The document discusses implantable contact lenses (ICL) for correcting high refractive errors. Key points include:
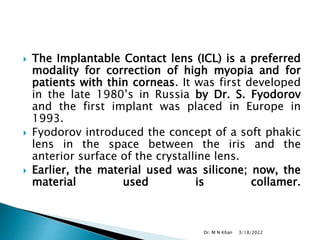
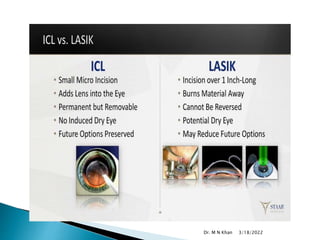
- ICL is preferred over LASIK for high myopia or thin corneas, as it has fewer risks of complications.
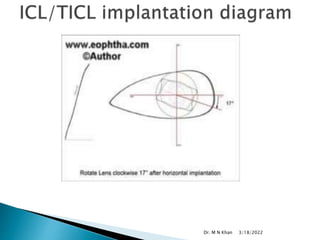
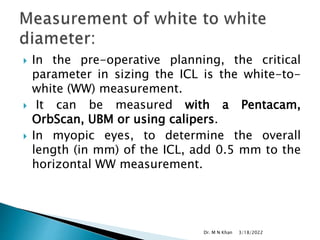
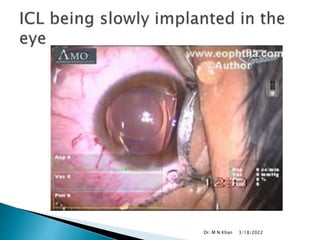
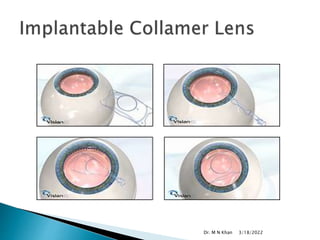
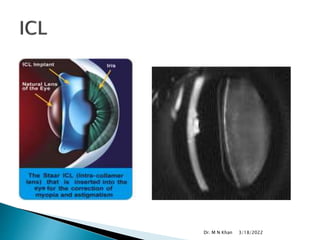
- ICL is made of a biocompatible collamer material and is implanted in the posterior chamber behind the iris.
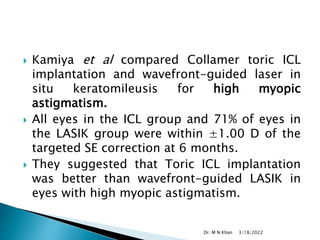
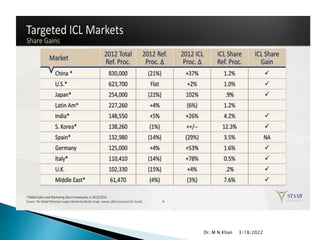
- A clinical trial found nearly 60% of eyes achieved 20/20 vision and 95% achieved 20/40 vision or better after 3 years with ICL implantation.
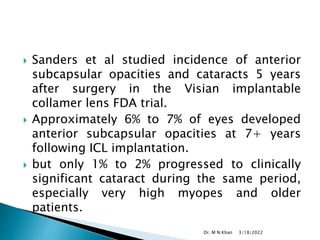
- Complications are generally low but can include cataracts, increased eye pressure, damage to the natural lens, and other rare issues like infections. Most risks are





















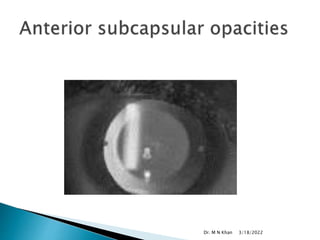
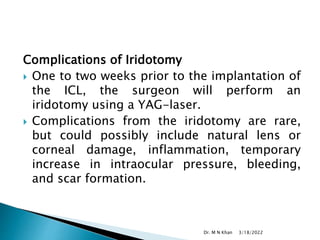












![ Kamiya K, Shimizu K, Igarashi A, Komatsu M. Comparison of Collamer
toric implantable [corrected] contact lens implantation and wavefront-
guided laser in situ keratomileusis for high myopic astigmatism. J
Cataract Refract Surg. 2008 Oct; 34(10):1687-93.
Sanders DR. Anterior subcapsular opacities and cataracts 5 years after
surgery in the visian implantable collamer lens FDA trial. J Refract Surg.
2008 Jun; 24(6):566-70.
Chung TY, Park SC, Lee MO, Ahn K, Chung ES. Changes in iridocorneal
angle structure and trabecular pigmentation with STAAR implantable
collamer lens during 2 years. J Refract Surg. 2009 Mar; 25(3):251-8.
Chan KC, Birchall W, Gray TB, Wells AP. Acute angle closure after
implantable contact lens insertion unresponsive to surgical peripheral
iridectomy. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2008 Apr; 34(4):696-9.
R. Kaufer, G. Kaufer. Late subluxation of an ICL Journal of Cataract &
Refractive Surgery, Volume 31, Issue 6, Pages 1254-1255.
Allan BD, Argeles-Sabate I, Mamalis N. Endophthalmitis rates after
implantation of the intraocular Collamer lens: survey of users between
1998 and 2006. J Cataract Refract Surg. 2009 Apr; 35(4):766-9.
Domènech NP, Arias L, Prades S, Pujol O, Rubio M, Caminal JM. Acute
onset of retinal detachment after posterior chamber phakic intraocular
lens implantation. Clin Ophthalmol. 2008 Mar; 2(1):227-31
3/18/2022
Dr. M N Khan](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/icl-140115122939-phpapp01/85/Implantable-Collamer-Contact-Lens-52-320.jpg)