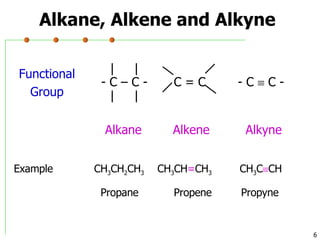
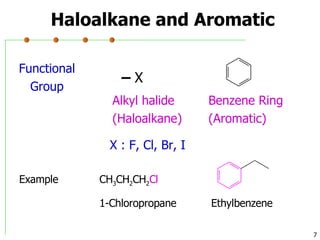
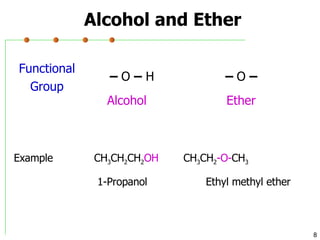
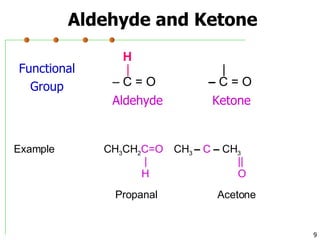
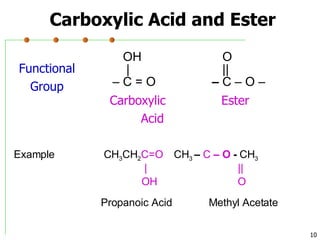
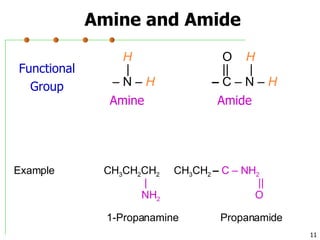
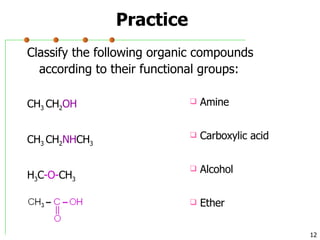
This document discusses common functional groups found in organic compounds. It defines functional groups as atoms or groups of atoms that confer similar chemical properties and reactivity. The document then lists and provides examples of common functional groups including alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, aromatics, haloalkanes, alcohols, ethers, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids, esters, amines, and amides. It emphasizes that functional groups are important for classifying organic compounds, identifying sites of chemical reactions, and naming organic compounds.