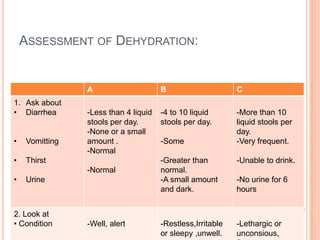
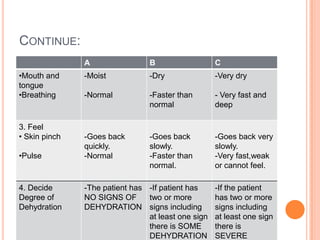
Diarrhea is characterized by loose or watery stool more than 3 times per day. It is a major cause of death in developing countries and infants worldwide. Diarrhea can be acute lasting 1-2 weeks, chronic lasting more than 3 weeks, or persistent lasting 2 weeks or more. Causes include viruses, bacteria, parasites, and fungi transmitted through the fecal-oral route. Management involves oral rehydration therapy with continued feeding. For severe dehydration intravenous fluids are given along with monitoring until rehydration is complete. Diet emphasizes continued breastfeeding and eating small, frequent meals high in nutrients.