IB Chemistry on Organic nomenclature and functional groups.
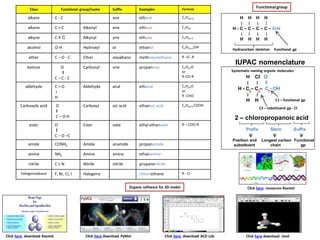
- 1. Class Functional group/name Suffix Examples Formula alkane C - C ane ethane CnH2n+2 alkene C = C Alkenyl ene ethene CnH2n alkyne C ≡ C Alkynyl yne ethyne CnH2n-2 alcohol O-H Hydroxyl ol ethanol CnH2n+1OH ether C – O - C Ether oxyalkane methoxymethane R –O -R ketone O ‖ C – C - C Carbonyl one propanone CnH2nO or R-CO-R aldehyde C = O ׀ H Aldehyde anal ethanal CnH2nO or R -CHO Carboxylic acid O ‖ C – O H Carboxyl oic acid ethanoic acid CnH2n+1COOH ester O ‖ C – O –C Ester oate ethyl ethanoate R – COO-R amide CONH2 Amide anamide propanamide amine NH2 Amine amine ethanamine nitrile C ≡ N Nitrile nitrile propanenitrile halogenoalkane F, Br, CI, I Halogeno chloroethane R - CI Functionalgroup H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – O-H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp IUPAC nomenclature Systematic naming organic molecules H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H C1 – functional gp C2 – substituent gp - CI 2 – chloropropanoic acid Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp Organic software for 3D model Click here resources Rasmol Click here download Rasmol Click here download PyMol Click here download ACD Lab Click here download Jmol 3 2 1
- 2. H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – O-H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Hydrocarbon Aliphatic Aromatic Saturated Unsaturated benzene alkylbenzene H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H H H ׀ ׀ C = C ׀ ׀ H H Alkane Cycloalkane Compound Ethane Ethanoic acid Empirical formula CH3 CH2O Molecular formula C2H6 C2H4O2 Full SF Condensed SF CH3CH3 CH3COOH Stereochemical formula (3D) H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H H O ׀ ‖ H - C - C - OH ׀ H Organic Chemistry Cycloalkene Alkene IUPAC nomenclature Ring form Functionalgroup Structural formula 2 – chloropropanoic acid no aromatic ring Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H C1 – functional gp C2 – substituent gp - CI CH3(CH2)3CH3 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Use of parenthesis Repeat CH2 x 3 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CH3 Repeat CH2 x 2CH3 branch H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 3 2 1 benzene ring inside
- 3. H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI Br H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H IUPAC nomenclature 2 – chloropropanoic acid Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H C1 – functional gp C2 – substituent gp - CI CH3(CH2)3CH3 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Use of parenthesis Repeat CH2 x 3 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CH3 Repeat CH2 x 2CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch Number carbon Alkyl gp Structure formula 1 Methyl CH3 - 2 Ethyl CH3CH2 - 3 Propyl CH3CH2CH2 - 4 Butyl CH3(CH2)2CH2 - 5 Pentyl CH3(CH2)3CH2 - 6 Hexyl CH3(CH2)4CH2 - 7 Heptyl CH3(CH2)5CH2 - 8 Octyl CH3(CH2)6CH2 - R Alkyl R - Substituents - Gp attach to main carbon chain R - Alkyl gp (carbon branches) H C2H5 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H 2 -methylbutane 2 - ethylpentane 2, 3- dimethylbutane 1 2 2 3 4 51 1 2 3 4 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI CI H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI CH3 H 1 1 2 2 3 1 2 3 1 - chloro-2-bromopropane 1, 2 - dichloropropane 1-chloro-2-methylpropane C2H5 ׀ C2H5 - C – H ׀ C2H5 H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H 4 3 2 1 but – 1- ene butan – 2- ol 1 2 3 4 3 - ethylpentane 3 Start with smallest number Start with smallest number Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number 3 2 1 substituents – attached to main carbon chain
- 4. C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 Nomenclature for Organic Molecules Name the parent (longest unbranched carbon chain) Choose chain which has more alkyl groups attached 1 C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 7 carbon - heptane C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 7 carbon - heptane 2 C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 4 alkyl gps Number from end giving substituent lowest possible number3 C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 2 or more identical substituent present 2 - di , 3- tri , 4 - tetra . 2, 4, 5 trimethyl 3 - ethyl 4 Use comma, to separate numbers Use hyphen – to separate number and word Write prefix and parent as one word Arrange substituents according alphabetical order C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 -ethyl-2, 4, 5-trimethylheptane Choose chain which has more alkyl groups attached 3 alkyl gps C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 CH3 ׀ CH3 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 3, 4, 6 trimethyl 5 - ethyl 2, 4, 5 -trimethyl-3-ethylheptane Name the parent (longest unbranched carbon chain) wrong wrong wrong Click here organic notesClick here e text organic Click here chemical search.
- 5. • memberdifferby CH2 gp • same functionalgroup • similar chemicalproperties • chemicalformulaCnH2n+2 • end with ane Class Functionalgp Suffix Example Formula Alkane C - C - ane ethane CnH2n+2 Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Alkene Alkenyl - ene ethene CnH2n H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H • memberdiffer by CH2 gp • same functionalgroup • similar chemicalproperties • chemicalformula CnH2n • end with ene H ׀ H - C – H ׀ H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Number carbon Word IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Meth Methane CH4 CH4 2 Eth Ethane CH3CH3 C2H6 3 Prop Propane CH3CH2CH3 C3H8 4 But Butane CH3(CH2)2CH3 C4H10 5 Pent Pentane CH3(CH2)3CH3 C5H12 6 Hex Hexane CH3(CH2)4CH3 C6H14 7 Hept Heptane CH3(CH2)5CH3 C7H16 8 Oct Octane CH3(CH2)6CH3 C8H18 9 Non Nonane CH3(CH2)7CH3 C9H20 10 Dec Decane CH3(CH2)8CH3 C10H22 methane ethane propane butane Saturated hydrocarbon (C – C single bond) Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 2 Ethene CH2CH2 C2H4 3 Propene CH2=CHCH3 C3H6 4 Butene CH2=CHCH2CH3 C4H8 5 Pentene CH2=CH(CH2)2CH3 C5H10 6 Hexene CH2=CH(CH2)3CH3 C6H12 7 Heptene CH2=CH(CH2)4CH3 C7H14 8 Octene CH2=CH(CH2)5CH3 C8H16 9 Nonene CH2=CH(CH2)6CH3 C9H18 10 Decene CH2=CH(CH2)7CH3 C10H20 H H ׀ ׀ C = C ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C - H ׀ ׀ H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Unsaturated hydrocarbon (C = C double bond) H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H ethene propene butene pentene
- 6. Class Functional group/name Examples alkene C = C Alkenyl ethene alkyne C ≡ C Alkynyl ethyne alcohol OH Hydroxyl ethanol ether C – O - C Ether methoxymethane ketone O ‖ C – C - C Carbonyl propanone aldehyde CHO Aldehyde ethanal Carboxylic acid COOH Carboxyl ethanoic acid ester O ‖ C – O -R Ester ethyl ethanoate amide O ‖ C – NH2 Amide propanamide amine NH2 Amine ethanamine nitrile C ≡ N Nitrile propanenitrile Class Functional gp Suffix Example Formula Alkane C - C - ane ethane CnH2n+2 Homologous Series carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula Boiling point 1 Methane CH4 CH4 Gas 2 Ethane CH3CH3 C2H6 Gas 3 Propane CH3CH2CH3 C3H8 Gas 4 Butane CH3(CH2)2CH3 C4H10 Gas 5 Pentane CH3(CH2)3CH3 C5H12 Liquid 6 Hexane CH3(CH2)4CH3 C6H14 Liquid Physical properties • Increase RMM / molecular size •RMM increase ↑ - Van Der Waals forces stronger ↑ ↓ Melting /boiling point increases ↑ (Increasing polarisability ↑) London dispersion forces/temporary dipole ↑ 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 number carbons – RMM ↑ 150 100 50 0 -50 -100 -150 -200 m/p+ b/p increase ↑ boiling point room temp gas liquid Homologous Series number Carbons / RMM ↑1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 boiling point boiling point increase with increase carbon atoms alcohol alkane alkene alkyne London dispersion force (temporary dipole) H2 bonding carboxylic acid > alkane/alkene/alkyne alcohol carboxylic acid
- 7. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+2 • end with ane Class Functionalgp Suffix Example Formula Alkane C - C - ane ethane CnH2n+2 Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Alkene C = C - ene ethene CnH2n H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n • end with ene H ׀ H - C – H ׀ H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Number carbon Word IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Meth Methane CH4 CH4 2 Eth Ethane CH3CH3 C2H6 3 Prop Propane CH3CH2CH3 C3H8 4 But Butane CH3(CH2)2CH3 C4H10 5 Pent Pentane CH3(CH2)3CH3 C5H12 methane ethane propane butane Saturated hydrocarbon Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 2 Ethene CH2=CH2 C2H4 3 Propene CH2=CHCH3 C3H6 4 Butene CH2=CHCH2CH3 C4H8 5 Pentene CH2=CH(CH2)2CH3 C5H10 6 Hexene CH2=CH(CH2)3CH3 C6H12 H H ׀ ׀ C = C ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C - H ׀ ׀ H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Unsaturated hydrocarbon H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H ethene propene butene pentene Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling ethane CH3CH3 H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H propene Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ C = C – C - H ׀ ׀ H H CH2=CHCH3
- 8. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n-2 • end with yne Class Functional gp Suffix Example Formula Alkyne C ≡ C - yne ethyne CnH2n-2 Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Alcohol Hydroxyl - ol methanol CnH2n+1OH H - C ≡ C – H • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1OH • end with ol H ׀ H - C ≡ C – C – H ׀ H Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 2 Ethyne CH≡CH C2H2 3 Propyne H-C≡C-CH3 C3H4 4 Butyne H-C≡C-CH2CH3 C4H6 5 Pentyne H-C≡C-(CH2)2CH3 C5H8 6 Hexyne H-C≡C-(CH2)3CH3 C6H10 ethyne propyne butyne Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanol CH3OH CH3OH 2 Ethanol CH3CH2OH C2H5OH 3 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH C3H7OH 4 Butanol CH3(CH2)2CH2OH C4H9OH 5 Pentanol CH3(CH2)3CH2OH C5H11OH methanol ethanol propanol butanol H H ׀ ׀ H - C ≡ C – C – C- H ׀ ׀ H H H ׀ H - C – OH ׀ H H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Functional gp Hydrocarbon skeleton Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Ball /stick model SpacefillingCondensed SFDisplay full SF H ׀ H - C ≡ C – C – H ׀ H CH≡C-CH3 propyne Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H CH3CH2OH ethanol
- 9. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2nO • end with one Class Functionalgp Suffix Example Formula Ketone Carbonyl (C=O) - one propanone CnH2nO Homologous Series Class Fumctional Suffix Example Formula Aldeyde Aldeyde - al methanal CnH2nO • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2nO • end with al Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 3 Propanone CH3COCH3 C3H6O 4 Butanone CH3COCH2CH3 C4H8O 5 Pentanone CH3CH2COCH2CH3 C5H10O 6 Hexanone CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 C6H12O 7 Heptanone CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH2CH3 C7H14O propanone butanone pentanone Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanal HCHO CH2O 2 Ethanal CH3CHO C2H4O 3 Propanal CH3CH2CHO C3H6O 4 Butanal CH3(CH2)2CHO C4H8O 5 Pentanal CH3(CH2)3CHO C5H10O methanal ethanal propanal butanal H - C = O ׀ H H ׀ H - C – C = O ׀ ׀ H H H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = O ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C = O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H H O H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Functional gp Hydrocarbon skeleton Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H CH3COCH3 propanone ethanal H ׀ H - C – C = O ׀ ׀ H H CH3CHO
- 10. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1COOH • end with oic acid Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Carboxylic acid Carboxyl - oic acid ethanoic acid CnH2n+1COOH Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Formula Ester Ester - oate R –COO-R • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2nO2 • end with oate methanoic acid ethanoic acid propanoic acid Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methyl methanoate HCOOCH3 R–COO-R 2 Methyl ethanoate CH3COOCH3 R–COO-R 3 Methyl propanoate CH3CH2COOCH3 R–COO-R 4 Methyl butanoate CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 R–COO-R methyl methanoate methyl ethanoate methyl propanoate Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanoic acid HCOOH HCOOH 2 Ethanoic acid CH3COOH CH3COOH 3 Propanoic acid CH3CH2COOH C2H5COOH 4 Butanoic acid CH3(CH2)2COOH C3H7COOH 5 Pentanoic acid CH3(CH2)3COOH C4H9COOH O ‖ H - C - O H H O ׀ ‖ H - C - C - OH ׀ H H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H O H ‖ ׀ H - C – O – C - H ׀ H H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C - C – O - C - H ׀ ׀ H H H H O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – O - C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling O ‖ H - C - O H methanoic acid HCOOH Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling O H ‖ ׀ H - C – O – C - H ׀ H HCOOCH3 Methyl methanoate
- 11. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1NH2 • end with amine Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Amine NH2 - amine ethanamine CnH2n+1NH2 Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Amide Amide - amide ethanamide CnH2n+1CONH2 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – N - H ׀ ׀ H H • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1CONH2 • end with amide H H ׀ ׀ H - C – N - H ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – N - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanamine CH3NH2 CH3NH2 2 Ethanamine CH3CH2NH2 C2H5NH2 3 Propanamine CH3CH2CH2NH2 C3H7NH2 4 Butanamine CH3(CH2)2CH2NH2 C4H9NH2 5 Pentanamine CH3(CH2)3CH3NH2 C5H11NH2 methanamine ethanamine propanamine Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanamide HCONH2 HCONH2 2 Ethanamide CH3CONH2 CH3CONH2 3 Propanamide CH3CH2CONH2 C3H7CONH2 4 Butanamide CH3(CH2)2CONH2 C4H9CONH2 5 Pentanamide CH3(CH2)3CONH2 C5H11CONH2 O H ‖ ׀ H - C – N - H H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – N - H ׀ H H H O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – N - H ׀ ׀ H H methanamide ethanamide propanamide Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling methanamine H H ׀ ׀ H - C – N - H ׀ H CH3NH2 Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling methanamide O H ‖ ׀ H - C – N - H HCONH2
- 12. • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1CN • end with nitrile Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Nitrile C ≡ N - nitrile ethanenitrile CnH2n+1CN Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Ether Ether -oxyalkane methoxymethane H ׀ H - C – C ≡ N ׀ H • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula R – O - R • end with oxyalkane H - C ≡ N H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C ≡ N ׀ ׀ H H Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanenitrile HCN HCN 2 Ethanenitrile CH3CN CH3CN 3 Propanenitrile CH3CH2CN C2H5CN 4 Butanenitrile CH3(CH2)2CN C3H7CN 5 Pentanenitrile CH3(CH2)3CN C4H9CN methanenitrile ethanenitrile propanenitrile butanenitrile Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methoxymethane CH3 - O – CH3 R –O -R 2 Methoxyethane CH3CH2 - O – CH3 R –O -R 3 Methoxypropane CH3CH2CH2 - O –CH3 R –O -R 4 Methoxybutane CH3(CH2 )3 - O –CH3 R –O -R 5 Methoxypentane CH3(CH2 )4 - O –CH3 R –O -R methoxymethane methoxyethane methoxypropane H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C ≡ N ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ H - C – O – C - H ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – O - C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – O - C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling ethanenitrile H ׀ H - C – C ≡ N ׀ H CH3CN Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling methoxymethane H H ׀ ׀ H - C – O – C - H ׀ ׀ H H CH3–O– CH3 Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp
- 13. H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – CI ׀ ׀ H H Class Functional Prefix Example Halogenoalkane F, CI, Br, I - chloro chloroethane • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n-1 X Homologous Series Class Functional Suffix Example Formula Alcohol Hydroxyl - ol methanol CnH2n+1OH • member differ by CH2 gp • same functional group • similar chemical properties • chemical formula CnH2n+1OH • end with ol chloromethane chloroethane chloropropane Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanol CH3OH CH3OH 2 Ethanol CH3CH2OH C2H5OH 3 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH C3H7OH 4 Butanol CH3(CH2)2CH2OH C4H9OH 5 Pentanol CH3(CH2)3CH2OH C5H11OH methanol ethanol propanol butanol H ׀ H - C – OH ׀ H H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Ball /stick model SpacefillingCondensed SFDisplay full SF CH3CI chloromethane Structural formula – arrangement atoms in molecule Display full SF Condensed SF Ball /stick model Spacefilling H H ׀ ׀ H - C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H CH3CH2OH ethanol H ׀ H - C – CI ׀ H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – CI ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Hydrocarbon skeleton Functional gp Number carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 chloromethane CH3CI CH3CI 2 chloroethane CH3CH2CI C2H5CI 3 chloropropane CH3CH2CH2CI C3H7CI 4 chlorobutane CH3(CH2)2CH2CI C4H9CI 5 chloropentane CH3(CH2)3CH2CI C5H11CI H ׀ H - C – CI ׀ H
- 14. H CH3 CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C = C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H C – C – C – C – C = C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ H Br H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C = C – C – C - CI ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H 1 2 3 4 5 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C = C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C2H5 ׀ CI – C = C – C – C – C ׀ C H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C = C – H ׀ CI C2H5 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ C2H5 - C – C = C – H ׀ C2H5 H C2H5 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H IUPAC nomenclature 1 – chloropent-2-ene Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C = C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H CH3(CH2)2CHCH2 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)CH2CHCH2 CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH=C(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 3 -methylbut-1-ene 4 – methylhex-2-ene 2-chloro- 4-ethylhex-2-ene 3 2 1 4 3 2 1 3 - chloropropene 5-chloro-3-methylpent-2-ene 3 –bromobut-1-ene 4 3 2 1 3, 3-diethylpent-1-ene Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Alkene and Nomenclature CI - substituent 6 5 4 3 2 12 3 4 5 6 1 Double bond Alkene start from 2 carbon - ethene 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 – chloropent-2-ene 5 – chloropent- 4 -ene Ethene/propene – no numberingneeded 3, 5 – dimethylhex-1-ene carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 2 Ethene CH2=CH2 C2H4 3 Propene CH2=CHCH3 C3H6 4 Butene CH2=CHCH2CH3 C4H8 5 Pentene CH2=CH(CH2)2CH3 C5H10 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 CH3CH(CH3)CHC(CH3)CH3
- 15. H CH3 CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C = C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H C – C – C – C – C = C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 H CH3 CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C = C – C – C - F ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H 1 2 3 4 5 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C = C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C2H5 ׀ Br – C - C – C – C – C ‖ C CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 - C – C = C – H ׀ H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C = C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H IUPAC nomenclature 1 – chloropent-2-ene Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C = C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H CH3(CH2)2CHCH2 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)CH2CHCH2 CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CHC(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 2- methylbut-2-ene 3-methylpent-1-ene 2-bromo- 3-ethylhex-1-ene 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 2, 3 –dimethylbut-2-ene 5-fluoro-3,4-dimethylpent-2-ene 2, 3, 3 trimethylbut-1-ene 4 3 2 1 3-methylbut-1-ene Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Alkene and Nomenclature CI - substituent 6 5 4 3 2 12 3 4 5 6 1 Double bond Alkene start from 2 carbon - ethene 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 – chloropent-2-ene 5 – chloropent- 4 -ene Ethene/propene – no numberingneeded 3, 5 – dimethylhex-1-ene carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 2 Ethene CH2CH2 C2H4 3 Propene CH2=CHCH3 C3H6 4 Butene CH2=CHCH2CH3 C4H8 5 Pentene CH2=CH(CH2)2CH3 C5H10 1 2 3 4 CH3 H ׀ ׀ CH3 - C = C - C – H ׀ ׀ H CH3 1 2 3 4 C – C ׀ CH3 – C – C = C 4 5 CH3CH(CH3)CH=C(CH3)CH3
- 16. H CH3 H CH3 O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ H- C=O H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ CI CI H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ CI Br C2H5 O ׀ ‖ C2H5 - C – C – H ׀ C2H5 O C2H5 H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H IUPAC nomenclature 2 – chloropropanal Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - O ׀ ׀ H H C1 – functional gp (numbering start here) C2 – substituent gp - CI CH3(CH2)3CHO H H H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Repeat CH2 x 3 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CHO Repeat CH2 x 2CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)CHO CH3 branch 3 - methylbutanal 2 - ethylpentanal 2-ethyl- 4-methylpentanal 12 2 3 4 51 1 1 2 3 2 3 - chloro- 2- bromopropanal 2, 3 - dichloropropanal O H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H H O H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H But – 3 –en-1-al 2 -hydroxybutanal 1 2 3 4 2, 2 - diethylbutanal 3 Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Aldehyde and Nomenclature carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanal HCHO CH2O 2 Ethanal CH3CHO C2H4O 3 Propanal CH3CH2CHO C3H6O 4 Butanal CH3(CH2)2CHO C4H8O 5 Pentanal CH3(CH2)3CHO C5H10O 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 -hydroxypropanal functional gp aldehyde – at the end OH - substituent 3 -aldehydepropanol 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 1 Double bond (3 – butenal) CHO – functional gp, not OH 3 2 1 H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ HO - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H
- 17. H CH3 CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ H H O H H H CH3 H O H ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ H H H H O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H 1 2 3 4 5 H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H O C2H5 ‖ ׀ CI – C – C – C – C – C ׀ C H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ CI H C2H5 O H ׀ ‖ ׀ C2H5 - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ C2H5 H H C2H5 O H H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ H H IUPAC nomenclature 1 – chloropentan- 2-one Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H CH3(CH2)2COCH3 H H H O H ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)CH2COCH3 CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)COCH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 3 - methylbutanone 4 – methylhexan–3-one 2-chloro- 4-ethylhexan-3-one 3 2 1 4 3 2 1 1 - chloropropanone pentan-2-one 3 -hydroxybutanone 4 3 2 1 3, 3 – diethylpentan-2-one Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Ketone and Nomenclature functional gp ketone – inside carbon chain CI - substituent 1 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5 6 1 Double bond Ketone start from 3 carbon - propanone carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 3 Propanone CH3COCH3 C3H6O 4 Butanone CH3COCH2CH3 C4H8O 5 Pentanone CH3CH2COCH2CH3 C5H10O 6 Hexanone CH3CH2COCH2CH2CH3 C6H12O 1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 1 – chloropentan- 2 -one 5 – chloropentan- 4 -one Propanone/Butanone – no numberingneeded Pent-4-en-2-one CO – functional gp, not OH 4 3 2 1 1 2 3
- 18. H OH H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C - C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H OH H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H C – C – C – C = C ׀ OH H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H OH H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH CH3 H H 1 2 3 4 5 CH3 ׀ HO– C – C – C ׀ C H H OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C - OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H H H IUPAC nomenclature 5–chloropent-4-ene-1-ol Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C = C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H CH3(CH2)2CH(OH)CH3 H H H OH H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CH2OH CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH(OH)CH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 2- methylbutan-1-ol 4 – methylpentan-1-ol 2- methylbutan--2-ol 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 2- methylpropan-1-ol 3,3 -dimethylpentan-2-ol propane-1,2-diol 1 2 3 Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Alcohol and Nomenclature CI - substituent 1 2 3 4 52 3 4 1 Double bond 5 4 3 2 1 5– chloropentan-1-ol 1– chloropentan-5-ol Methanol/Ethanol – no numberingneeded pen-4-ene-2-ol 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 Repeat CH2 x 2 carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanol CH3OH CH3OH 2 Ethanol CH3CH2OH C2H5OH 3 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH C3H7OH 4 Butanol CH3(CH2)2CH2OH C4H9OH 5 Pentanol CH3(CH2)3CH2OH C5H11OH OH – functional gp, not alkene 2- methylpropan-2-ol OH – functional gp, not alkene
- 19. H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C - C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H OH H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H OH ׀ C – C – C – C – C = C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ H OH H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - CI ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H H H 1 2 3 4 5 OH C2H5 ׀ ׀ CI – C - C – C – C – C ׀ C H H OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI H H C2H5 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ C2H5 - C – C - C – OH ׀ C2H5 H C2H5 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H OH H H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ l H H OH H IUPAC nomenclature 5–chloropent-4-ene-1-ol Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C = C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H CH3(CH2)2CH(OH)CH3 H H H OH H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CH2OH CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH(OH)CH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 3 – methylbutan-2-ol 4 – methylhexan-3-ol 2-chloro-4-ethylhexan-2-ol 3 2 1 4 3 2 1 3 – chloropropan-1-ol 5-chloro-3-methylpentan-2-ol But-3-ene-2-ol 1 2 3 4 3, 3 – diethylpentan-1-ol Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Alcohol and Nomenclature CI - substituent 6 5 4 3 2 12 3 4 5 6 1 Double bond 5 4 3 2 1 5– chloropentan-1-ol 1– chloropentan-5-ol Methanol/Ethanol – no numberingneeded 3, 5 – dimethylhex-1-ene-3-ol 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 Repeat CH2 x 2 OH – functional gp, not alkene carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanol CH3OH CH3OH 2 Ethanol CH3CH2OH C2H5OH 3 Propanol CH3CH2CH2OH C3H7OH 4 Butanol CH3(CH2)2CH2OH C4H9OH 5 Pentanol CH3(CH2)3CH2OH C5H11OH
- 20. H CH3 H CH3 O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ COOH H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ CI CI H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ CI Br C2H5 O ׀ ‖ C2H5 - C – C – OH ׀ C2H5 O C2H5 H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ HO- C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H IUPAC nomenclature 2 – chloropropanoic acid Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp C1 – functional gp (numbering start here) C2 – substituent gp - CI CH3(CH2)3COOH H H H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Repeat CH2 x 3 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2COOH Repeat CH2 x 2CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)COOH CH3 branch 3-methylbutanoic acid 2 -ethylpentanoic acid 2-ethyl-4-methylpentanoic acid 12 2 3 4 51 13 2 3 - chloro- 2- bromopropanoic acid 2, 3 - dichloropropanoic acid O H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ HO- C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H H O H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ HO- C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H But -3 -enoic acid 2 –hydroxybutanoic acid 1 2 3 4 2, 2 – diethylbutanoic acid 3 2 1 Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Carboxylic acid and Nomenclature 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 –hydroxypropanoic acid functional gp acid – at the end OH - substituent 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 1 Double bond (3 – butenoic acid) COOH – functional gp, not OH carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanoic acid HCOOH HCOOH 2 Ethanoic acid CH3COOH CH3COOH 3 Propanoic acid CH3CH2COOH C2H5COOH 4 Butanoic acid CH3(CH2)2COOH C3H7COOH 5 Pentanoic acid CH3(CH2)3COOH C4H9COOH 3 2 1 H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ HO - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H
- 21. H CH3 H CH3 O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ COOH H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ Br H H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H CH3 CH3 O ׀ ‖ CH3 - C – C – C – OH ׀ CH3 O H H H OH ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ HO- C – C – C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H H CH3 IUPAC nomenclature 2 – chloropropanoic acid Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Suffix Position and substituent Longest carbon chain Functional gp H CI O ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C – C – C - OH ׀ ׀ H H C1 – functional gp (numbering start here) C2 – substituent gp - CI CH3(CH2)3COOH H H H H O ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ H - C - C – C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Repeat CH2 x 3 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2COOH Repeat CH2 x 2CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH(CH3)COOH CH3 branch 2, 3 -dimethylbutanoic acid 5 – hydroxypentanoic acid 2-ethyl- 4-methylpentanoic acid 12 2 3 4 51 13 2 2- methylpropanoic acid 3- bromopropanoic acid O H H O ‖ ׀ ׀ ‖ HO- C – C – C – C -OH ׀ ׀ H H O H H H ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ HO- C – C – C = C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H But-3 -enoic acid Butanedioic acid 1 2 3 4 3, 3 -dimethylbutanoic acid Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Carboxylic acid and Nomenclature 4 3 4 3 2 1 3 2 1 3 –hydroxypropanoic acid functional gp acid – at the end OH - substituent 1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5 1 Double bond (3 – butenoic acid) H H O ׀ ׀ ‖ HO - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ H H (1, 4 butanedioic acid) 3 2 1 carbon IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula 1 Methanoic acid HCOOH HCOOH 2 Ethanoic acid CH3COOH CH3COOH 3 Propanoic acid CH3CH2COOH C2H5COOH 4 Butanoic acid CH3(CH2)2COOH C3H7COOH 5 Pentanoic acid CH3(CH2)3COOH C4H9COOH 3 2 1
- 22. H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C –O – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H O H H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – O – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – O – C – H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H H O H H CH3 H O H ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – O – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H O ׀ ‖ H – C – C – O – C – C - C – C ׀ ׀ H C H H O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – O – C- H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H O H H ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ H – C- O – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H O ‖ C – C – C – O – C – C – C ׀ C H O H ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ H H CH3 O H ׀ ‖ ׀ C2H5 - C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ CH3 H H C2H5 O H H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C– O - C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 O H ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C – C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H IUPAC nomenclature Propyl ethanoate Systematic naming organic molecules Ethanoate Propyl (Ethanoic acid) (Propanol) CH3(CH2)2COOCH3 H H H O H ׀ ׀ ׀ ‖ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – O– C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)CH2COOCH3 CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)COOCH3 CH3 branch Methyl 2-methylpropanoate Ethyl 2-methylbutanoate Propyl 2-methylpropanoate Methyl ethanoate Methyl propanoate (same structure) Methyl 2,2 dimethylbutanoate Ester and Nomenclature Ethyl propanoate 2-methylbutyl ethanoate IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula Methyl methanoate HCOOCH3 R–COO-R Methyl ethanoate CH3COOCH3 R–COO-R Methyl propanoate CH3CH2COOCH3 R–COO-R Methyl butanoate CH3CH2CH2COOCH3 R–COO-R Propyl ethanoate Ethanoate = Acetate Propyl acetate
- 23. H H H H H ׀ l ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C –O – C – C – C – H ׀ l ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H H H ׀ l ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – O – C – C – C – H ׀ l ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – O – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – O – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H ׀ H – C – C – O – C – C - C – C – C ׀ ׀ H C H H H H ׀ ׀׀׀ H - C – C – C – O – C- H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C- O – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H C – C – C – C – O – C – C ׀ C H H H ׀׀׀ H - C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H CH3 H H ׀׀׀ C2H5 - C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 H H H C2H5 H H H ׀ ׀׀׀ ׀ H - C – C – C– O - C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀׀׀ H - C – C – C – O - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H IUPAC nomenclature Ethoxy propane Systematic naming organic molecules Ethoxy Propane (Ethane) CH3(CH2)2CH2OCH3 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C –O – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH2OCH3 CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH2OCH3 CH3 branch Methoxy 2-methylpropane Ethoxy 2-methylbutane Ethoxy 2-methylbutane Methoxy ethane Methoxy propane (same structure) Methoxy 2,2-dimethylbutane Ether and Nomenclature Propoxy ethane Ethoxy 2-methylpentane Ethyl Propyl ether IUPAC name Structure formula Molecular formula Methoxymethane CH3 - O – CH3 R –O -R Methoxyethane CH3CH2 - O – CH3 R –O -R Methoxypropane CH3CH2CH2 - O –CH3 R –O -R Methoxybutane CH3(CH2 )3 - O –CH3 R –O -R Click here, diff naming system ether Ethoxy propane Shorter carbon 1st Longer carbon 2nd
- 24. H H H CI H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C – C – H l l ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H Br H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C - C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H CI H H H CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – CI ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ CI - C – C – C – C = C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H C – C – C – C = C ׀ CI H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI H CI H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI CH3 H H 1 2 3 4 5 CH3 ׀ CI – C – C – C ׀ C H H CI ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C - F ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ I H H H IUPAC nomenclature 2–chloropentane Systematic naming organic molecules Prefix Stem Position and functional gp Longest carbon chain CH3(CH2)2CH(CI)CH3 H H H CI H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H H Repeat CH2 x 2 CH3CH(CH3)(CH2)2CH2CI CH3 branch CH3CH(CH3)CH(CI)CH(CH3)CH3 CH3 branch 1-iodo-2-methylbutane 1-fluoro-4–methylpentane 2-chloro-2-methylbutane 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 1-chloro-2-methylpropane 2-chloro-3,3-dimethylpentane 1,3-dichloropropane 1 2 3 Number from end of chain giving substituent lowest possible number Halogenoalkane and Nomenclature CI - halogen 5 4 3 2 12 3 4 1 Double bond 5 4 3 2 1 5– chloropent- 1-ene 1– chloropent-4-ene 4-chloropen-1-ene 1 2 3 4 3 2 1 5 4 3 2 1 Repeat CH2 x 2 2-bromo-2-methylpropane C=C – functional gp, not halogen carbon IUPAC name Structureformula Molecular formula 1 chloromethane CH3CI CH3CI 2 chloroethane CH3CH2CI C2H5CI 3 chloropropane CH3CH2CH2CI C3H7CI 4 chlorobutane CH3(CH2)2CH2CI C4H9CI 5 chloropentane CH3(CH2)3CH2CI C5H11CI
- 25. Nomenclature for Organic Molecule (Alkane) C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 4- ethyl-2-methylhexane 1 2 3 4 5 6 3- ethyl- 5-methylhexane wrong C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 Number from end giving substituent lowest possible number 2, 3 -dimethylpentane C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 4-ethyl- 2, 3, 6 -trimethyloctane CH2CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 2, 2, 4-trimethylpentane CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 5 4 3 2 1 C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 ׀ CH3 3 -ethyl-2, 5-dimethylheptane 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H- C-H H ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H-C – C – C – C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H- C-H H H ׀ H- C- H ׀ H- C- H ׀ H 2-methylpropane 4 -ethylheptane 1 2 3 1 2 3 4 C ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ C C ׀ C ׀ C 4- ethyl -2, 2- dimethylheptane C ׀ C C ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ C ׀ C 4-ethyl-3, 5- dimethyloctane 1 2 3 4 1 2 348 7 6 5 5 Give IUPAC names for alkanes CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 (CH3)3 – C – C2H5 2 methylbutane CH(C2H5)3 CH(C3H7)3 2,2 - dimethylbutane 3-ethylpentane 4-propylheptane 6 5 6 7 5 6 7
- 26. Nomenclature for Organic Molecule (Alkane) C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 4- ethyl-2-methylhexane 1 2 3 4 5 6 3- ethyl- 5-methylhexane wrong C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 Number from end giving substituent lowest possible number 2, 3 - dimethylpentane C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 4 -ethyl- 2, 3, 6 -trimethyloctane CH2CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 2, 2, 4 - trimethylpentane CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 5 4 3 2 1 C – C – C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 ׀ CH3 3 -ethyl -2, 5- dimethylheptane 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 Give IUPAC names for following molecule CH3CH2CH(CH3)2 2-methylbutane (CH3)3CC2H5 2,2 - dimethylbutane CH(C2H5)3 3-ethylpentane CH(C3H7)3 4-propylheptane (CH3 )3C-Br 2-bromo-2-methylpropane CH3CH=C(CH3)2 2-methylbut-2-ene (CH3)3C-CH=CH2 3, 3-dimethylbut-1-ene CH2=C(CH3)CH=CH2 2-methylbut-1,3-diene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 but-1,3-diene (CH3)2CH-CH=CH2 3-methylbut-1-ene CH2 =C(CH3)2 2-methylpropene CH3-CH(CH3)COCH2CH3 2 -methylpentan-3-one CH3(CH2)2CH2NH2 butanamine 3 CH3(CH2)2COOCH2CH3 ethyl butanoate CH3(CH2)2OCH3 methoxypropane
- 27. Nomenclature for Organic Molecules (Alkene) C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 4- ethyl-2-methylhex-2-ene 1 2 3 4 5 6 3- ethyl- 5-methylhex-4-ene wrong C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 Number from end giving substituent lowest possible number 2, 3 -dimethylpent-2-ene C – C = C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 4 -ethyl- 2, 3, 6 -trimethyloct-3-ene CH2CH3 ׀ C – C – C = C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 2, 2, 4 -trimethylpent-1-ene CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C = C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 5 4 3 2 1 C – C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 ׀ CH3 3 -ethyl -2, 5- dimethylhept-3-ene 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C = C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H- C-H H ׀ H H H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H-C – C – C = C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H H H H- C-H H H ׀ H- C- H ׀ H- C- H ׀ H 2-methylpropene 4 – ethylhept-3-ene 1 2 3 4 C ׀ C = C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ C C ׀ C ׀ C 4- ethyl -2, 2- dimethylhept-1-ene C ׀ C C ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C = C – C ׀ C ׀ C 4-ethyl-3, 5- dimethyloct-3-ene 1 2 3 4 1 2 348 7 6 5 5 Give IUPAC names for alkenes CH3CH=C(CH3)2 (CH3)3C-CH=CH2 2 methylbut-2-ene CH2=CH-CH=CH2 3, 3- dimethylbut-1-ene 2-methylbut-1,3-diene but-1,3-diene 6 No numbering needed 1 2 3 4 CH2=C(CH3)CH=CH2 5 6 7 5 6 7
- 28. Nomenclature for Organic Molecules (Alkene) C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 4- ethyl- 2-methylhex-2-ene 1 2 3 4 5 6 3- ethyl- 5-methylhex-4-ene wrong C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 6 5 4 3 2 1 Number from end giving substituent lowest possible number 2, 3 -dimethylpent-2-ene C – C = C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 4 -ethyl- 2, 3, 6 -trimethyloct-3-ene CH2CH3 ׀ C – C – C = C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 1 2 2, 2, 4 -trimethylpent-1-ene CH3 ׀ C – C – C – C = C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 5 4 3 2 1 C – C – C = C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ CH3 CH2 CH3 ׀ CH3 3 -ethyl -2, 5- dimethylhept-3-ene 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 3 4 5 Give IUPAC names for following molecule CH3CHBrCH2CH2OH 3- bromobutan-1-ol CH3-CH(OH)-CH3 propan-2–ol CH3CH(OH)-CH2CH3 butan-2-ol (CH3)2C(OH)CH2CH3 2-methylbutan-2-ol (CH3)2CHCH2OH 2-methylpropan-1-ol CH3CH2CH(CH3)OH (CH3 )3C-OH 2-methylpropan-2-ol CH3-CH2CH(CH3)CHO 2-methylbutanal (CH3)2CHCH(CH3)CHO 2,3 -dimethylbutanal CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)COCH3 3-methylhexan-2-one CH3CH2CH(CI)CH(CI)COOH 2, 3-dichloropentanoic acid CH3(CH2)2COOH butanoic acid HO-C(CH3)2CH2CH2-COOH 4- hydroxy-4-methylpentanoic acid CH3(CH2)2CH(CH3)CH(CH3)COOH 2, 3-dimethylhexanoic acid CH3-C(CH3)2-CH2CHO 3, 3-dimethylbutanal
- 29. H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C – F ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H CH3 ׀ ׀ CI – C – C – C ׀ ׀ H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – Br ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ I H H H H C ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C - C ׀ CI C CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ CI H H CH3 ׀ CI – C – C – C ׀ H H H CI ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H Halogenoalkane and Nomenclature H ׀ CH3 – C – CI ׀ H Types of halogenoalkane Primary 1 0 NO alkyl /1 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to halogen H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – CI ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H ׀ H - C – CI ׀ H Secondary 2 0 2 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to halogen H ׀ CH3 – C – CI ׀ CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI H H ׀ R – C – CI ׀ R Tertiary 3 0 3 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to halogen CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – CI ׀ CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI H R ׀ R – C – CI ׀ R H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI H CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – CI ׀ CH3 C CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H Br H CH3 ׀ CI – C – C – C ׀ C – C Br CH3 ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 C CI C ׀ ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ C Primary 1 o Secondary2 o Tertiary 3 o H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H F H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CI CH3 H H H ׀ CH3 – C – CI ׀ CH3
- 30. CH3 ׀ HO – C – C – C ׀ C – C H CH3 ׀ ׀ HO – C – C – C ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H H H H C ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C - C ׀ OH C CH3 ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ OH H H CH3 ׀ HO – C – C – C ׀ H H H OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H Alcohol and Nomenclature H ׀ CH3 – C – OH ׀ H Types of alcohol Primary 1 0 NO alkyl /1 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to OH H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – OH ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H ׀ H - C – OH ׀ H Secondary 2 0 2 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to OH H ׀ CH3 – C – OH ׀ CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H H ׀ R – C – OH ׀ R Tertiary 3 0 3 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to OH CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – OH ׀ CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H R ׀ R – C – OH ׀ R H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – OH ׀ CH3 C CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH H OH CH3 ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 C OH C ׀ ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ C Primary 1 o Secondary2 o Tertiary 3 o H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H OH H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H OH CH3 H H H ׀ CH3 – C – OH ׀ CH3
- 31. H H H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – C –NH2 ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H H H CH3 ׀ ׀ NH2 – C – C – C ׀ ׀ H CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – NH2 ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ NH2 H H H H C ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C - C ׀ NH2 C CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ NH2 H H CH3 ׀ NH2 – C – C – C ׀ H H H NH2 ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H Amines and Nomenclature H ׀ CH3 – C – NH2 ׀ H Types of amines Primary 1 0 NO alkyl /1 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to nitrogen H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – NH2 ׀ ׀ ׀ H CH3 H H ׀ H - C – NH2 ׀ H Secondary 2 0 2 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to nitrogen H ׀ CH3 – C – NH2 ׀ CH3 H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 H H ׀ R – C – NH2 ׀ R Tertiary 3 0 3 alkyl/R gp bond to C attach to nitrogen CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – NH2 ׀ CH3 H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 H R ׀ R – C – NH2 ׀ R H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 H H CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 H CH3 ׀ CH3 – C – NH2 ׀ CH3 C CH3 H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C – C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 H CH3 ׀ NH2 – C – C – C ׀ C – C NH2 CH3 ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ ׀ CH3 CH3 C NH2 C ׀ ׀ ׀ C – C – C – C – C ׀ C Primary 1 o Secondary2 o Tertiary 3 o H H H ׀ ׀ ׀ H - C – C - C – H ׀ ׀ ׀ H H NH2 H H CH3 H H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H – C – C - C – C – C - H ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ ׀ H NH2 CH3 H H H ׀ CH3 – C – NH2 ׀ CH3
