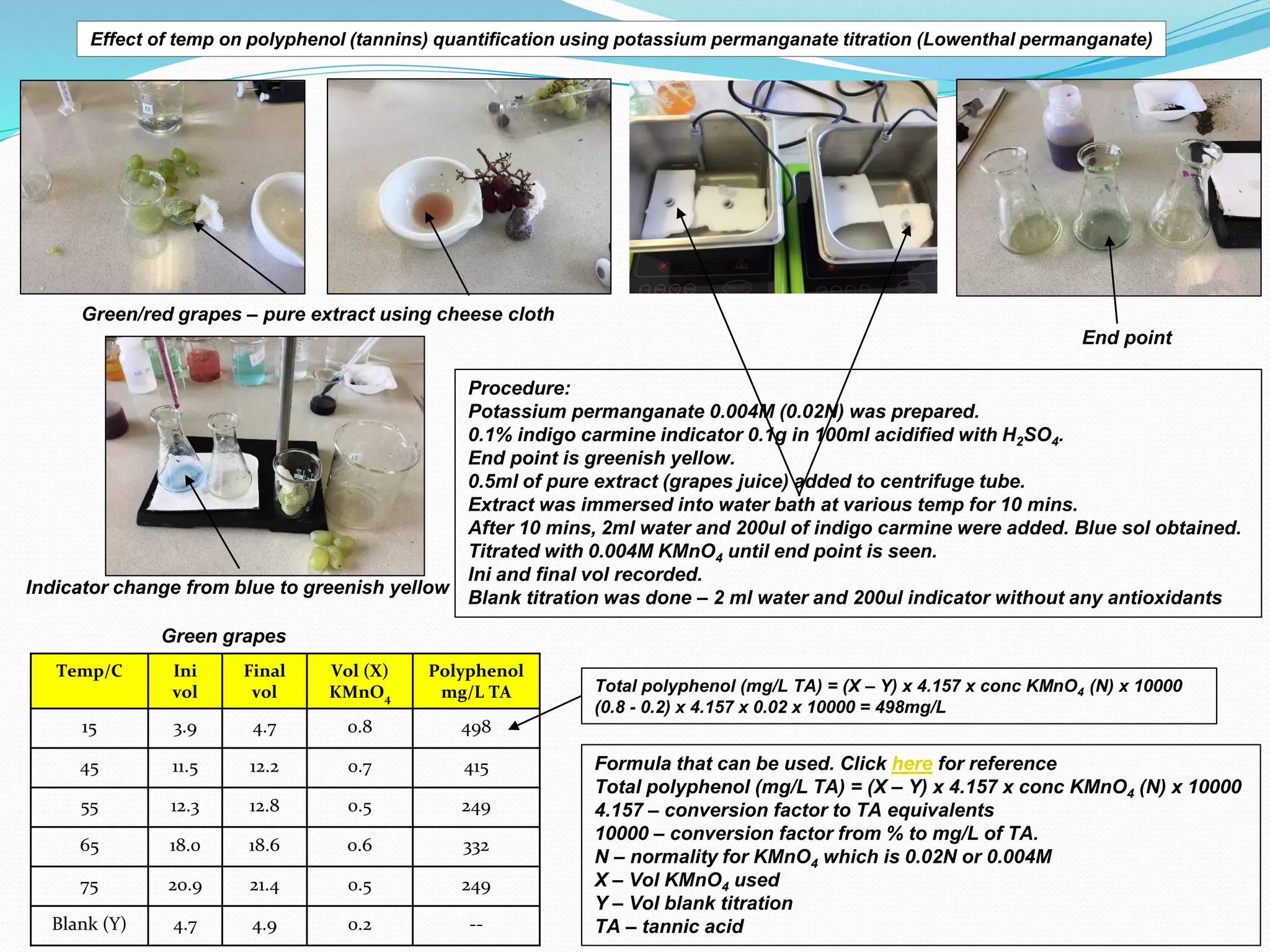
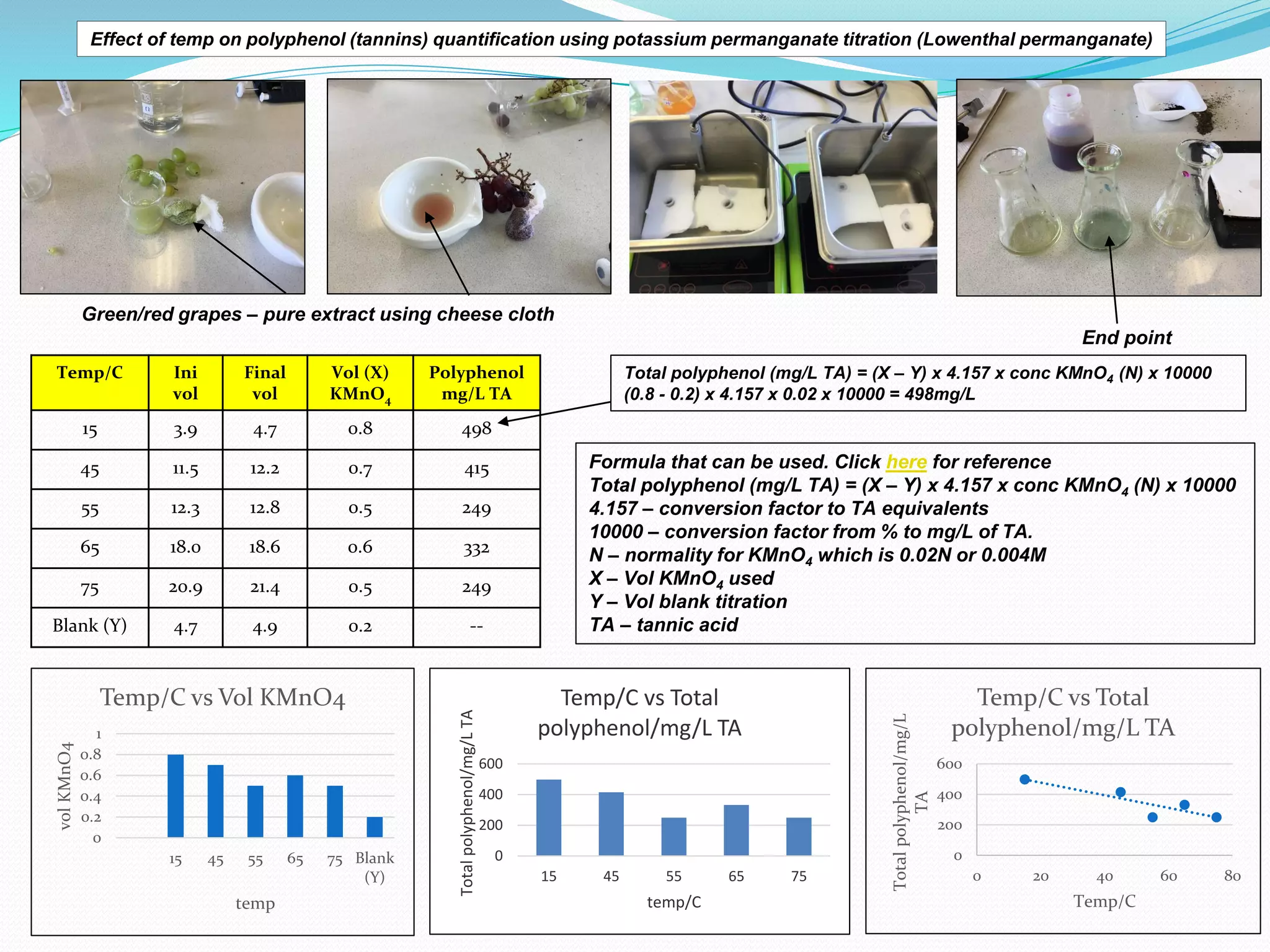
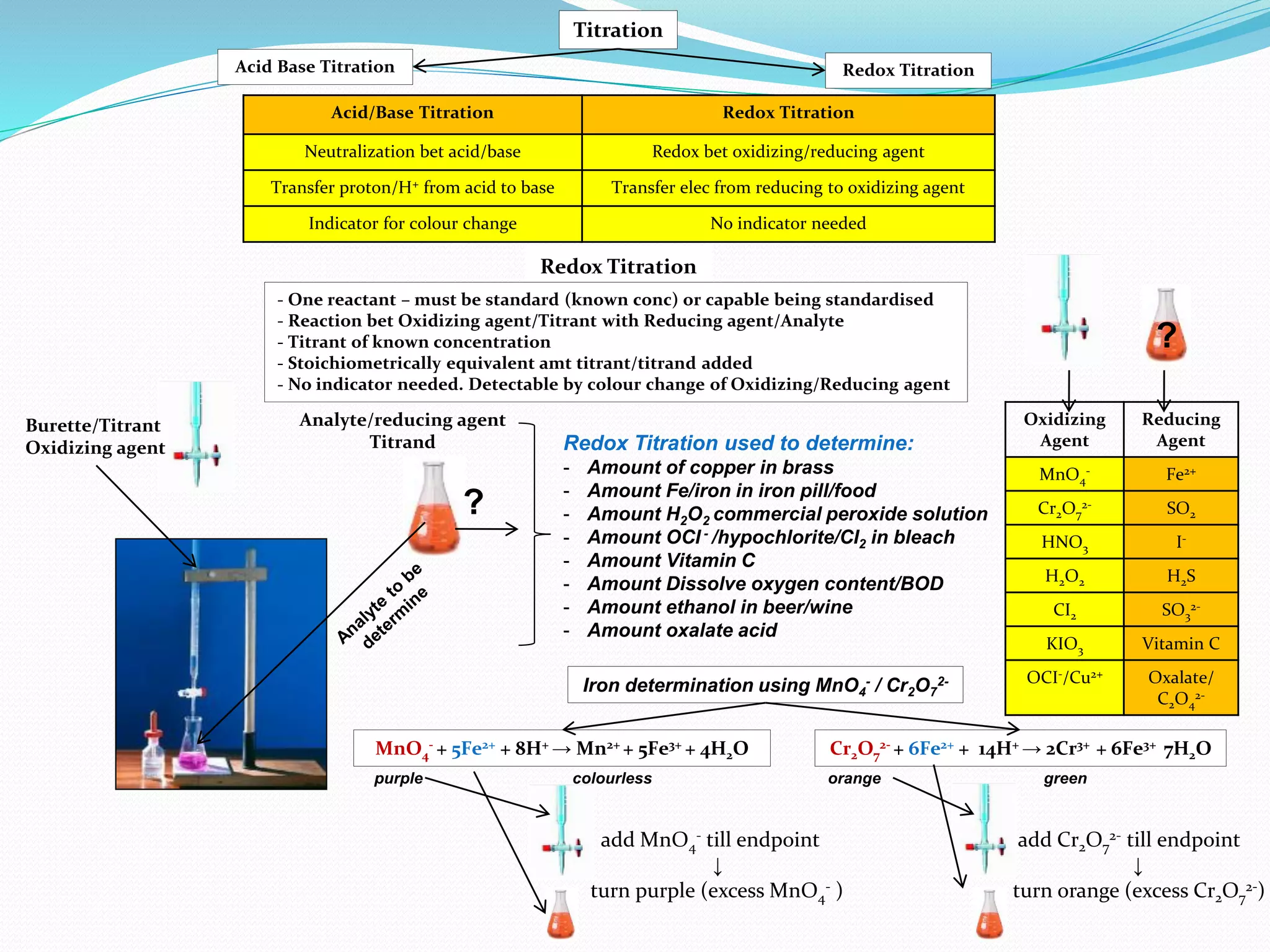
The document discusses the quantification of polyphenols (tannins) using potassium permanganate titration, emphasizing the effect of temperature on this process. It outlines the preparation of potassium permanganate and indigo carmine, along with the procedure for titration, which involves immersing pure grape extract in varying temperatures. The study highlights limitations, assumptions, and provides a formula for calculating total polyphenol concentration based on titration results.