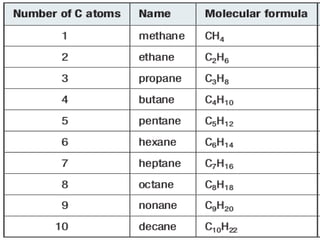
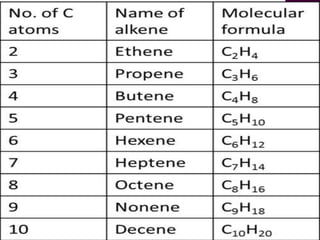
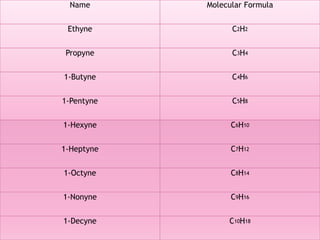
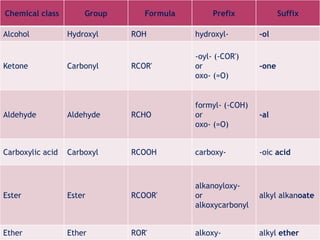
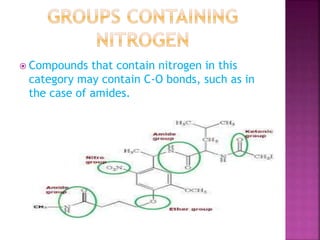
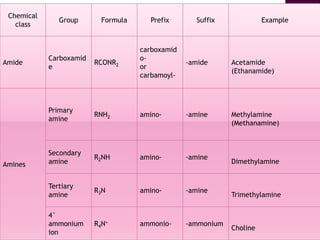
Functional groups are moieties within molecules that determine chemical reactivity. Common functional groups include hydrocarbons, halogens, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus and boron groups. Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Alkenes contain carbon-carbon double bonds with the formula CnH2n, while alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds with the formula CnH2n-2. Haloalkanes contain carbon-halogen bonds and undergo substitution or elimination reactions. Oxygen-containing groups like alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, carboxylic acids, esters and ethers have differing reactivities