Embed presentation
Downloaded 11 times


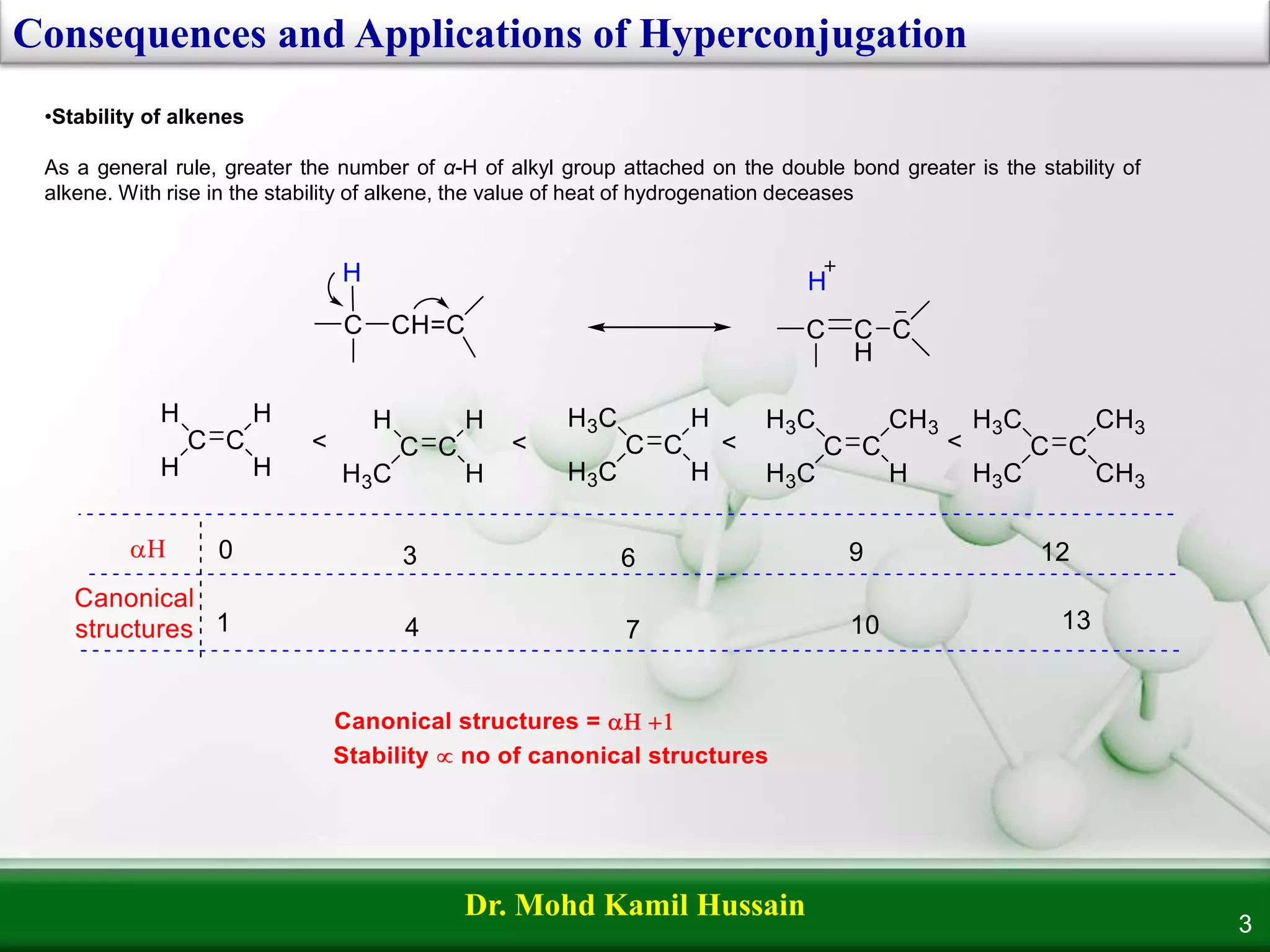
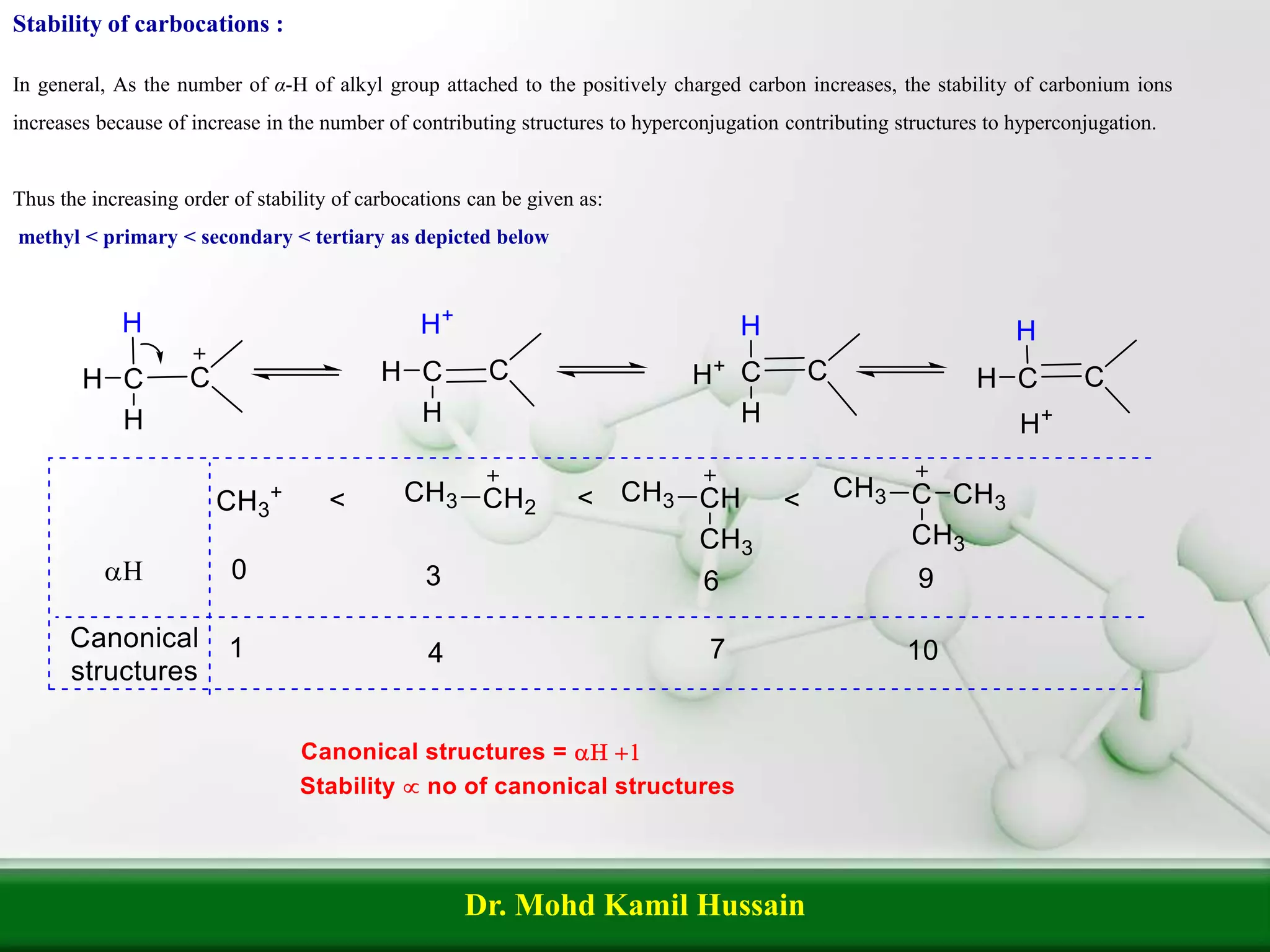

Hyperconjugation refers to the delocalization of σ-electrons from C-H bonds into adjacent π or p-orbitals, also known as 'no bond resonance.' It plays a critical role in determining the stability of alkenes, carbocations, and free radicals, with increased α-hydrogens leading to greater stability. The stability hierarchy for carbocations and free radicals follows the order: methyl < primary < secondary < tertiary.




