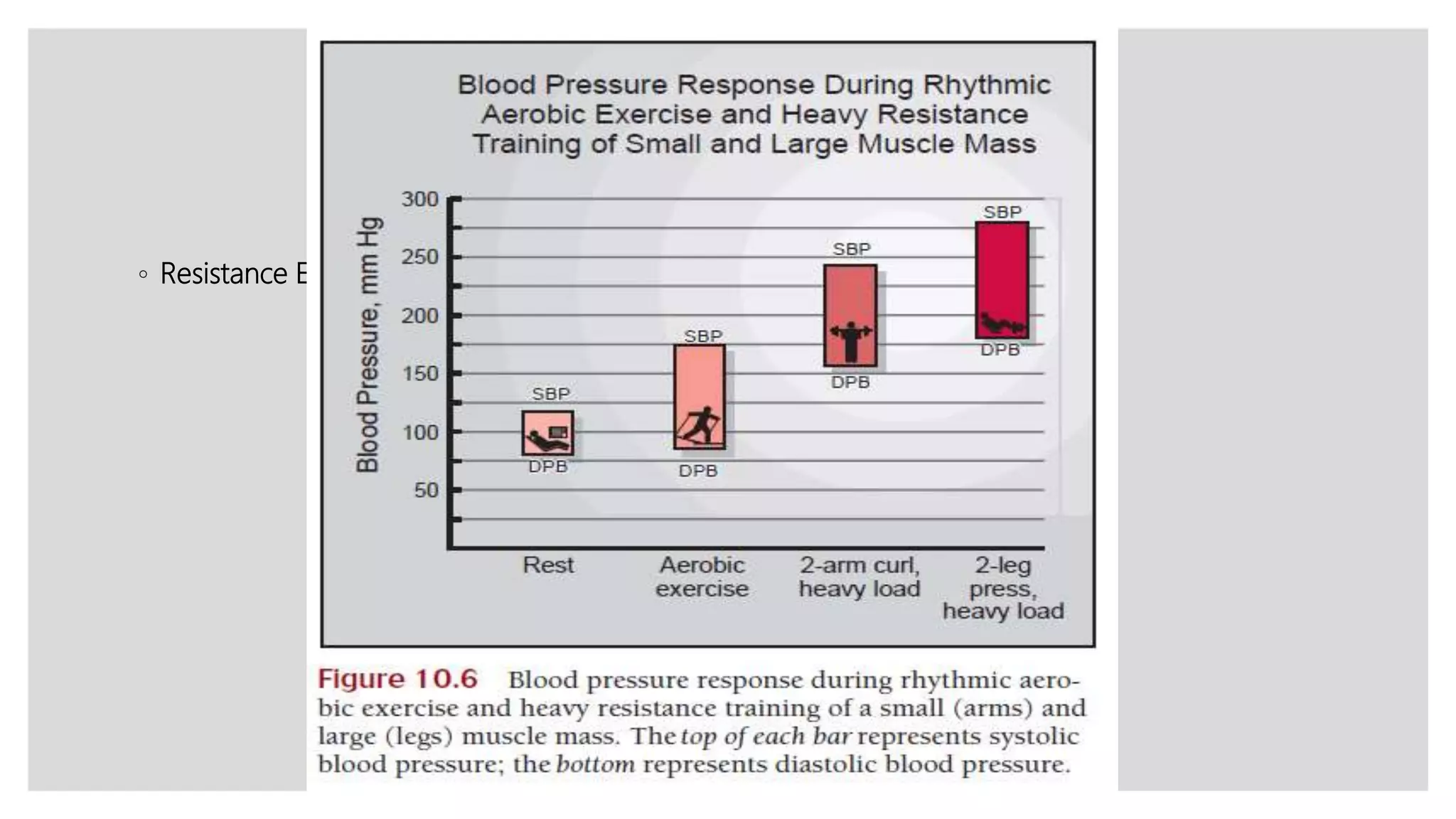
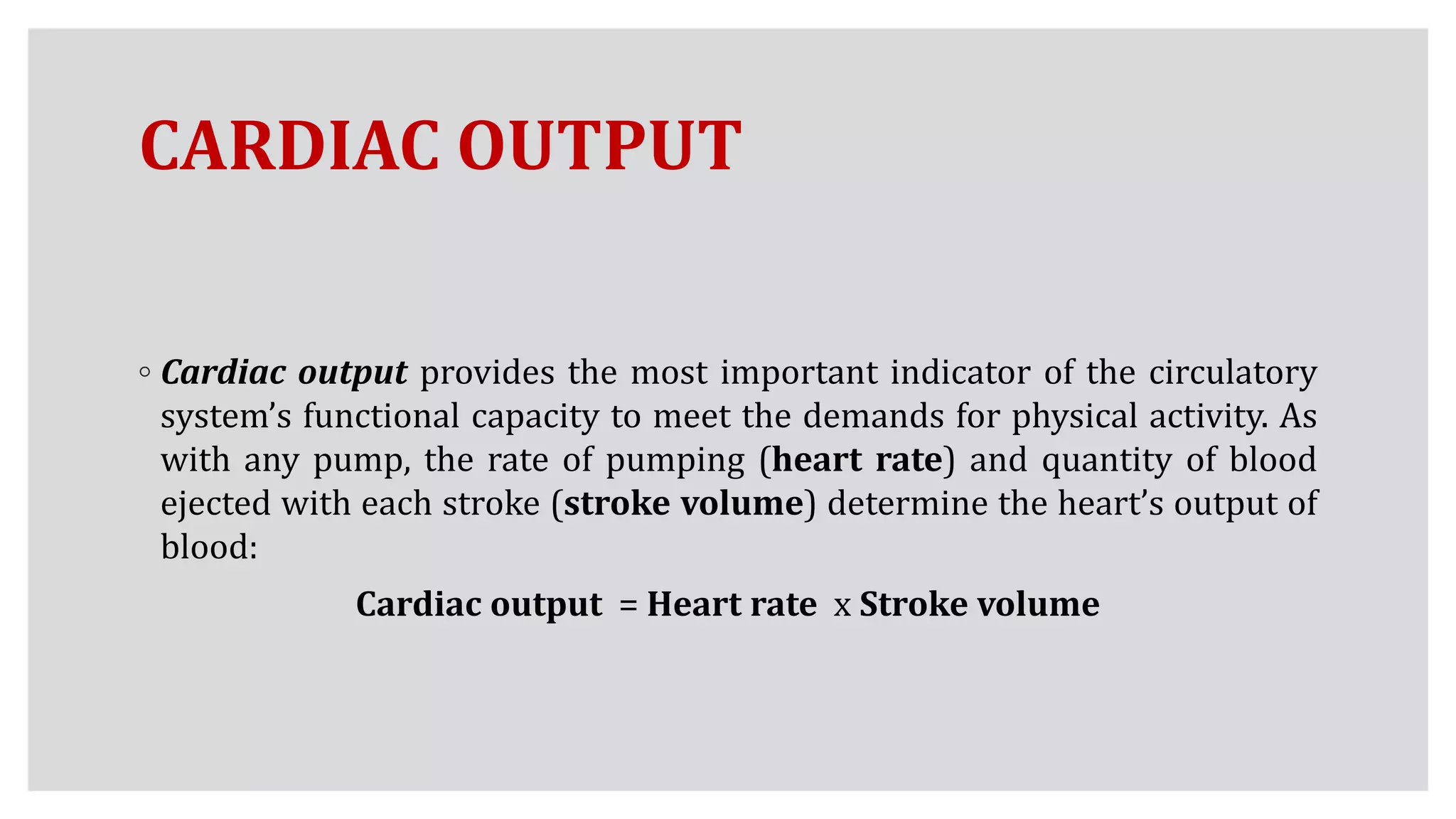
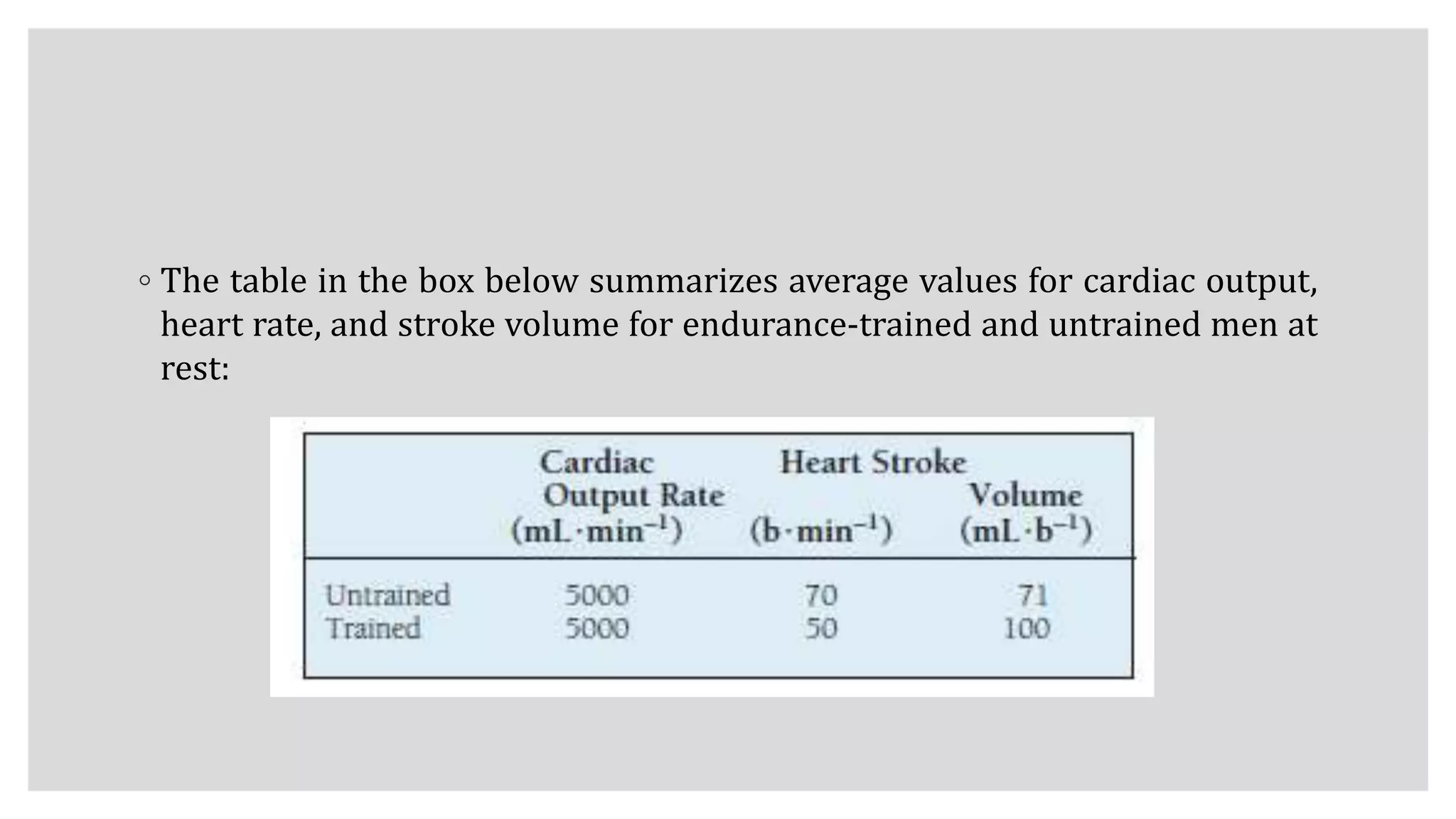
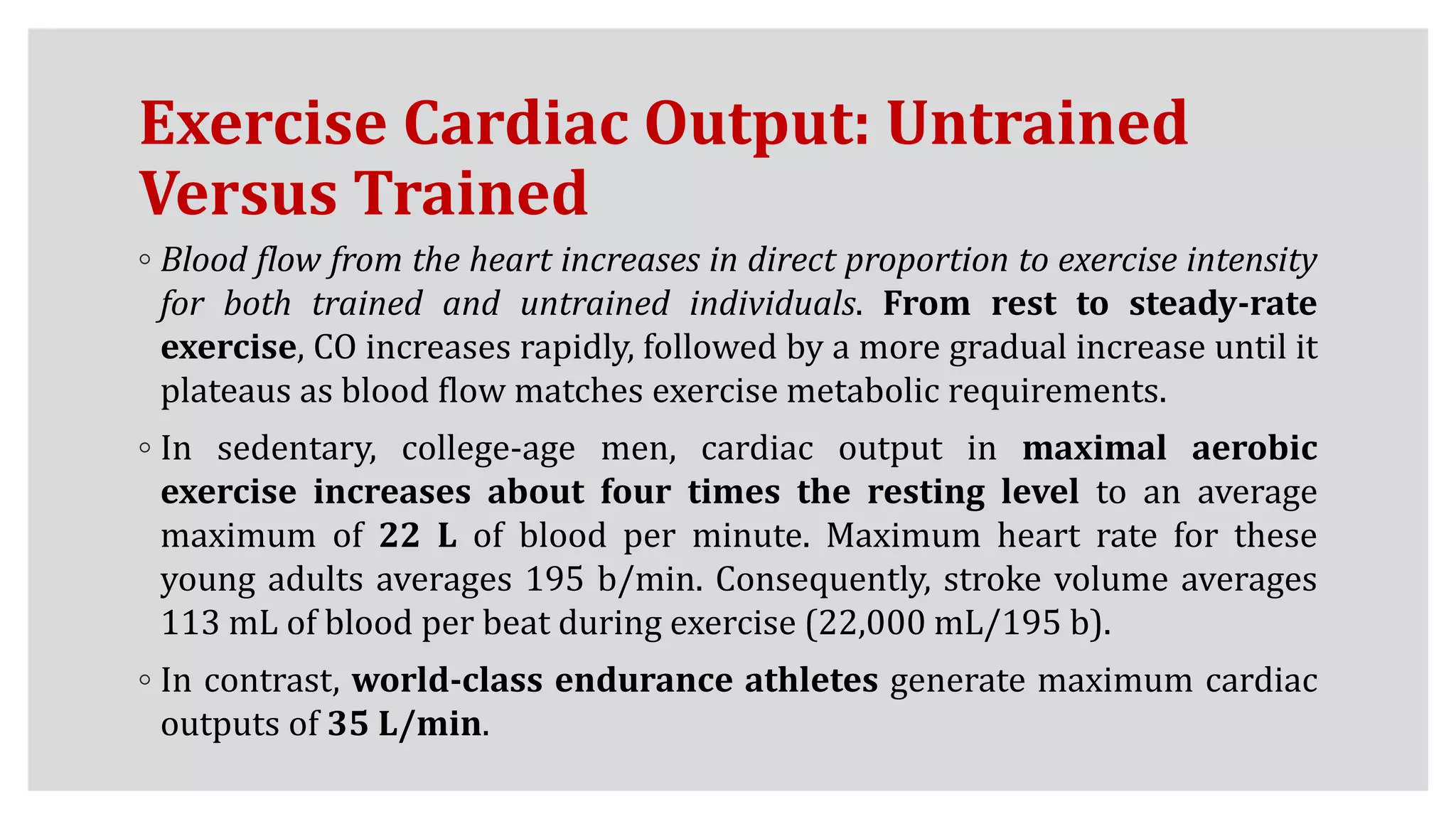
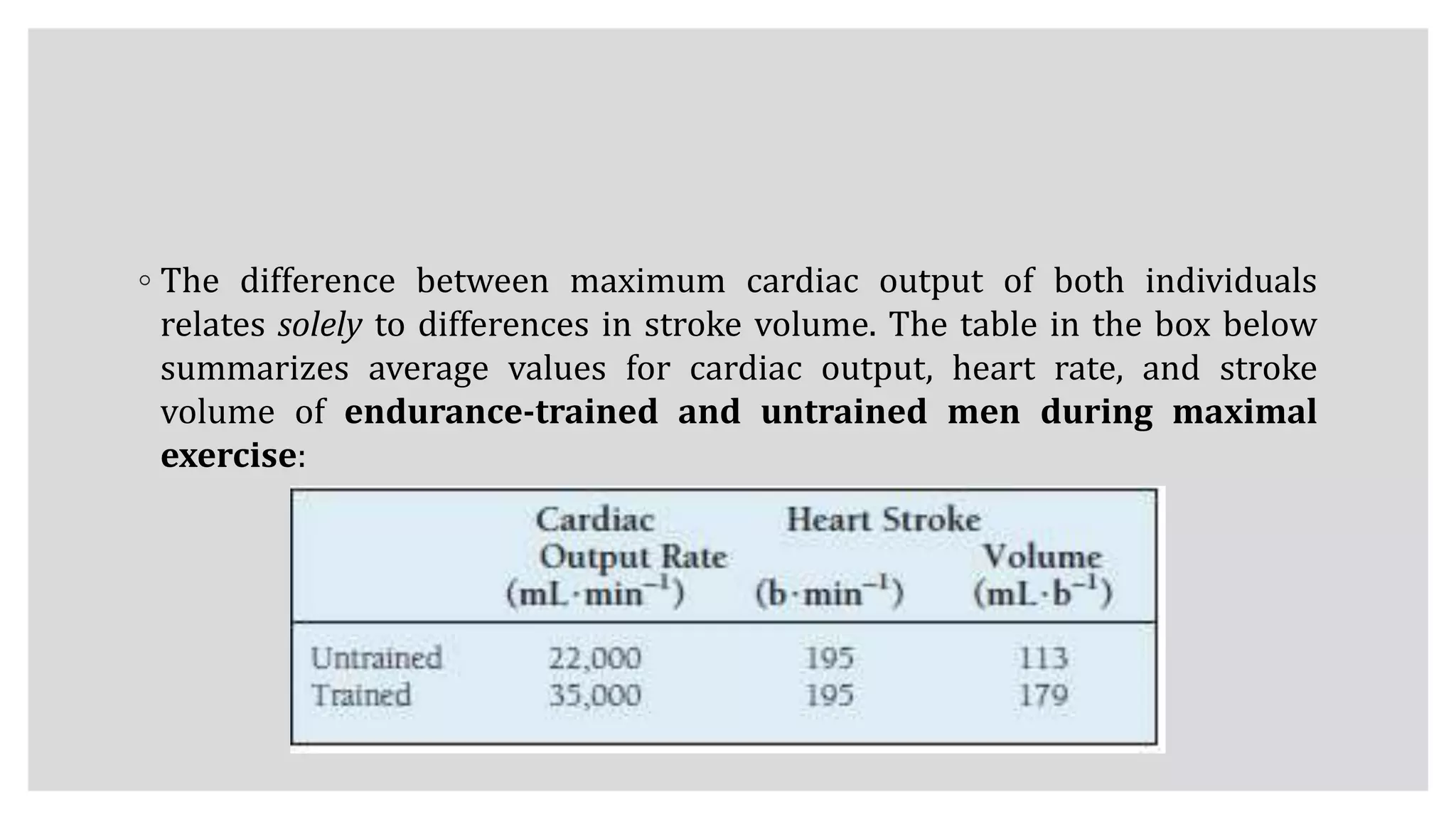
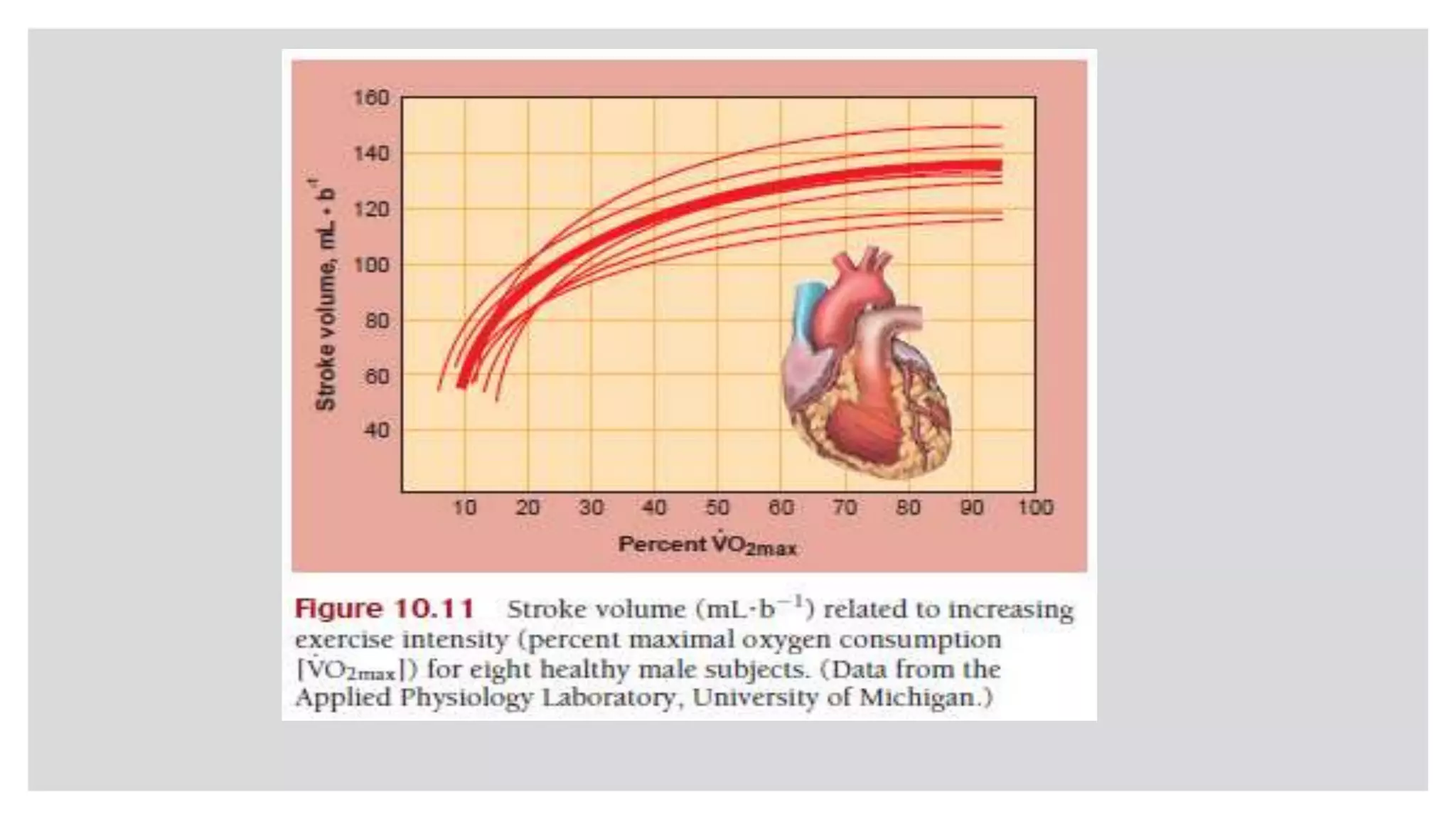
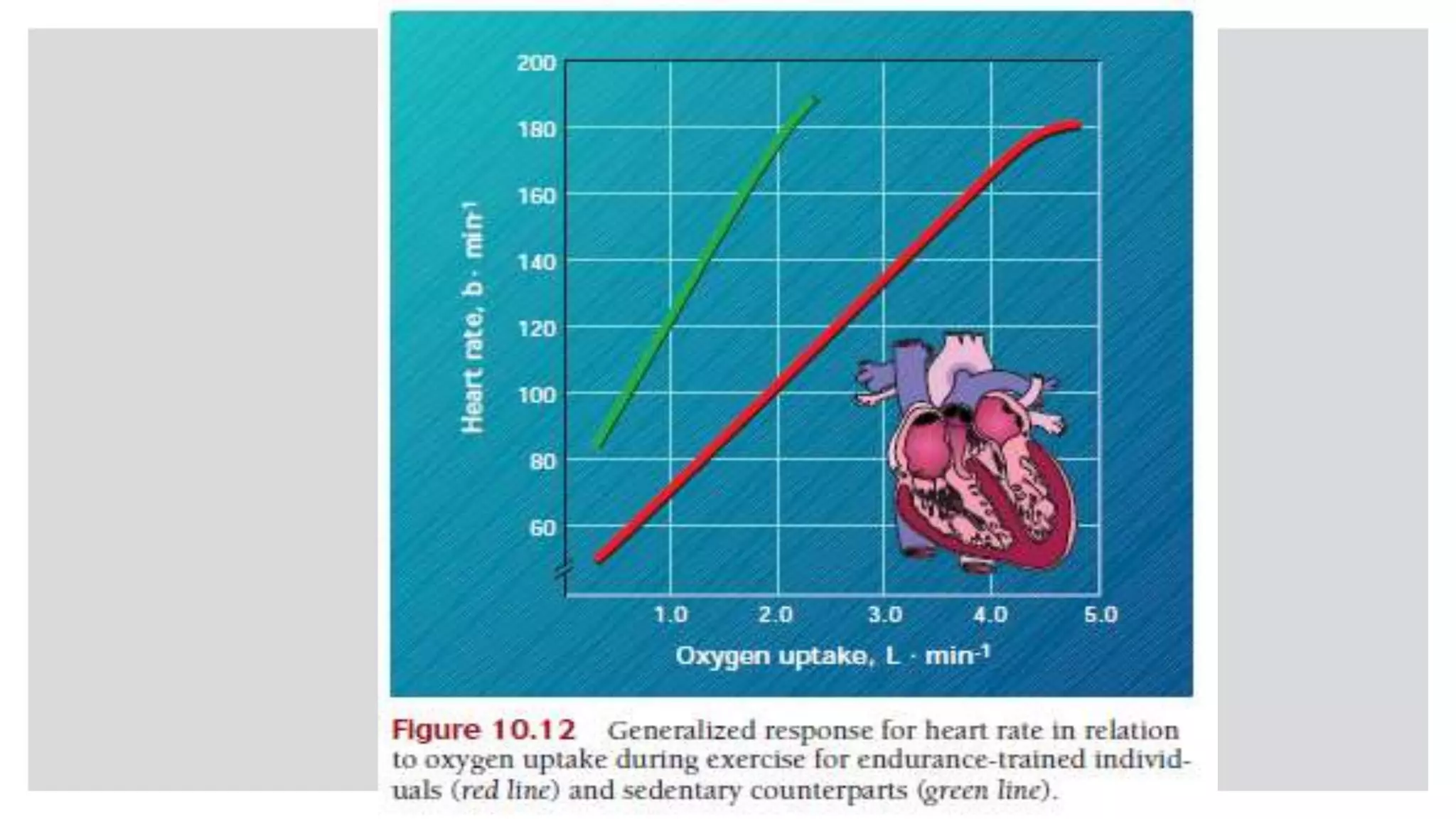
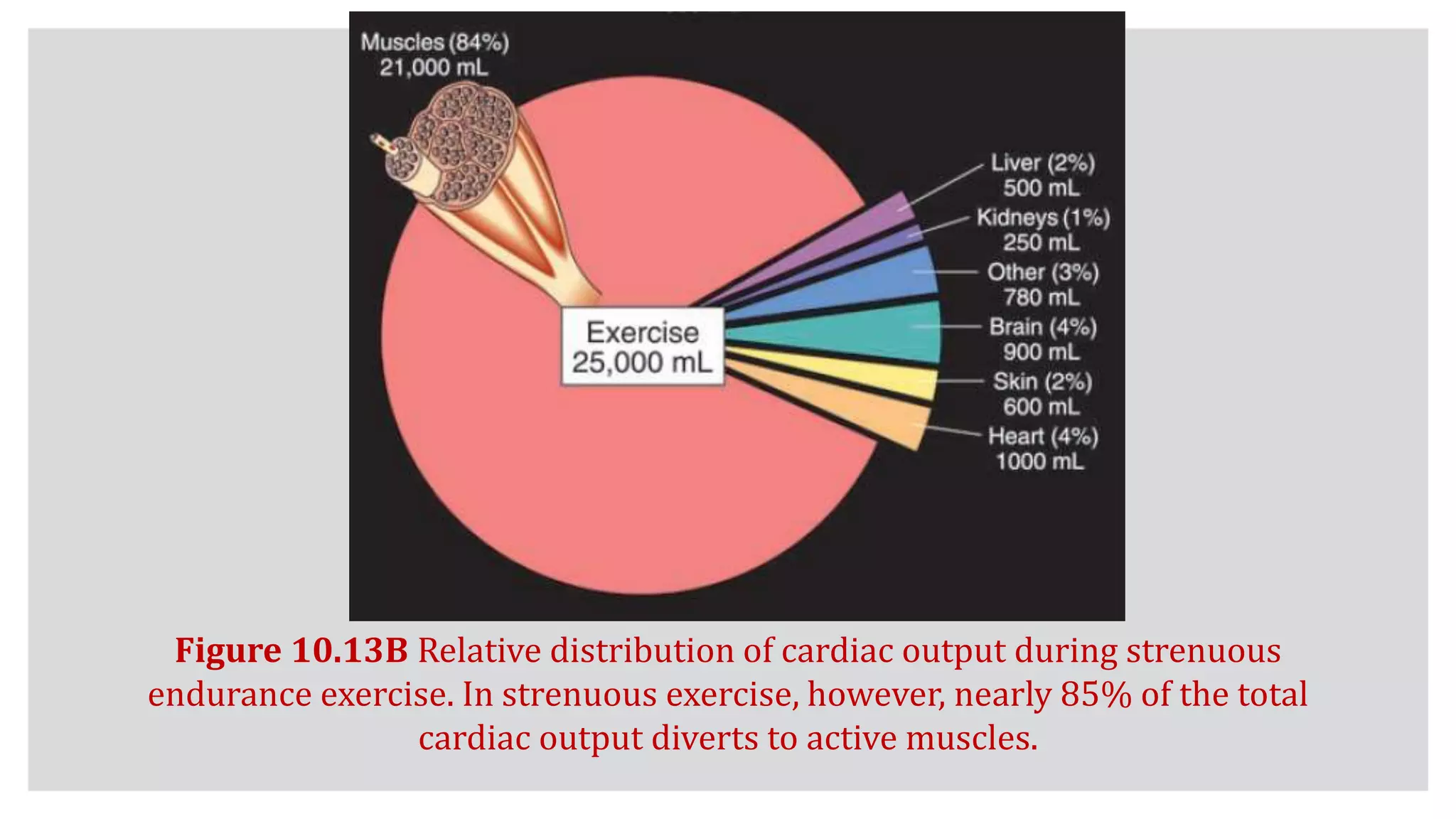
During exercise, the cardiovascular system undergoes changes to meet increased demands. Blood pressure typically increases during moderate exercise but remains stable during intense exercise. Cardiac output, the product of heart rate and stroke volume, also increases substantially during exercise through higher heart rates and larger stroke volumes. Trained athletes can achieve much higher maximum cardiac outputs than untrained individuals through greater maximal stroke volumes. Prolonged exercise can cause cardiovascular drift, where stroke volume decreases and heart rate increases to compensate and maintain cardiac output.




















![Cardiac Output & Oxygen Transport
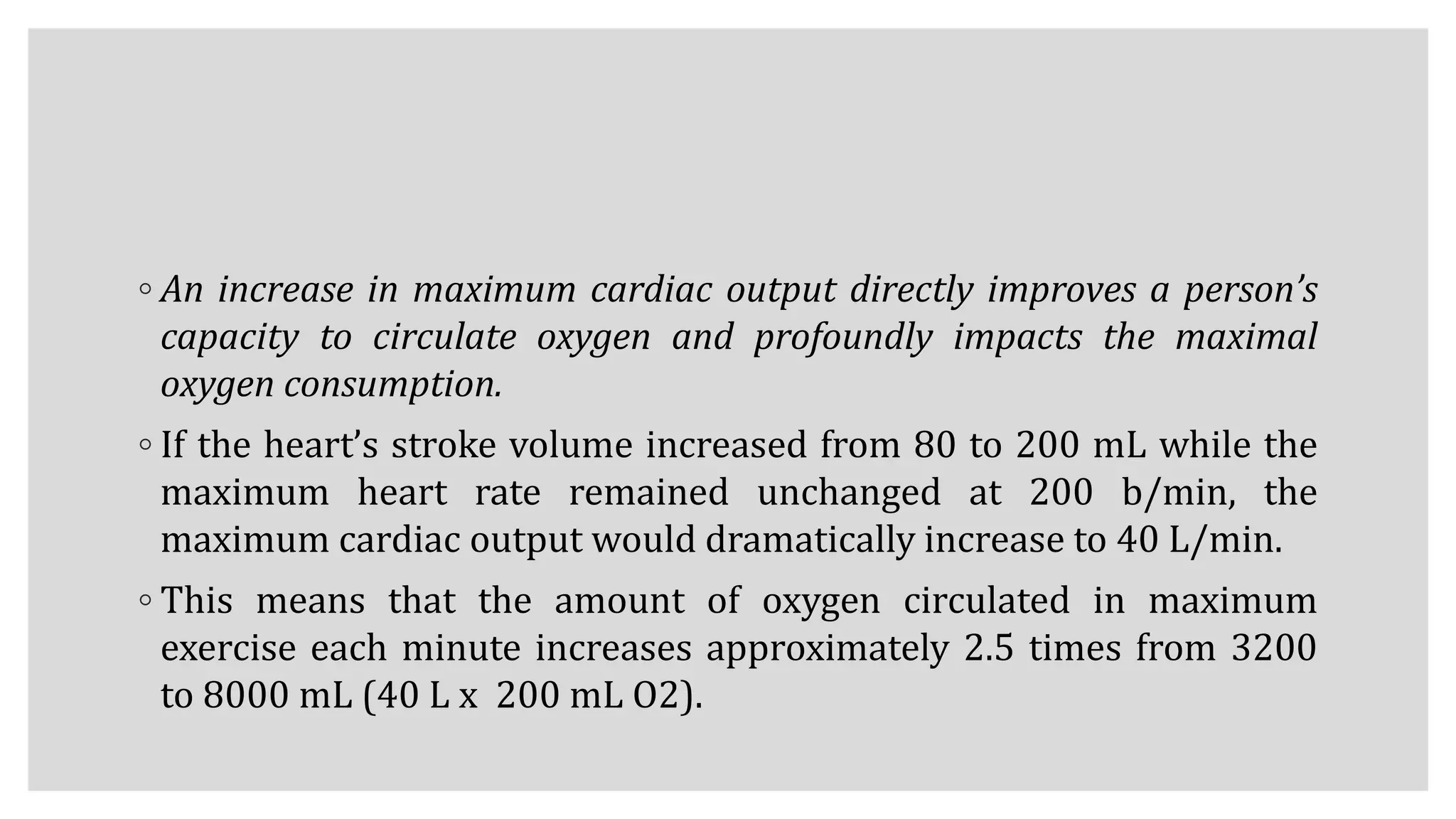
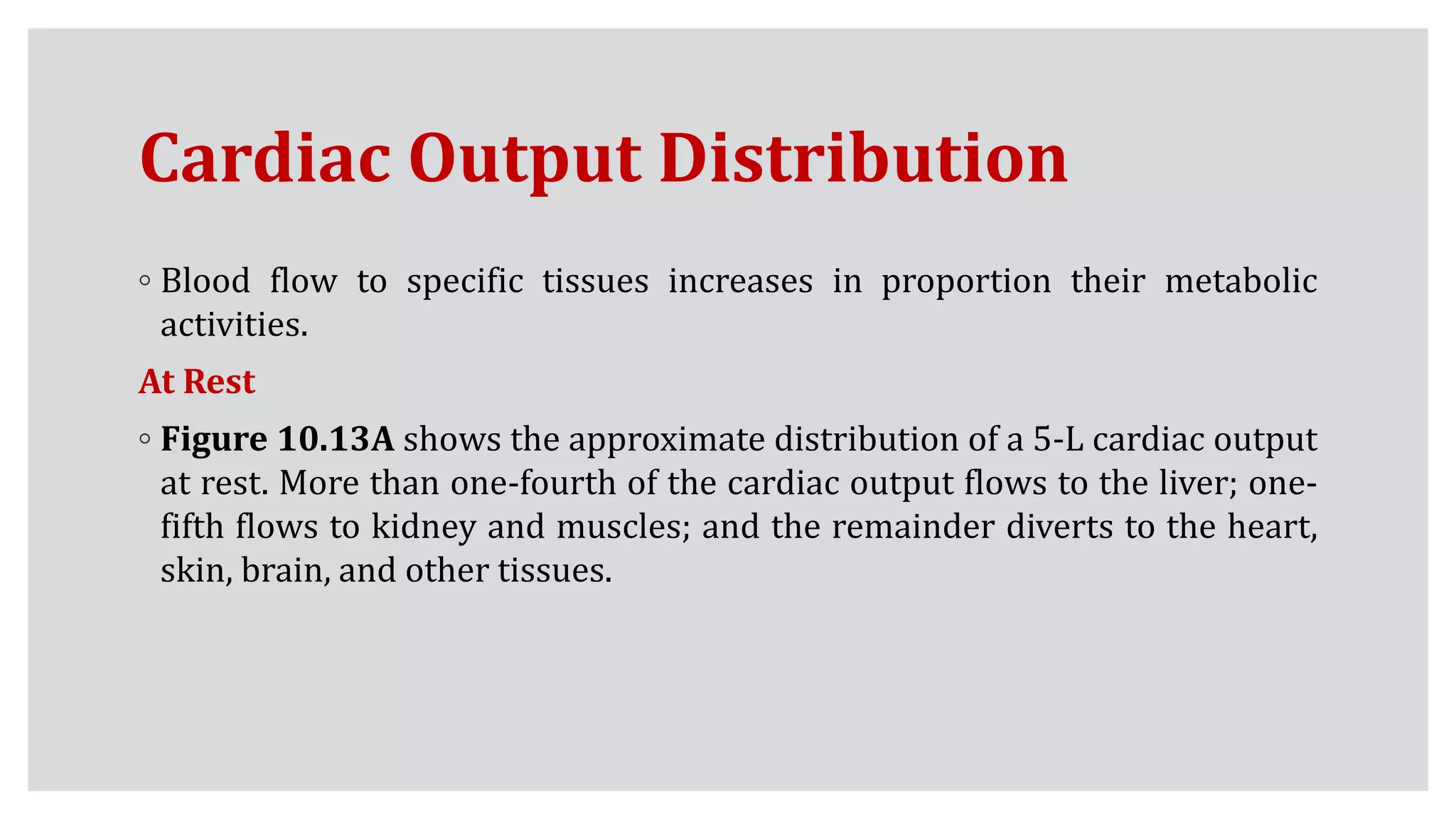
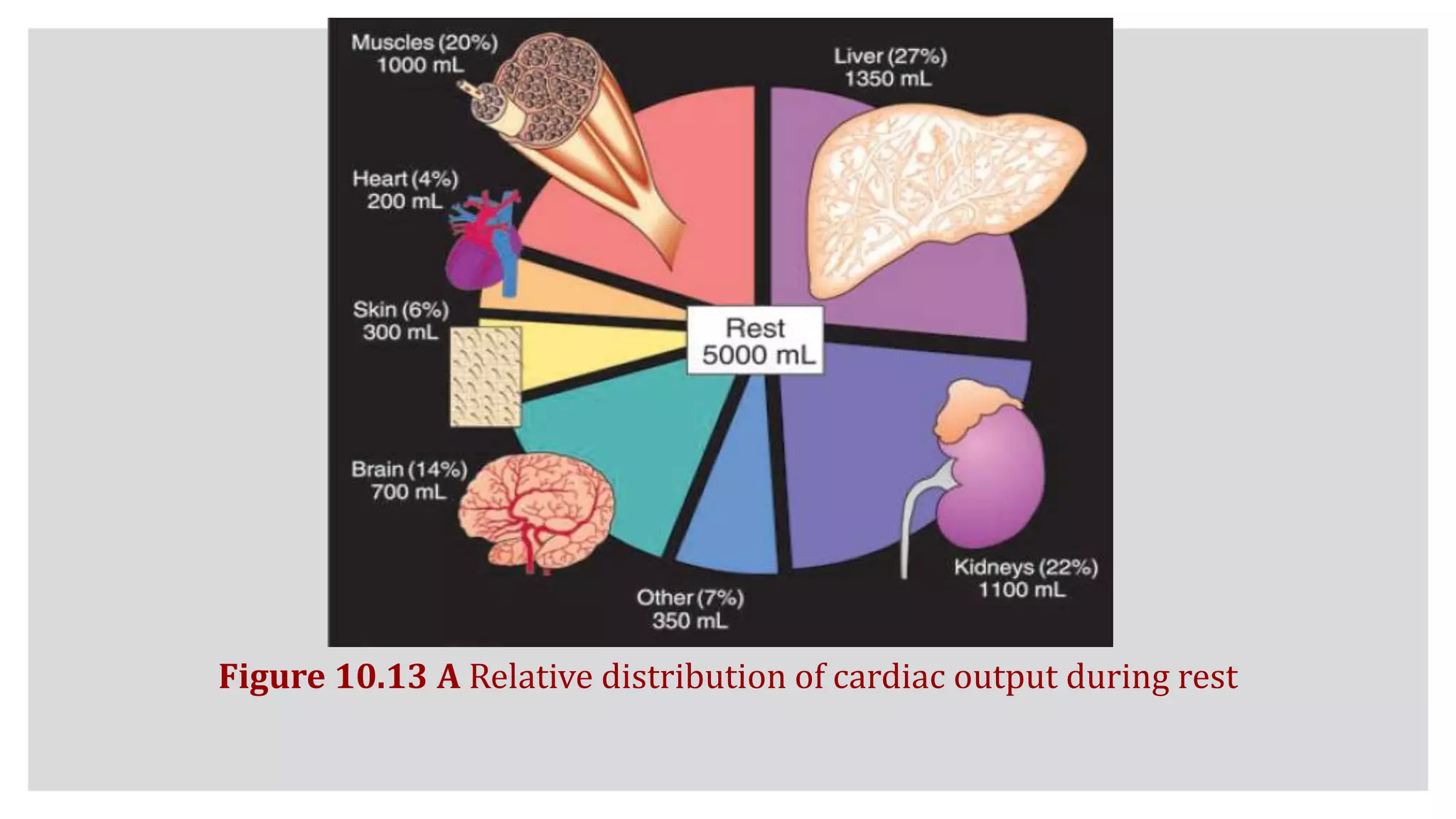
At Rest
◦ Each 100 mL (deciliter [dL]) of arterial blood normally carries about 20 mL of
oxygen or 200 mL of oxygen per liter of blood at sea level conditions.
◦ Trained and untrained adults circulate 5 L of blood each minute at rest, so
potentially 1000 mL of oxygen becomes available during 1 minute (5L
blood/200mL O2). Resting oxygen uptake averages only about 250 mL/min; this
means 750 mL of oxygen returns “unused” to the heart. This does not represent
an unnecessary waste of cardiac output.
◦ To the contrary, extra oxygen in the blood above the resting needs maintains
oxygen in reserve—a margin of safety for immediate use if the need arises.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiovascularchangesduringexercise-200813165837/75/Cardiovascular-changes-during-exercise-34-2048.jpg)