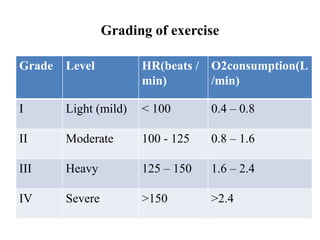
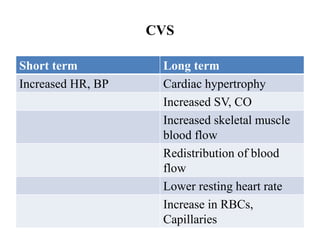
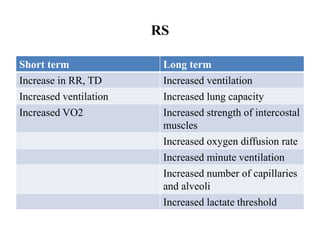
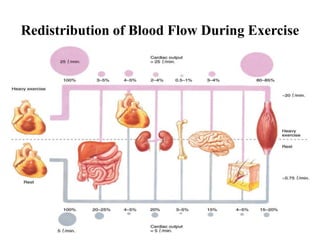
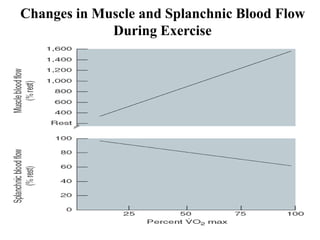
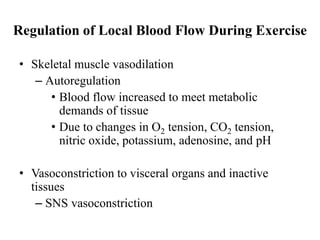
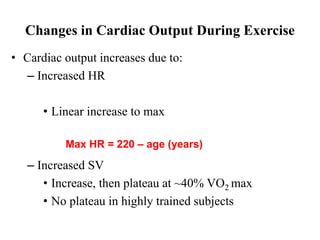
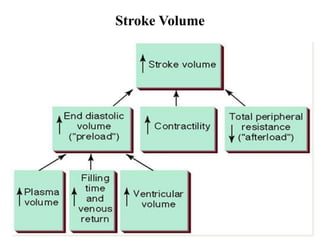
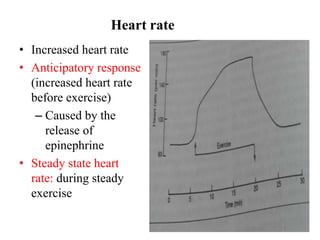
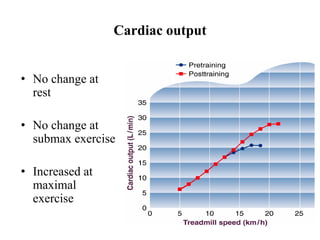
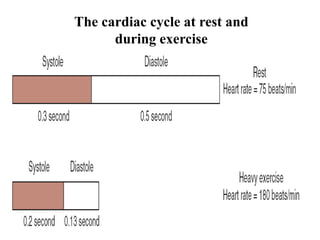
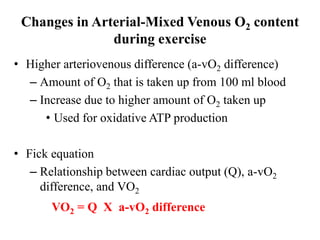
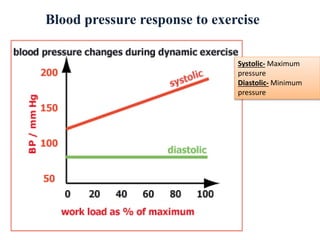
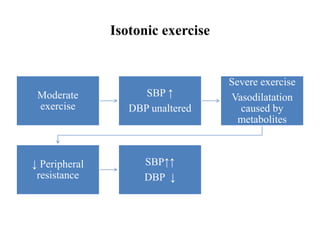
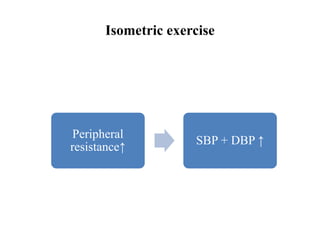
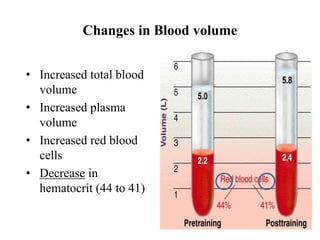
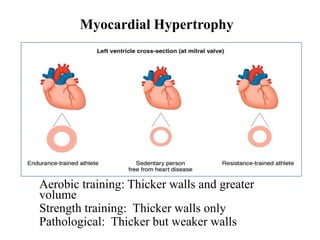
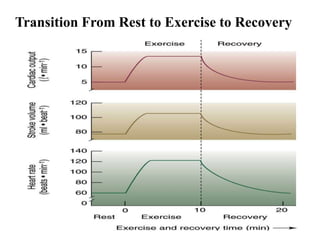
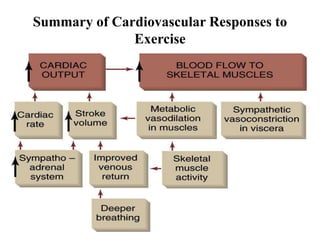
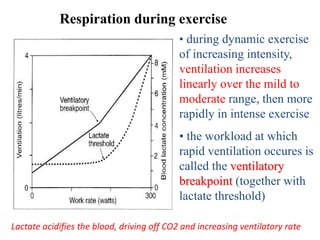
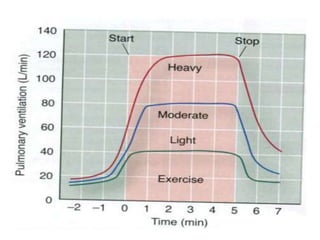
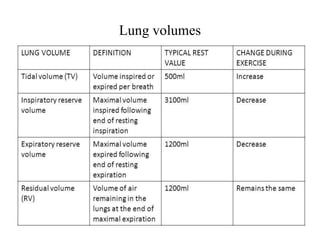
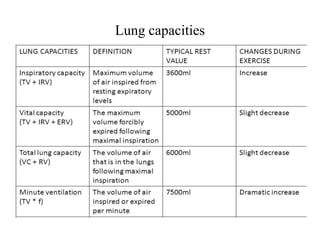
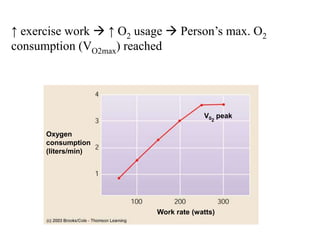
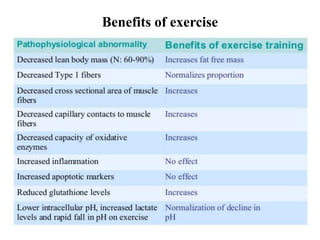
The document discusses the cardiopulmonary changes that occur during exercise, emphasizing the physiological responses of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems. It outlines types of exercises, the grading of exercise intensity, and the acute and long-term adaptations of the body in response to training, including increased heart rate, stroke volume, and oxygen uptake. Additionally, the document highlights the importance of factors like redistribution of blood flow and ventilatory responses as exercise intensity increases.