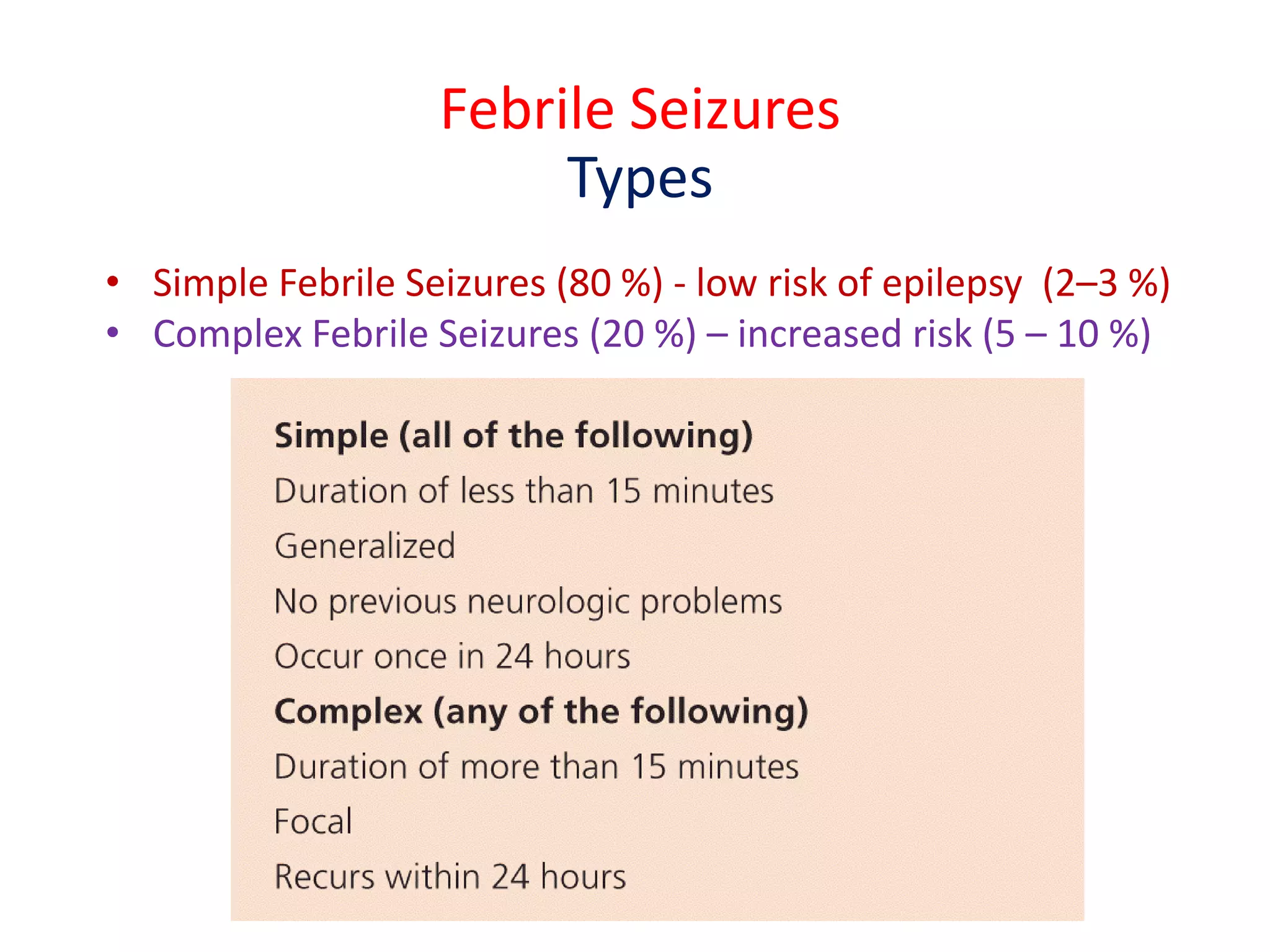
This document discusses febrile seizures in children. Febrile seizures are seizures caused by fever but without an underlying infection of the brain. They typically occur in children 6 months to 5 years old and are associated with a sudden spike in fever. While concerning when they occur, febrile seizures usually stop within 5 minutes and do not cause long-term problems in most cases. They are managed by bringing down the child's fever with medications like acetaminophen and sponging with water.