IB Chemistry on Gibbs Free Energy, Equilibrium constant and Cell Potential
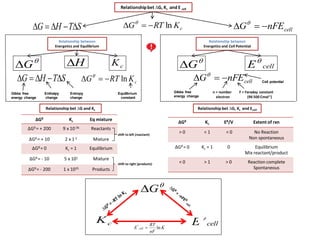
- 1. cellnFEG Relationship between Energetics and Equilibrium cKRTG ln STHG Enthalpy change Entropy change Equilibrium constant Gibbs free energy change H G Relationshipbet ∆G, Kc and E cell cellnFEG STHG cKRTG ln cK Relationship between Energetics and Cell Potential G cellE Gibbs free energy change Cell potential F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) n = number electron Relationship bet ∆G, Kc and Ecell ΔGθ Kc Eθ/V Extent of rxn > 0 < 1 < 0 No Reaction Non spontaneous ΔGθ = 0 Kc = 1 0 Equilibrium Mix reactant/product < 0 > 1 > 0 Reaction complete Spontaneous ΔGθ Kc Eq mixture ΔGθ = + 200 9 x 10-36 Reactants ΔGθ = + 10 2 x 1-2 Mixture ΔGθ = 0 Kc = 1 Equilibrium ΔGθ = - 10 5 x 101 Mixture ΔGθ = - 200 1 x 1035 Products Relationship bet ∆G and Kc shift to left (reactant) shift to right (products) cellE G cK K nF RT E cell ln
- 2. Magnitudeof Kc Extendof reaction How far rxn shift to right or left? Not how fast cK Positionof equilibrium cK Temp dependent Extend of rxn Not how fast Shift to left/ favour reactant Shift to right/ favour product cK Relationship between Equilibrium and Energetics cKRTG ln STHG Enthalpy change Entropy change Equilibrium constant Gibbs free energy change H G cK G Energetically Thermodynamically Favourable/feasible ΔGθ ln K Kc Eq mixture ΔGθ -ve < 0 Positive ( + ) Kc > 1 Product (Right) ΔGθ +ve > 0 Negative ( - ) Kc < 1 Reactant (left) ΔGθ = 0 0 Kc = 1 Equilibrium Measure work available from system Sign predict spontaneity of rxn Negative (-ve) spontaneous Positive (+ve) NOT spontaneous veG veG NOT favourable Energetically favourable Product formation NO product cKRTG ln
- 3. Magnitudeof Kc Extendof reaction How far rxn shift to right or left? Not how fast cK Positionof equilibrium cK Temp dependent Extend of rxn Not how fast Shift to left/ favour reactant Shift to right/ favour product cK Relationship between Equilibrium and Energetics cKRTG ln STHG Enthalpy change Entropy change Equilibrium constant Gibbs free energy change H G cK ΔGθ ln K Kc Eq mixture ΔGθ -ve < 0 Positive ( + ) Kc > 1 Product (Right) ΔGθ +ve > 0 Negative ( - ) Kc < 1 Reactant (left) ΔGθ = 0 0 Kc = 1 Equilibrium cKRTG ln STHG ∆Hsys ∆Ssys ∆Gsys Description - + ∆G = ∆H - T∆S ∆G = - ve Spontaneous, All Temp + - ∆G = ∆H - T∆S ∆G = + ve Non spontaneous, All Temp + + ∆G = ∆H - T∆S ∆G = - ve Spontaneous, High ↑ Temp - - ∆G = ∆H - T∆S ∆G = - ve Spontaneous, Low ↓ Temp Relationshipbet ∆G and Kc
- 4. G Energetically Thermodynamically Favourable/feasible Sign predict spontaneity of rxn veG veG NOT favourable Energetically favourable Product formation NO product KRTG ln Predictwill rxn occur with ΔG and Kc cK Very SMALL Kc < 1 Shift to right/ favour product Shift to left/ favour reactant Very BIG Kc > 1 veG veG KRTG ln 1cK 1cK Negative (-ve) spontaneous Positive (+ve) NOT spontaneous Relationship bet ∆G and Kc ΔGθ Kc Eq mixture ΔGθ = + 200 9 x 10-36 Reactant ΔGθ = + 10 2 x 1-2 Mixture ΔGθ = 0 Kc = 1 Equilibrium ΔGθ = - 10 5 x 101 Mixture ΔGθ = - 200 1 x 1035 Products shift to left (reactant) shift to right (product) G, Gibbs free energy A Mixture composition B 100% A 100% B ∆G decreases ↓ 30 % A 70 % B Equilibrium mixture ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 Free energy system is lowered on the way to equilibrium Rxn proceed to minimum free energy ∆G = 0 System seek lowest possible free energy Product have lower free energy than reactant ∆G < 0 product reactant
- 5. G Energetically Thermodynamically Favourable/feasible Sign predict spontaneity of rxn veG veG NOT favourable Energetically favourable Product formation NO product KRTG ln cK Very SMALL Kc < 1 Shift to right/ favour product Shift to left/ favour reactant Very BIG Kc > 1 veG veG KRTG ln 1cK 1cK Negative (-ve) spontaneous Positive (+ve) NOT spontaneous Relationship bet ∆G, Q and Kc G, Gibbs free energy A B 100% A 100% B ∆G decreases ↓ 30 % A 70 % B Equilibrium mixture ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 ∆G < 0 product reactant G, Gibbs free energy reactant product∆G < 0 A B ∆G decreases ↓ 100% A 100% B30 % A 70 % B ∆G = 0 Q = K ∆G < 0 Q < K ∆G > 0 ∆G < 0 Q > K ∆G > 0 A ↔ B A ↔ B Equilibrium mixture Predictwill rxn occur with ΔG and Kc
- 6. Relationship bet ∆G and Kc G, Gibbs free energy A B 100% A 100% B ∆G decreases ↓ 30 % A 70 % B Equilibrium mix close to product ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 ∆G < -10 Kc > 1 A ↔ B A ↔ B G, Gibbs free energy A B ∆G decreases ↓ ∆G < -100 100% A 100% B ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum Kc > 1Equilibrium mix close to product 10 % A 90 % B ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 ∆G very –ve → Kc > 1 → (more product/closeto completion)∆G –ve → Kc > 1 → (more product > reactant) A ↔ B G, Gibbs free energy 100% A 100% B A B ∆G +ve → Kc < 1 → (more reactant > product) ∆G > +10 ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum Kc < 1 ∆G increases ↑ 70 % A 30 % B Equilibrium mix close to reactant ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 A ↔ B G, Gibbs free energy ∆G more +ve → Kc < 1 → (All reactant / no product at all) A ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum Kc < 1100% A 100% B Equilibrium mix close to reactant/ No reaction. ∆G > +100 B 90 % A 10 % B ∆G increases ↑ ∆G = 0 ∆G < 0 reactant reactant reactant reactant productproduct product product
- 7. Relationship bet ∆G and Kc shift to left (reactant) shift to right (product) G, Gibbs free energy A B 100% A 100% B ∆G decreases ↓ 30 % A 70 % B Equilibrium mixture ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 Free energy system is lowered on the way to equilibrium Rxn proceed to minimum free energy ∆G = 0 System seek lowest possible free energy Product have lower free energy than reactant ∆G < -10 Kc > 1 A ↔ B A ↔ B G, Gibbs free energy A B ∆G decreases ↓ ∆G < -100 100% A 100% B ∆G = 0 (Equilibrium) ↓ Free energy minimum Kc > 1Equilibrium mixture 10 % A 90 % B ∆G < 0 ∆G < 0 ∆G = 0 ∆G very –ve → Kc > 1 → (All product/closeto completion)∆G –ve → Kc > 1 → (more product > reactant) ∆G ∆G = 0 ∆G > 0 ∆G < 0 No reaction/most reactants Kc <1 Complete rxn/Most products Kc > 1 Kc = 1 (Equilibrium) Reactants= Products reactant reactant ΔGθ Kc Eq mixture ΔGθ = + 200 9 x 10-36 Reactant ΔGθ = + 10 2 x 1-2 Mixture ΔGθ = 0 Kc = 1 Equilibrium ΔGθ = - 10 5 x 101 Mixture ΔGθ = - 200 1 x 1035 Products
- 8. 298314.8 )212000( ln RT G Kc Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e Eθ = +0.76 Cu2+ + 2e ↔ Cu Eθ = +0.34 Zn + Cu2+ → Zn 2+ + Cu Eθ = +1.10V Zn half cell (-ve) Oxidation Cu half cell (+ve) Reduction Anode Cathode Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s) Cell diagram Anode Cathode Half Cell Half Cell (Oxidation) (Reduction) Salt Bridge Flow electrons Zn/Cu Voltaic Cell -e -e Zn/Cu half cells Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = +0.34 – (-0.76) = +1.10V Zn 2+ + 2e ↔ Zn (anode) Eθ = -0.76V Cu2+ + 2e ↔ Cu (cathode) Eθ = +0.34V Std electrode potential as std reduction potential Find Eθ cell (use reduction potential)Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Zn 2+ + 2e ↔ Zn Eθ = -0.76V Cu2+ + 2e ↔ Cu Eθ = +0.34V Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 H2O + e- ↔ 1/2H2 + OH- -0.83 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn - 0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni -0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 Pb2+ + 2e- ↔ Pb -0.13 H+ + e- ↔ 1/2H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- ↔ H2SO3 +0.17 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu + 0.34 1/2O2 + H2O +2e- ↔ 2OH- +0.40 + +1.10 V Eθ Zn/Cu = 1.10V Cu2+ - - - - Zn Cu + + + + cellnFEG E cell with ∆G F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) n = number electron cellnFEG kJJG G 212212300 10.1965002 ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn SpontaneouscKRTG ln Equilibrium constant Gas constant, 8.314 ∆G with Kc cKRTG ln 37 103.1 cK Favour products
- 9. Zn ↔ Zn2+ + 2e Eθ = +0.76 2Ag++2e ↔ 2Ag Eθ = +0.80 Zn + Ag+ → Zn 2+ + Ag Eθ = +1.56V Zn half cell (-ve) Oxidation Ag half cell (+ve) Reduction Anode Cathode Zn(s) | Zn2+ (aq) || Ag+ (aq) | Ag (s) Cell diagram Anode Cathode Half Cell Half Cell (Oxidation) (Reduction) Salt Bridge Flow electrons Zn/Ag Voltaic Cell -e -e Zn/Ag half cells Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = +0.80 – (-0.76) = +1.56V Zn 2+ + 2e ↔ Zn (anode) Eθ = -0.76V Ag + + e ↔ Ag(cathode) Eθ = +0.80V Std electrode potential as std reduction potential Find Eθ cell (use reductionpotential)Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Zn 2+ + 2e ↔ Zn Eθ = -0.76V Ag+ + e ↔ Ag Eθ = +0.80V Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 H2O + e- ↔ 1/2H2 + OH- -0.83 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn - 0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni -0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 Pb2+ + 2e- ↔ Pb -0.13 H+ + e- ↔ 1/2H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- ↔ H2SO3 +0.17 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu +0.34 1/2O2 + H2O +2e- ↔ 2OH- +0.40 Cu+ + e- ↔ Cu +0.52 1/2I2 + e- ↔ I- +0.54 Fe3+ + e- ↔ Fe2+ +0.77 Ag+ + e- ↔ Ag + 0.80 1/2Br2 + e- ↔ Br- +1.07 + +1.56 V Ag Eθ Zn/Ag = +1.56V Ag+ - - - - + + + + Zn E cell with ∆G cellnFEG n = number electron F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) cellnFEG kJJG G 301301000 56.1965002 ∆G with Kc cKRTG ln Gas constant, 8.314 Equilibrium constant cKRTG ln 298314.8 )301000( ln RT G Kc 52 105.3 cK ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn Spontaneous Favour products
- 10. Mn ↔ Mn2+ + 2e Eθ = +1.19 Ni2+ + 2e ↔ Ni Eθ = -0.26 Mn + Ni2+ → Mn2+ + Ni Eθ = +0.93V Mn half cell (-ve) Oxidation Ni half cell (+ve) Reduction Anode Cathode Mn(s) | Mn2+ (aq) || Ni2+ (aq) | Ni (s) Cell diagram Anode Cathode Half Cell Half Cell (Oxidation) (Reduction) Salt Bridge Flow electrons Mn/Ni Voltaic Cell -e -e Mn/Ni half cells Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = -0.26 – (-1.19) = +0.93V Mn 2+ + 2e ↔ Mn (anode) Eθ = -1.19V Ni2+ + 2e ↔ Ni (cathode) Eθ = -0.26V Std electrode potential as std reduction potential Find Eθ cell (use reductionpotential)Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Mn 2+ + 2e ↔ Mn Eθ = -1.19V Ni2+ + 2e ↔ Ni Eθ = -0.26V Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 H2O + e- ↔ 1/2H2 -0.83 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn -0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni - 0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 Pb2+ + 2e- ↔ Pb -0.13 H+ + e- ↔ 1/2H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- ↔ H2SO3 + H2O +0.17 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu +0.34 1/2O2 + H2O +2e- ↔ 2OH- +0.40 Cu+ + e- ↔ Cu +0.52 1/2I2 + e- ↔ I- +0.54 + +0.93 V Eθ Mn/Ni = +0.93V Ni2+ - - - - NiMn + + + +Mn2+ E cell with ∆G cellnFEG n = number electron F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) cellnFEG kJJG G 179179490 93.0965002 cKRTG ln 298314.8 )179000( ln RT G Kc cKRTG ln ∆G with Kc Gas constant, 8.314 Equilibrium constant ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn Spontaneous 31 102.2 cK Favour products
- 11. Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 H2O + e- ↔ H2 + OH- -0.83 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn -0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni -0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 H+ + e- ↔ H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- ↔ H2S +0.17 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu +0.34 Cu ↔ Cu2+ + 2e Eθ = -0.34 2H+ + 2e ↔ H2 Eθ = +0.00 Cu + 2H+→ Cu2+ +H2 Eθ = -0.34V Rxn bet Cu + H+ Will it happen ? Eθ = -0.34V (NON spontaneous) О Cu(s) | Cu2+ (aq) || H+ H2 | Pt (s) (Oxidation) (Reduction) Anode Cathode Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = 0.00 – (+0.34) = -0.34V Eθ = -0.34V (NON spontaneous) О Rxn not feasible Determinespontaneityrxn. Will it HAPPEN? Find Eθ cell (use reductionpotential) Eθ Cu/H+ = - 0.34V E cell with ∆G cellnFEG n = number electron F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) cellnFEG kJJG G 6565620 34.0965002 cKRTG ln Gas constant, 8.314 Equilibrium constant ∆G with Kc cKRTG ln 298314.8 )65000( ln RT G Kc ∆G +ve, E -ve, K < 1 ∆G >0, E < 0, K < 1 ↓ Rxn Non Spontaneous 12 104 cK Favour reactants -0.34 V acid copper Predictingwill rxn occur with ΔG, E cell and Kc +
- 12. Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 H2O + e- ↔ H2 + OH- -0.83 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn -0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni -0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 H+ + e- ↔ H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 SO4 2- + 4H+ + 2e- ↔ H2S +0.17 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu +0.34 Au3+ + 3e- ↔ Au +1.58 Rxn bet Au + H+ Will it happen ? Eθ = -1.58 V (NON spontaneous) О Au(s) | Au3+ (aq) || H+ H2 | Pt (s) (Oxidation) (Reduction) Anode Cathode Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = 0.00 – (+1.58) = -1.58V Eθ = - 1.58 V (NON spontaneous) О Rxn not feasible Determinespontaneityrxn. Will it HAPPEN? Find Eθ cell (use reductionpotential) Eθ Au/H+ = - 1.58V E cell with ∆G cellnFEG n = number electron F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) cellnFEG kJJG G 914914820 58.1965006 cKRTG ln Gas constant, 8.314 Equilibrium constant ∆G with Kc cKRTG ln 298314.8 )914000( ln RT G Kc ∆G +ve, E -ve, K < 1 ∆G >0, E < 0, K < 1 ↓ Rxn Non Spontaneous 50 104 cK Kc too small – No reactionat all -1.58 V acid gold 2Au ↔ 2Au3+ + 6e Eθ = -1.58 6H+ + 6e ↔ 3H2 Eθ = 0.00 2Au + 6H+ → 2Au3+ + 3H2 Eθ = -1.58V + Predictingwill rxn occur with ΔG, E cell and Kc
- 13. Eθ = - 0.20 V (NON spontaneous) (Oxidation) (Reduction) Anode Cathode Find Eθ cell (use formula) Eθ cell = Eθ (cathode) – Eθ (anode) Eθ cell = 0.34 – (0.54) = - 0.20V Eθ = - 0.20 V (NON spontaneous) Determinespontaneityrxn. Will it HAPPEN? Find Eθ cell (use reductionpotential) Eθ Cu2+/I- = - 0.20V E cell with ∆G cellnFEG n = number electron F = Faraday constant (96 500 Cmol-1) cellnFEG kJJG G 3838600 20.0965002 cKRTG ln Gas constant, 8.314 Equilibrium constant ∆G with Kc cKRTG ln 298314.8 )38000( ln RT G Kc ∆G +ve, E -ve, K < 1 ∆G >0, E < 0, K < 1 ↓ Rxn Non Spontaneous 7 102.2 cK -1.58 V Cu2+ I-Rxn bet Cu2+ +I- Will it happen? 2I- ↔ I2 + 2e Eθ = -0.54 Cu2+ + 2e ↔ Cu Eθ = +0.34 2I- + Cu2+→ Cu + I2 Eθ = -0.20V Pt(s) | I-, I2 || Cu2+ (aq) | Cu (s) Favour reactants Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Li+ + e- ↔ Li -3.04 K+ + e- ↔ K -2.93 Ca2+ + 2e- ↔ Ca -2.87 Na+ + e- ↔ Na -2.71 Mg 2+ + 2e- ↔ Mg -2.37 Al3+ + 3e- ↔ AI -1.66 Mn2+ + 2e- ↔ Mn -1.19 Zn2+ + 2e- ↔ Zn -0.76 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.45 Ni2+ + 2e- ↔ Ni -0.26 Sn2+ + 2e- ↔ Sn -0.14 H+ + e- ↔ 1/2H2 0.00 Cu2+ + e- ↔ Cu+ +0.15 Cu2+ + 2e- ↔ Cu +0.34 1/2O2 + H2O +2e- ↔ 2OH- +0.40 Cu+ + e- ↔ Cu +0.52 I2 + 2e- ↔ I- +0.54 Rxn not feasible О О - 0.20 V Will I- oxidize Cu2+ to Cu Predictingwill rxn occur with ΔG, E cell and Kc
- 14. Click here to view free energy PredictingSpontaneity of Rxn Thermodynamic,ΔG Equilibrium, Kc 1cK 1cK KRTG ln G veG cK 1cK Energetically favourable 0G Predictingrxn will occur? N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g) H2O(l) ↔ H+ (aq)+ OH- (aq) Shift toward reactants Energetically unfavourable Non spontaneous Mixture reactant/productEquilibrium veG Spontaneous Shift toward product 79G 33G 6 10G 14 101 cK 5 105cK Fe(s) + 3O2(g) ↔ 2Fe2O3(s) 261 101cK Shift toward reactants Energetically unfavourable Shift toward product Energetically favourable Energetically favourable Kinetically unfavourable/(stable) Rate too slow due to HIGH activation energy Rusting Process Energy barrier Shift toward product Click here for notes cellnFEG Cell Potential cellE 0cellE 0cellE 0cellE 0cellE 0cellE 0cellE
- 15. Eθ = +0.44V IB Questions Esterification produce ethyl ethanoate. ΔG = -4.38kJmol-1 Cal Kc CH3COOH(l) + C2H5OH(l) ↔ CH3COOC2H5(l) + H2O(l) Kc = 5.9 cKRTG ln RT G Kc ln 29831.8 4380 ln cK 2 ?cK NO oxidized to NO2. Kc = 1.7 x 1012. Cal ∆G at 298K1 3 4 2NO+ O2 ↔ NO2 ?G cKRTG ln 11 12 7.6969772 )107.1ln(298314.8 kJmolJmolG G Predict if iron react with HCI in absence air. Cal E cell , ∆G and Kc Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.44 2H+ + 2e- ↔ H2 0.00 O2 +2H2O+4e ↔ 4OH- +0.40 Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.44 2H+ + 2e- ↔ H2 0.00 О О Fe ↔ Fe2+ + 2e Eθ = +0.44 2H+ + 2e ↔ H2 Eθ = 0.00V Fe + 2H+ → Fe2+ + H2 Eθ = +0.44V cellnFEG kJJG G 8584900 44.0965002 cKRTG ln 298314.8 )85000( ln RT G Kc 14 108.7 cK ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn Spontaneous Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.44 O2 +2H2O+4e ↔ 4OH- +0.40 2Fe ↔ 2Fe2+ + 4e Eθ = +0.44 O2+2H2O+4e↔ 4OH- Eθ = +0.40 2Fe+O2 +2H2O→2Fe2++4OH- Eθ = +0.84V Eθ = +0.84V Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Fe2+ + 2e- ↔ Fe -0.44 2H+ + 2e- ↔ H2 0.00 O2 +2H2O+4e ↔ 4OH- +0.40 Predict iron react HCI in presence of air. Cal E cell , ∆G and Kc О О cellnFEG kJJG G 324324000 84.0965004 cKRTG ln 298314.8 )324000( ln RT G Kc 56 108.2 cK ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn SpontaneousRusting is spontaneous x 2 О О О О
- 16. Predict if manganate will oxidize chloride ion? MnO2 + 4H+ + 2CI- → Mn2+ + 2H2O + CI2 5 MnO2 +4H+ + 2e- ↔ Mn2+ + 2H2O +1.23 1/2CI2 + e- ↔ CI- +1.36 2CI- ↔ CI2 + 2e Eθ = -1.36 MnO2 + 4H+ + 2e ↔ Mn2+ + 2H2O Eθ = +1.23 MnO2 + 4H++2CI- → Mn2++2H2O+CI2 Eθ= -0.13V Eθ = -0.13V Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Cr2O7 2-+ 14H+ + 6e- ↔ 2Cr3+ + 7H2O +1.33 MnO2 +4H+ + 2e- ↔ Mn2+ + 2H2O +1.23 1/2CI2 + e- ↔ CI- +1.36 MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- ↔ Mn2+ + 4H2O +1.51 Predict if MnO4 - able to oxidize aq CI- to CI2 2MnO4 + 16H+ + 10CI- → 2Mn2++ 8H2O + 5CI2 О О Oxidized sp ↔ Reduced sp Eθ/V Cr2O7 2-+ 14H+ + 6e- ↔ 2Cr3+ + 7H2O +1.33 MnO2 +4H+ + 2e- ↔ Mn2+ + 2H2O +1.23 1/2CI2 + e- ↔ CI- +1.36 MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- ↔ Mn2+ + 4H2O +1.51 О О 2CI- ↔ CI2 + 2e Eθ = -1.36 MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e ↔ Mn2+ + 4H2O Eθ = +1.51 2MnO4 + 16H++10CI- → 2Mn2++8H2O+5CI2 Eθ= +0.15V 1/2CI2 + e- ↔ CI- +1.36 MnO4 - + 8H+ + 5e- ↔ Mn2+ + 4H2O +1.51 Eθ = +0.15V IB Questions cellnFEG kJJG G 2525000 13.0965002 cKRTG ln 298314.8 )25000( ln RT G Kc 5 105.4 cK ∆G +ve, E -ve, K < 1 ∆G >0, E < 0, K < 1 ↓ Rxn Non Spontaneous 6 cellnFEG kJJG G 144144750 15.09650010 cKRTG ln 298314.8 )144000( ln RT G Kc 25 105.1 cK ∆G –ve, E +ve, K > 1 ∆G <0, E > 0, K > 1 ↓ Rxn Spontaneous x 5 x 2 О О О О
