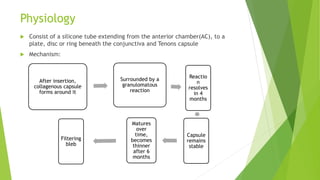
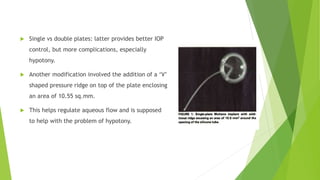
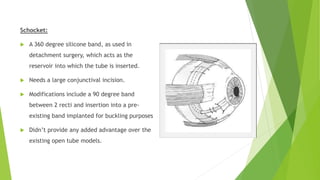
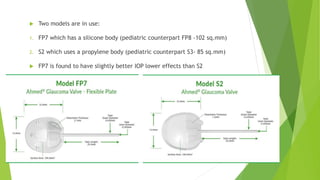
Glaucoma drainage devices are implants used to drain aqueous humor from the anterior chamber to control intraocular pressure. They consist of a silicone tube extending from the anterior chamber to a plate beneath the conjunctiva. Open tube designs like Molteno and Baerveldt and flow-restricted designs like Ahmed are commonly used. GDDs are generally used when filtering surgeries have failed or are likely to fail. While they effectively lower IOP, complications can include hypotony, elevated IOP, migration or erosion of the device, and diplopia. Long-term studies show success rates of 65-85% in maintaining IOP control.