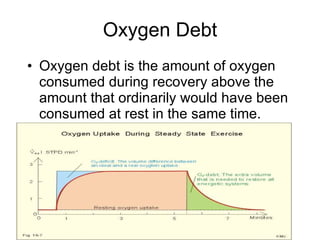
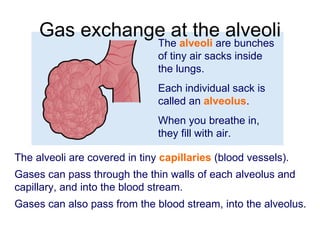
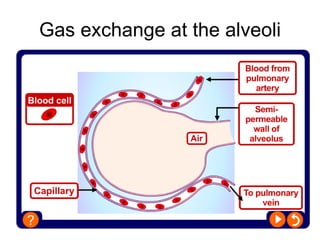
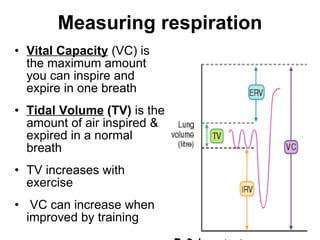
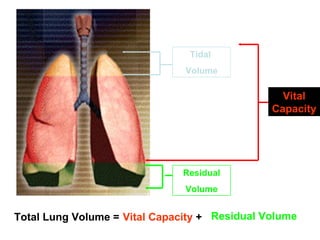
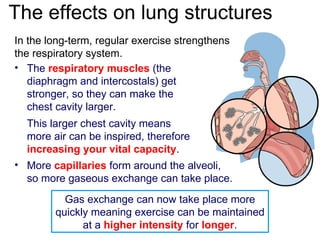
The document discusses the short-term and long-term effects of exercise on the respiratory system. In the short-term, exercise increases breathing rate, depth of breathing, oxygen demand and carbon dioxide removal. This leads to oxygen debt as the body takes in more oxygen than at rest to repay this debt after intense exercise. In the long-term, regular exercise strengthens the respiratory muscles and increases lung capacity and volume through developing more capillaries and an enlarged chest cavity.