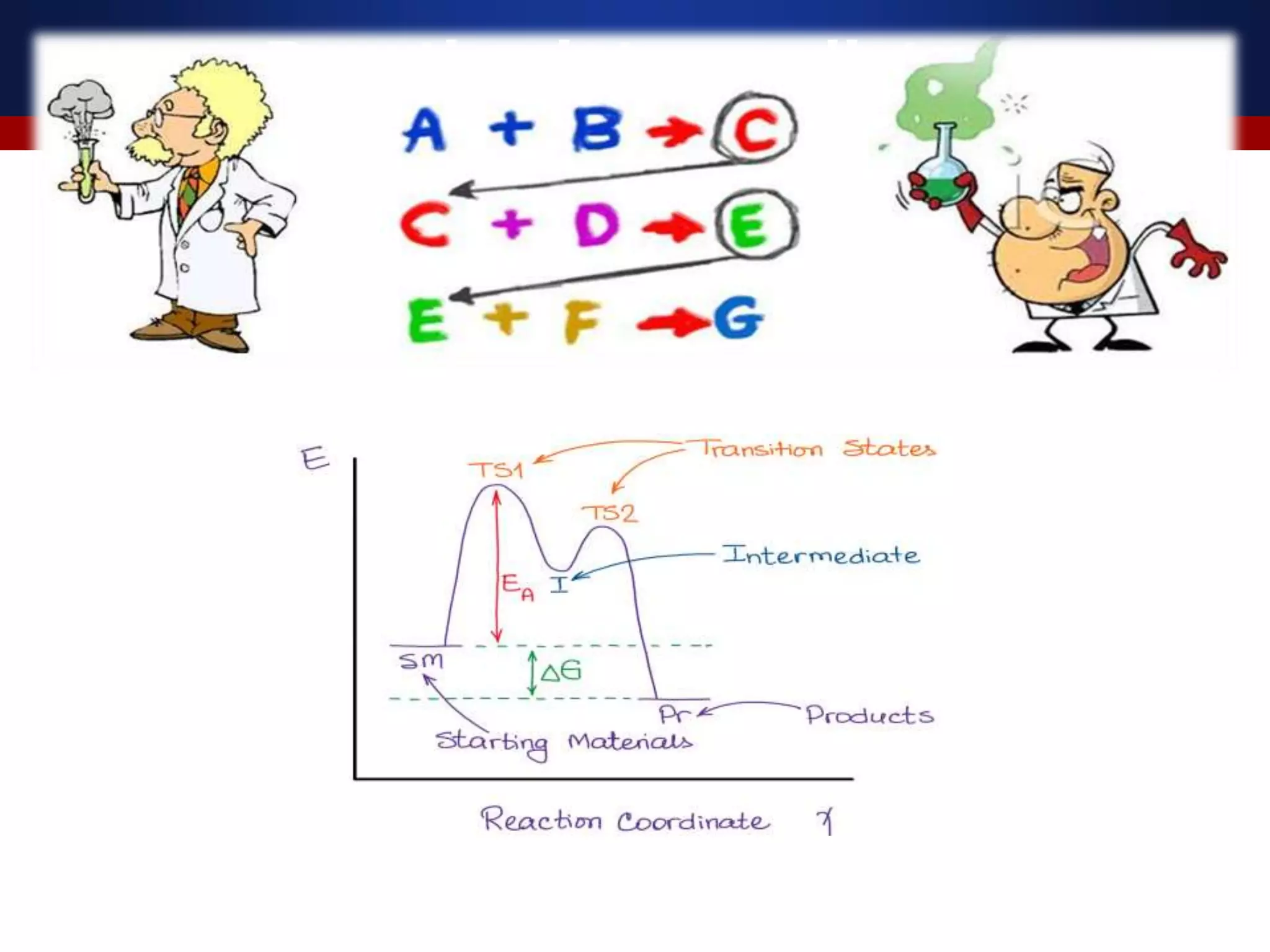
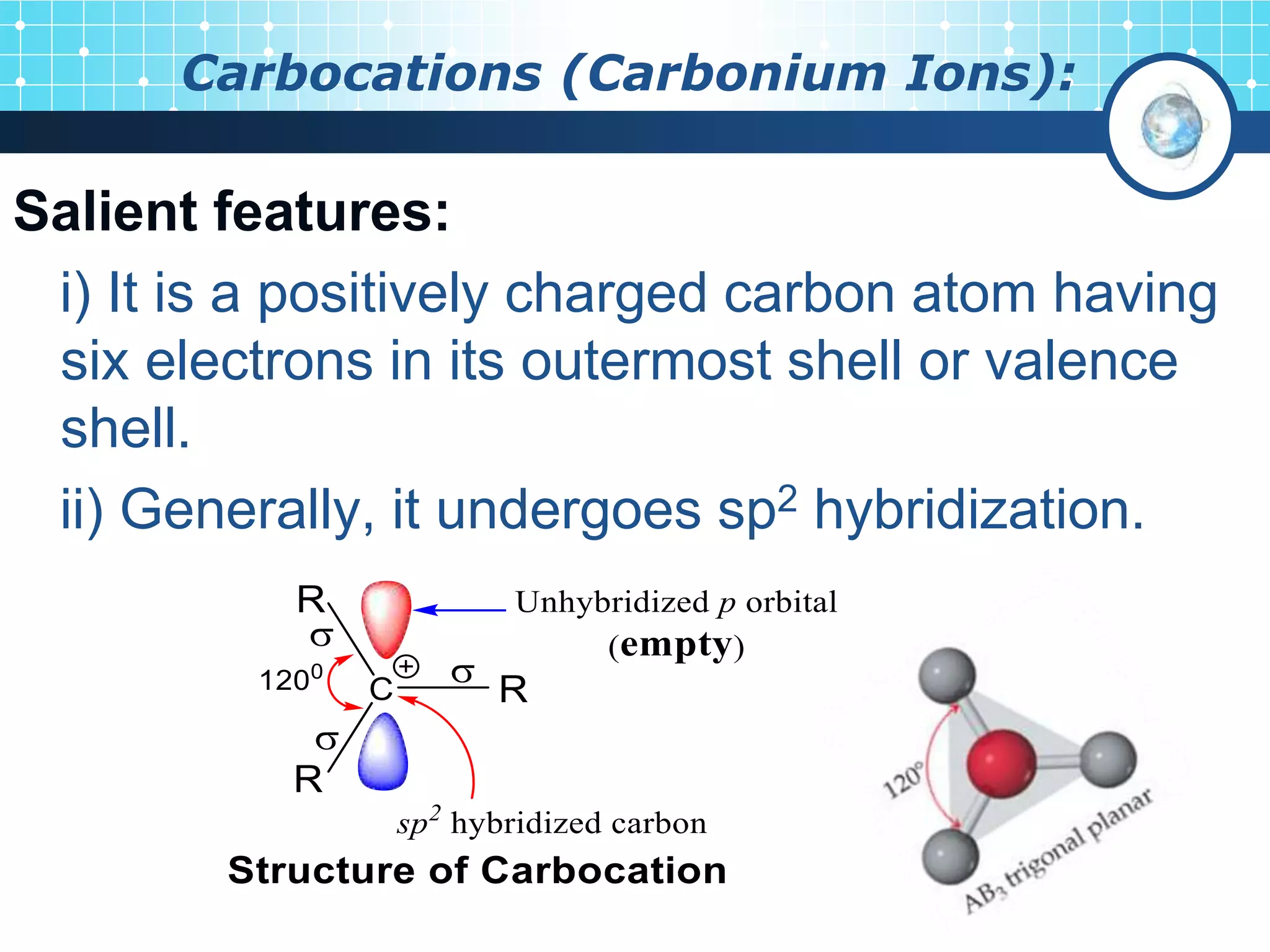
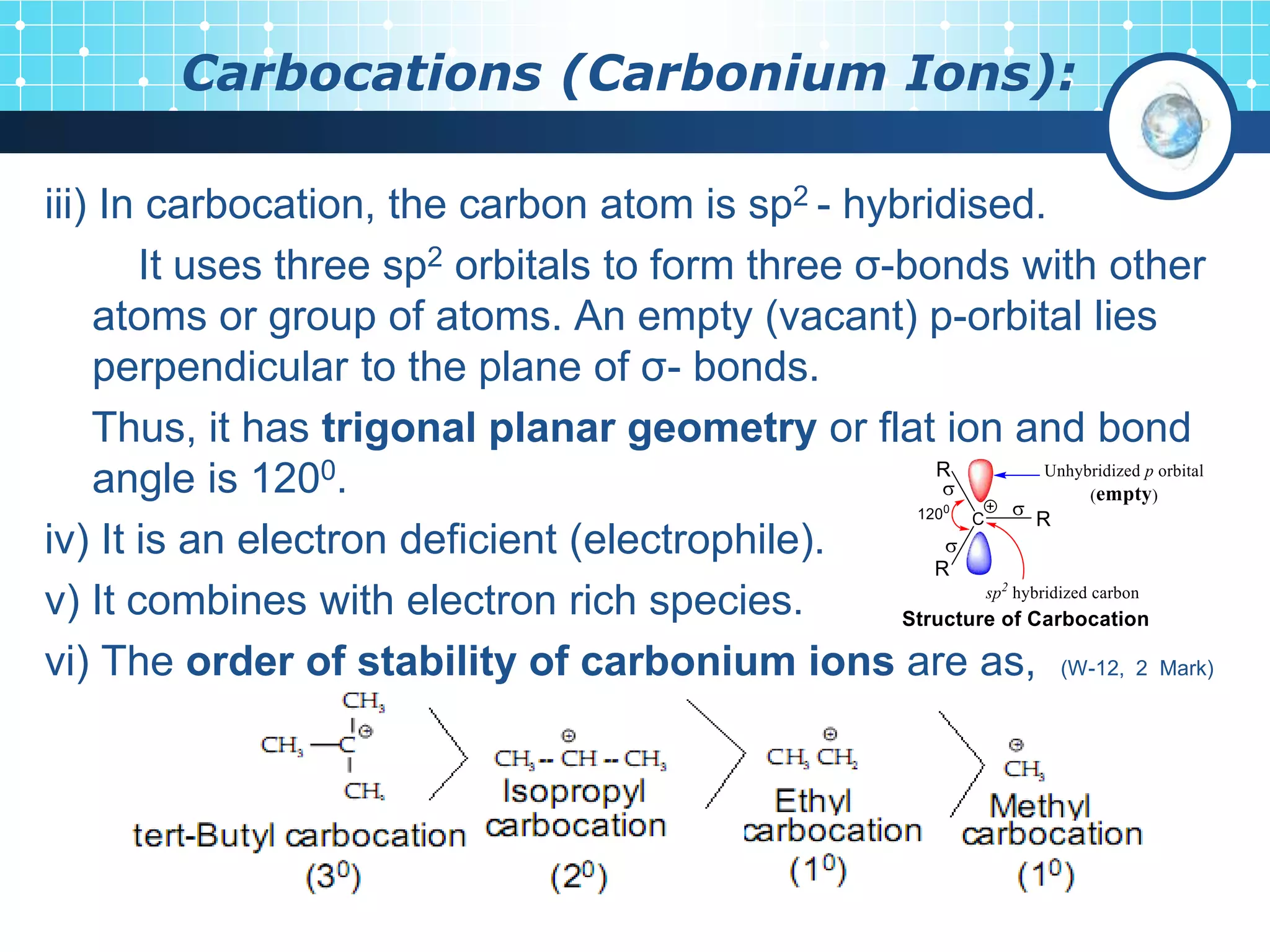
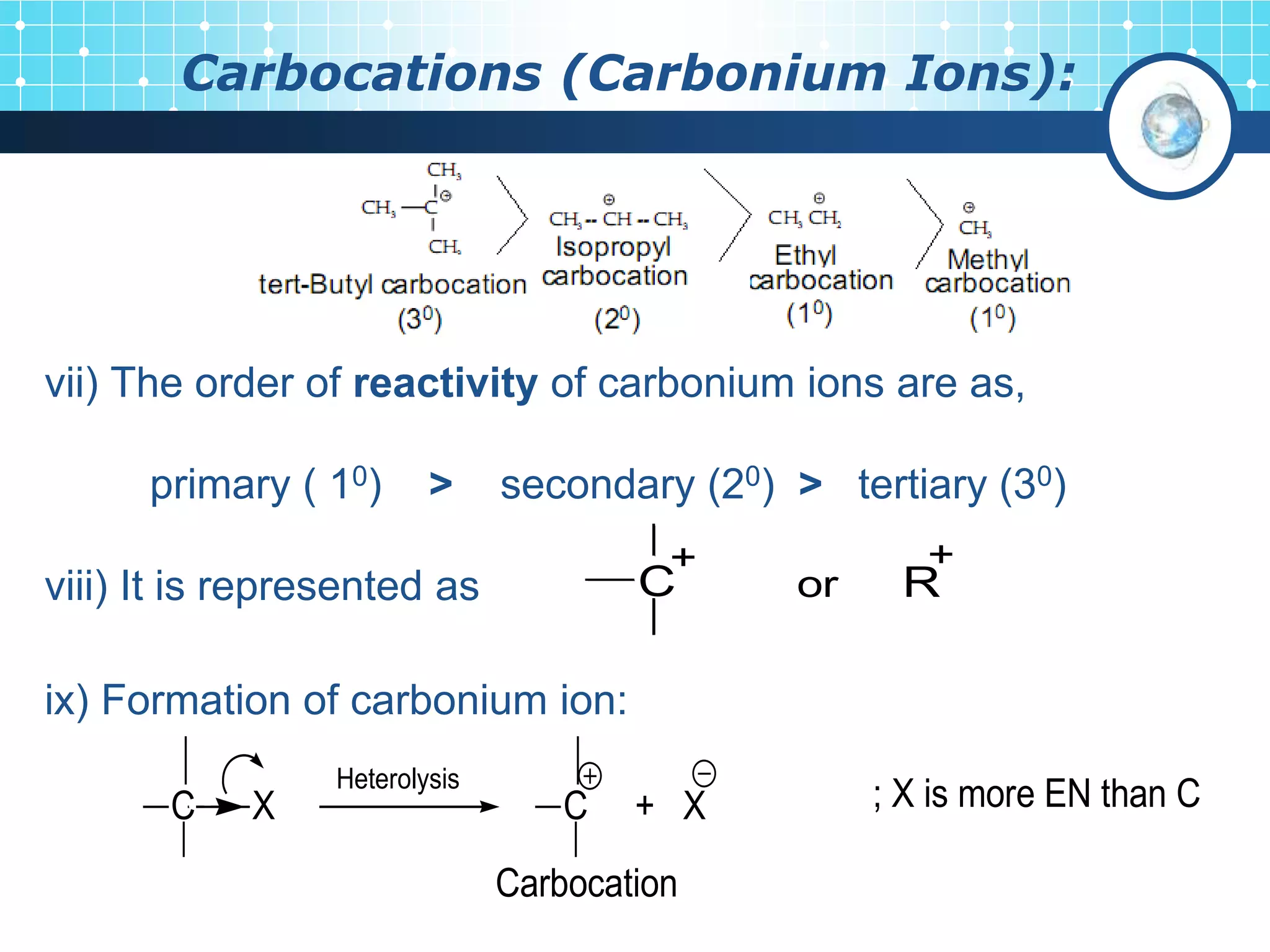
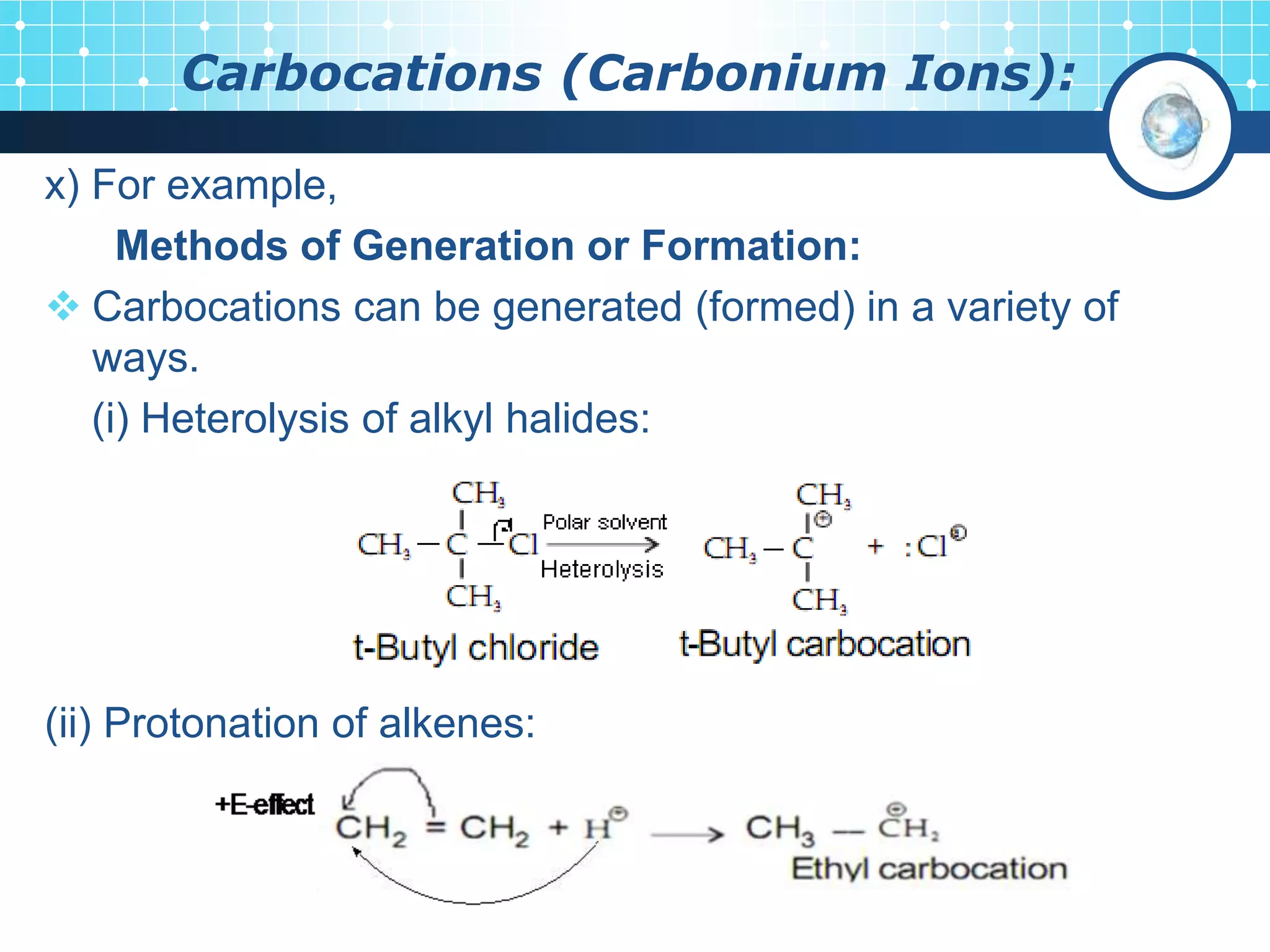
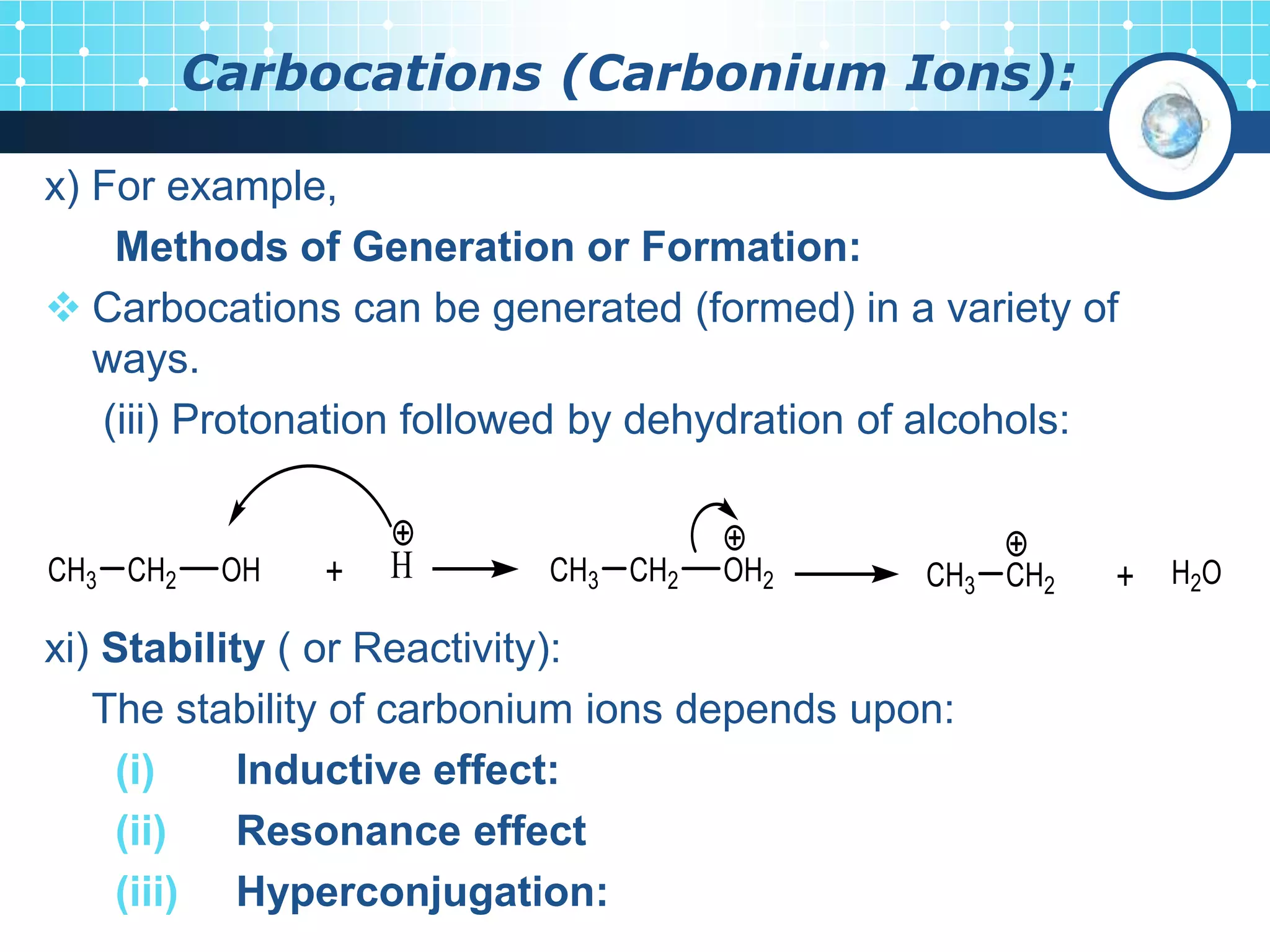
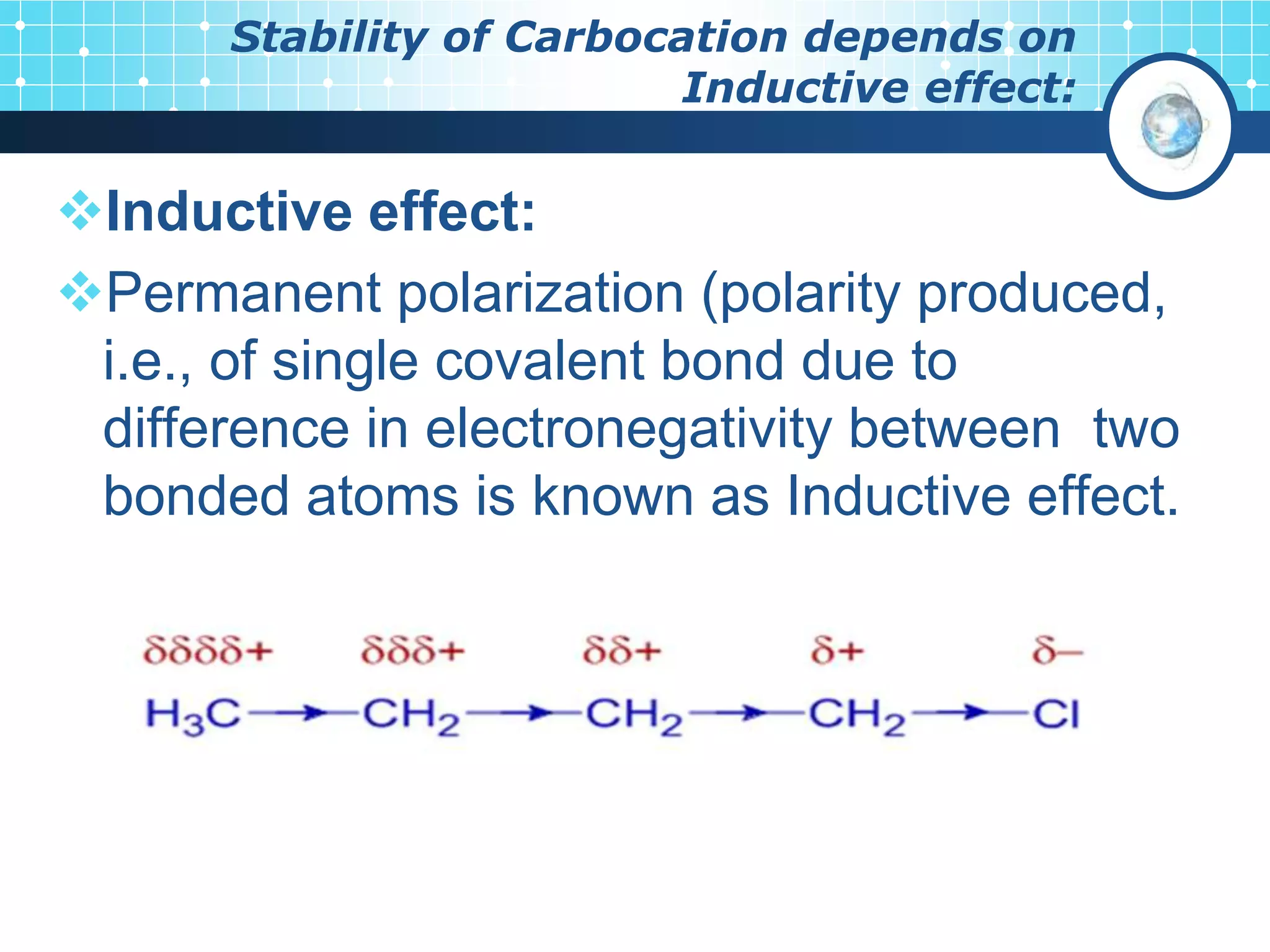
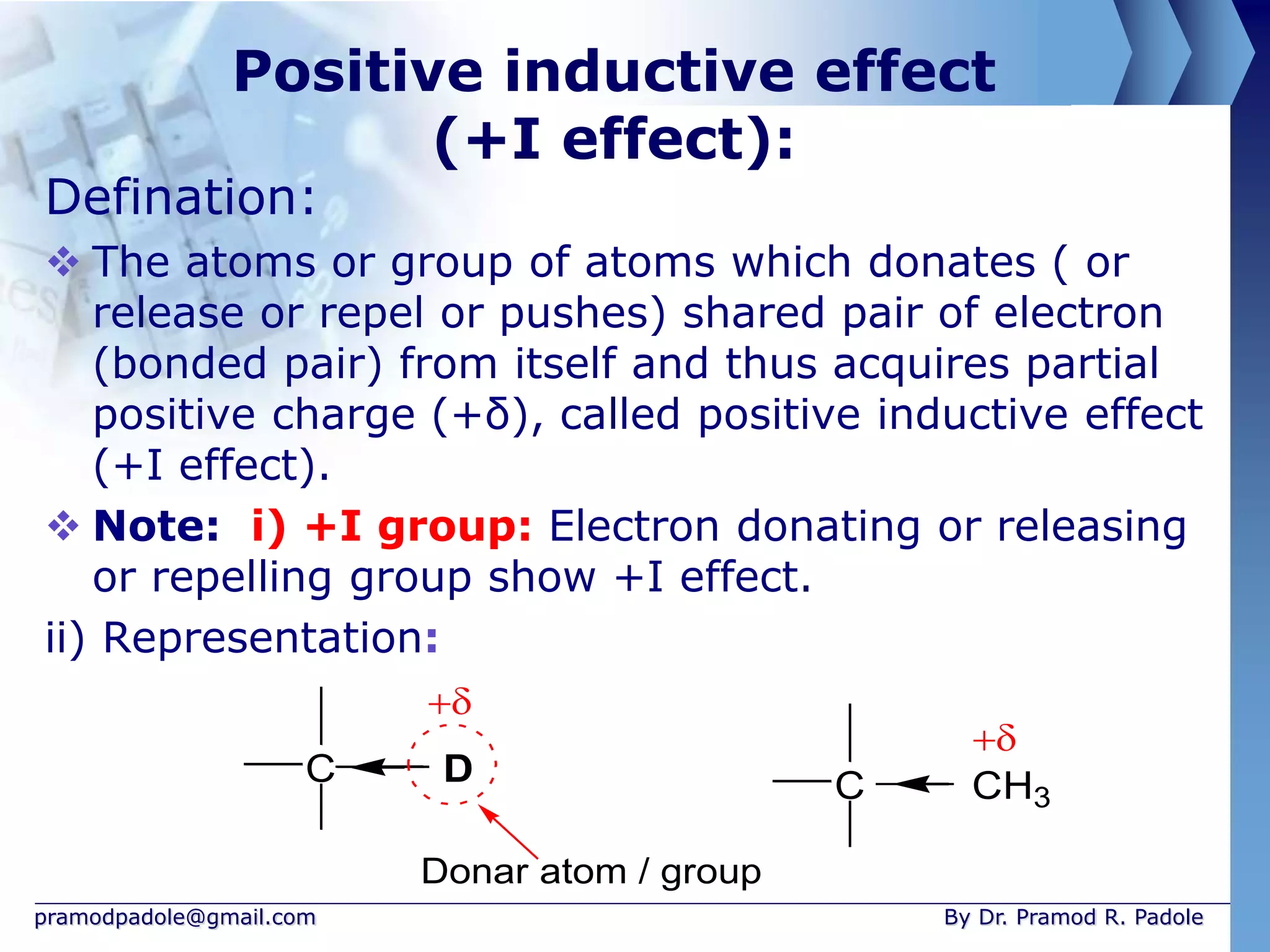
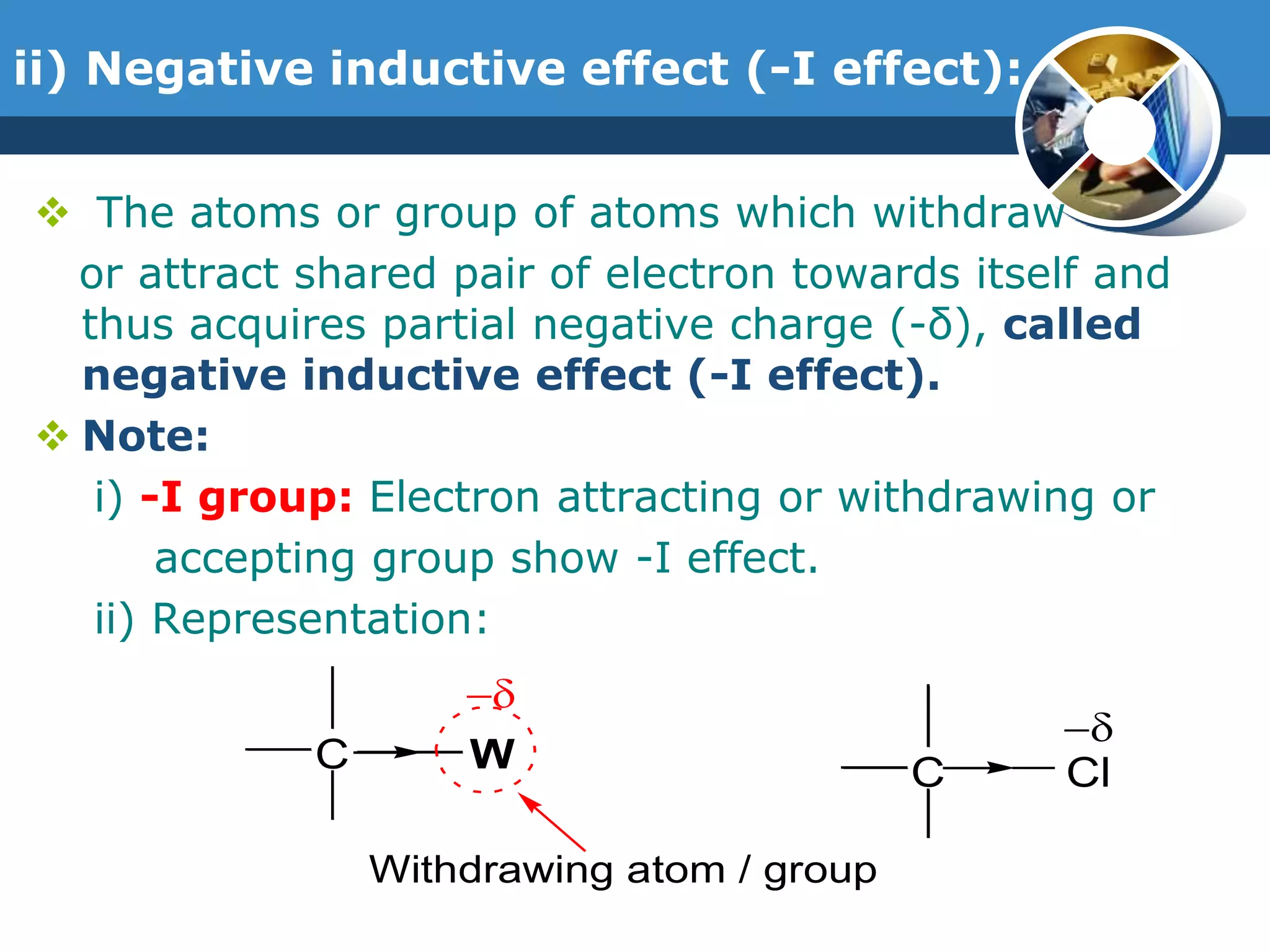
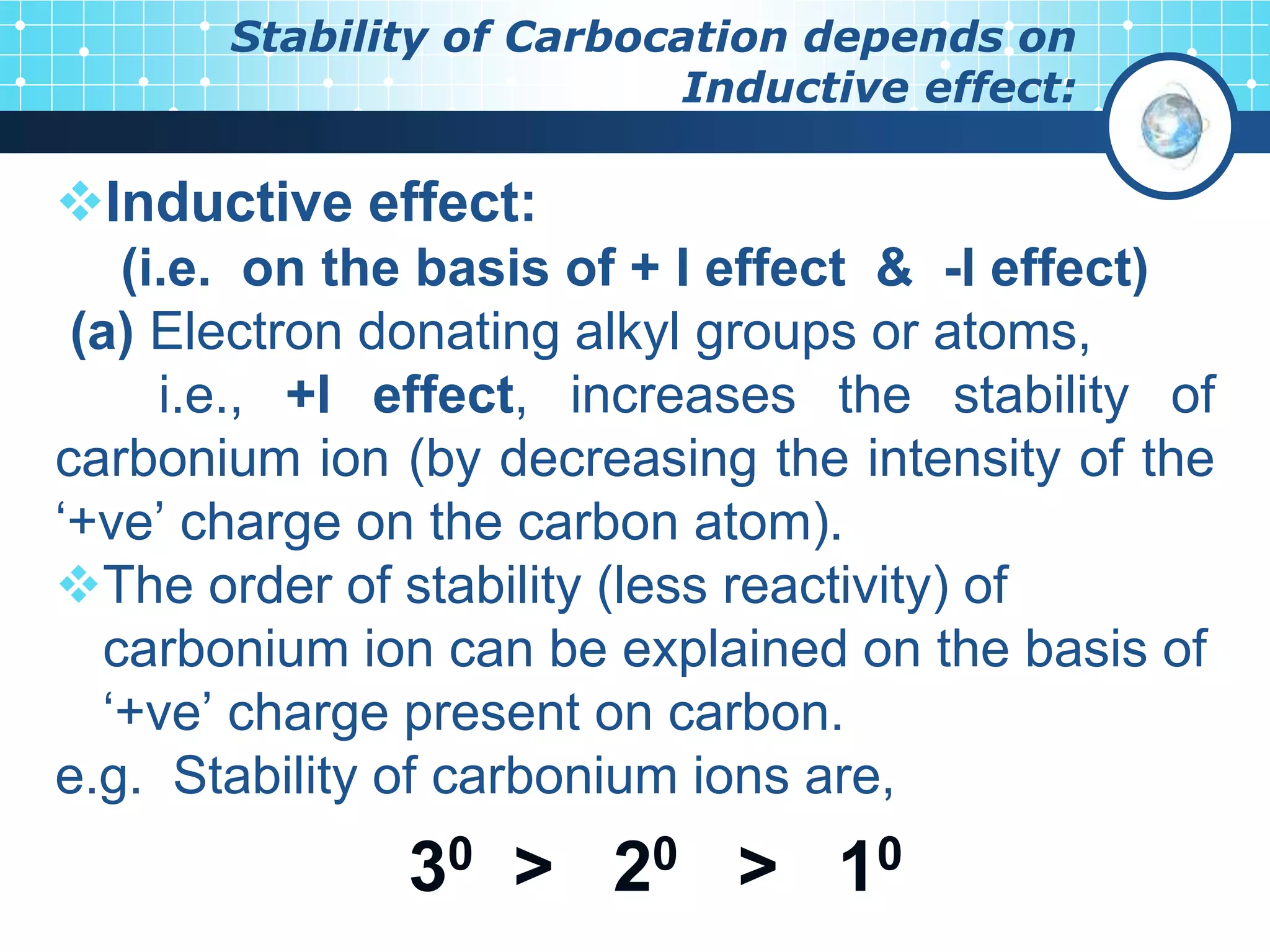
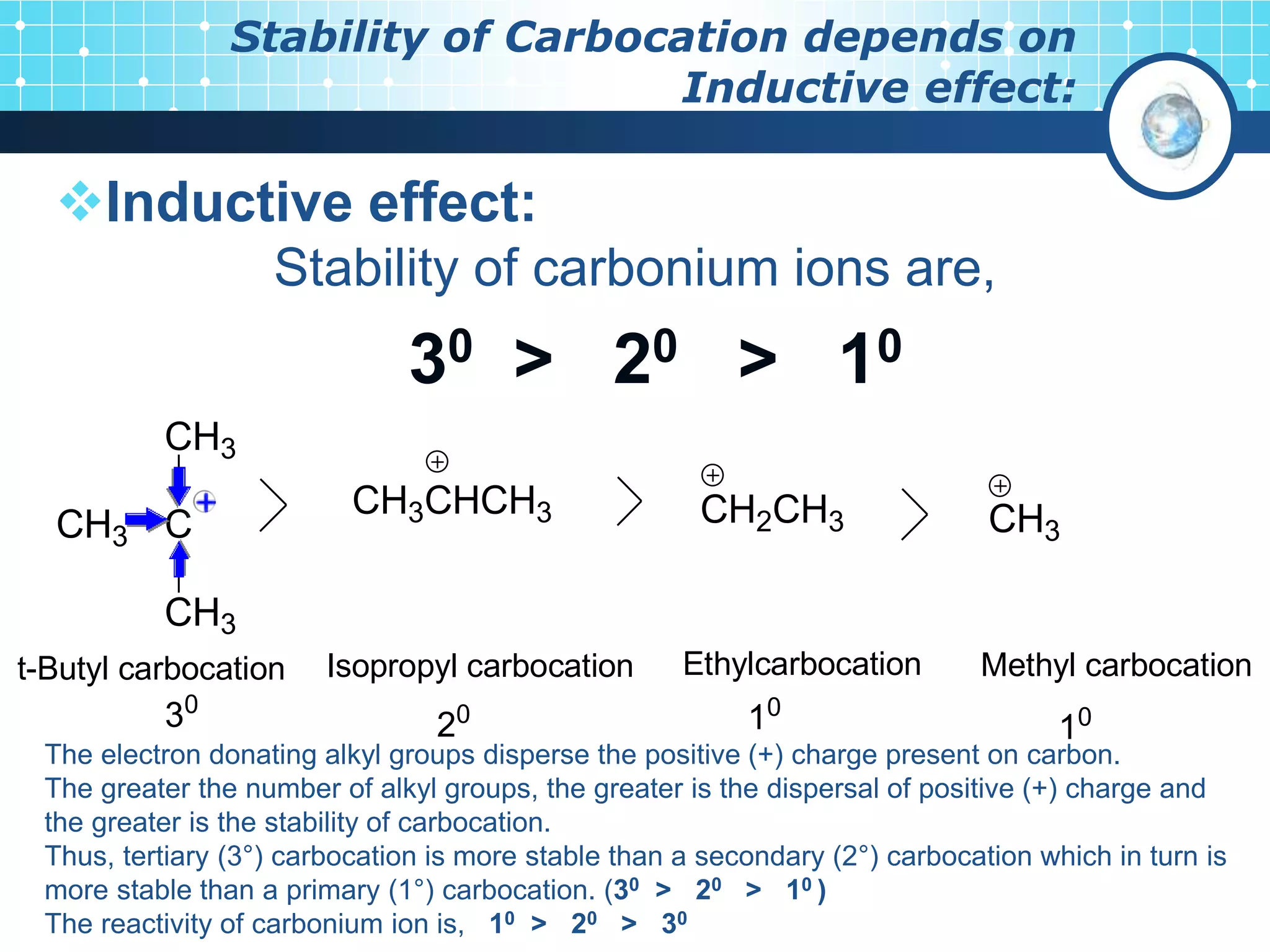
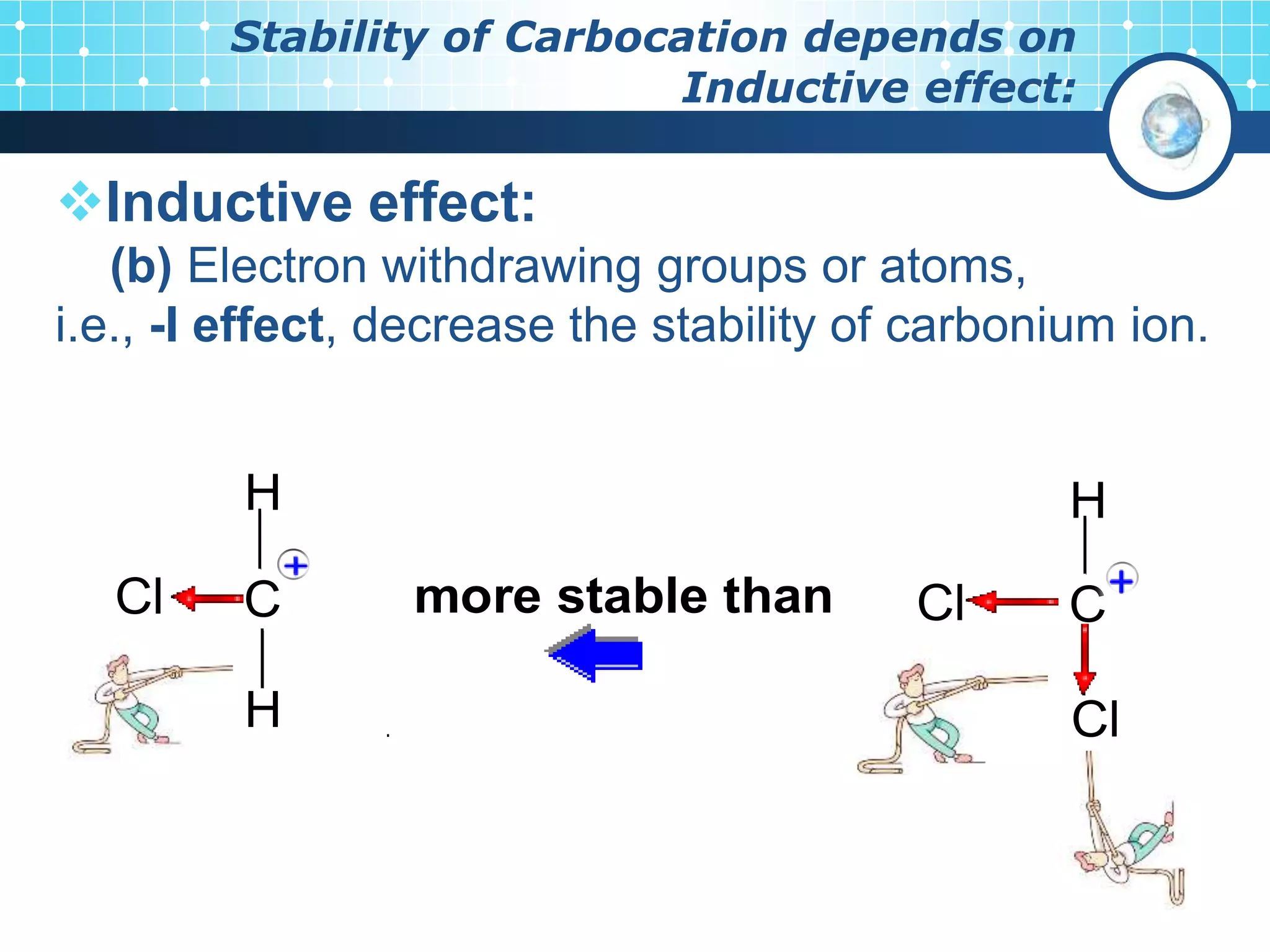
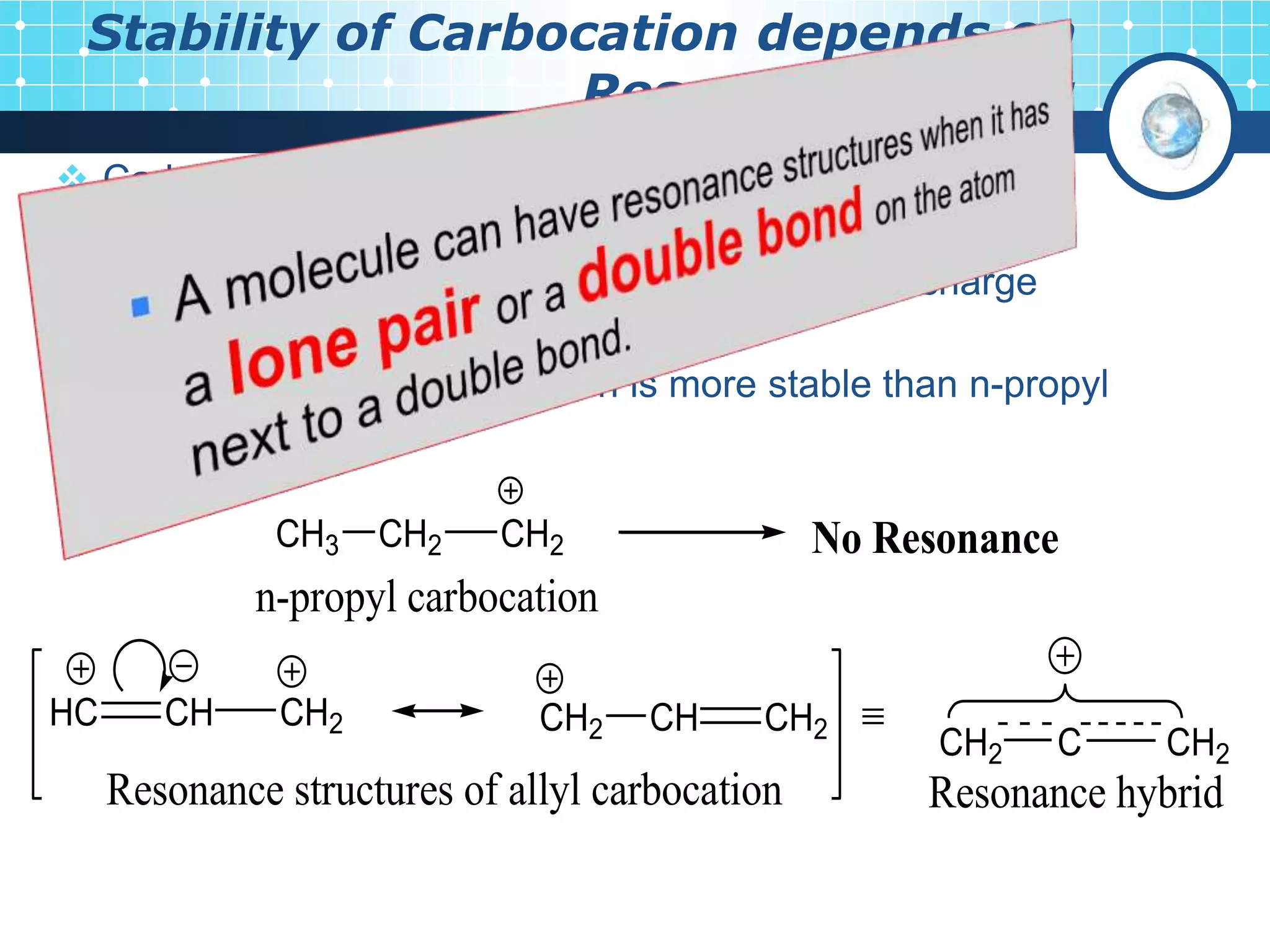
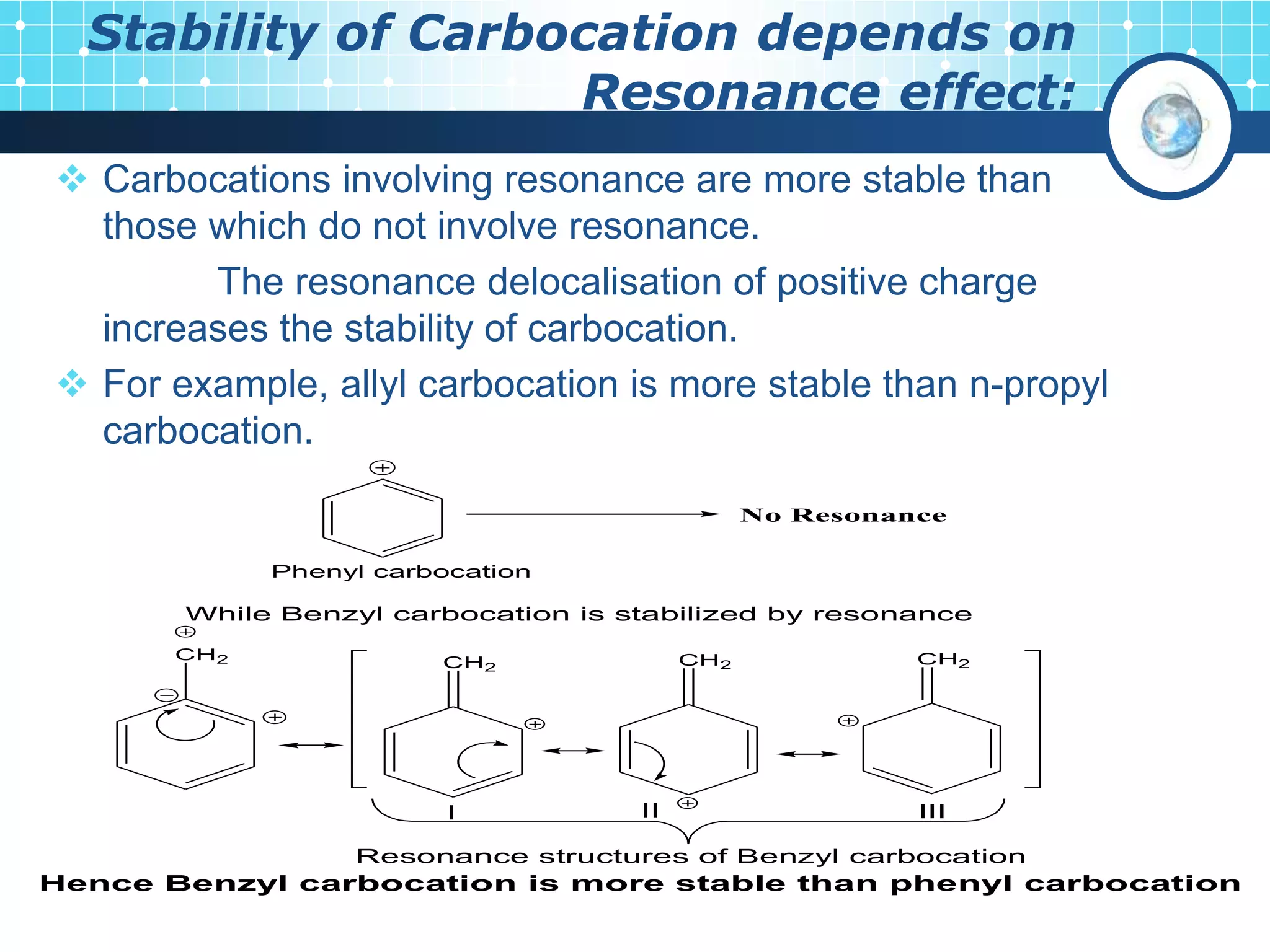
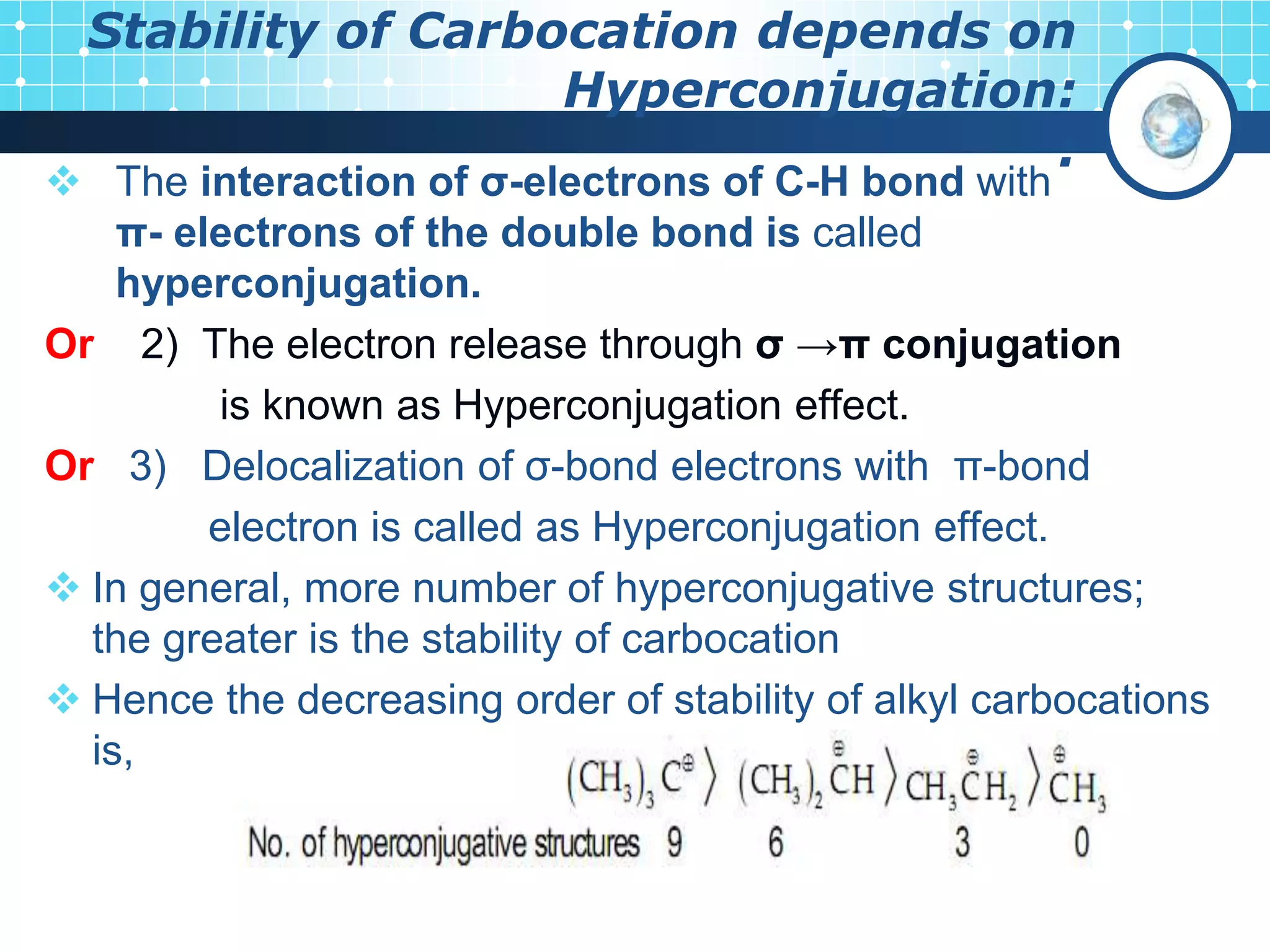
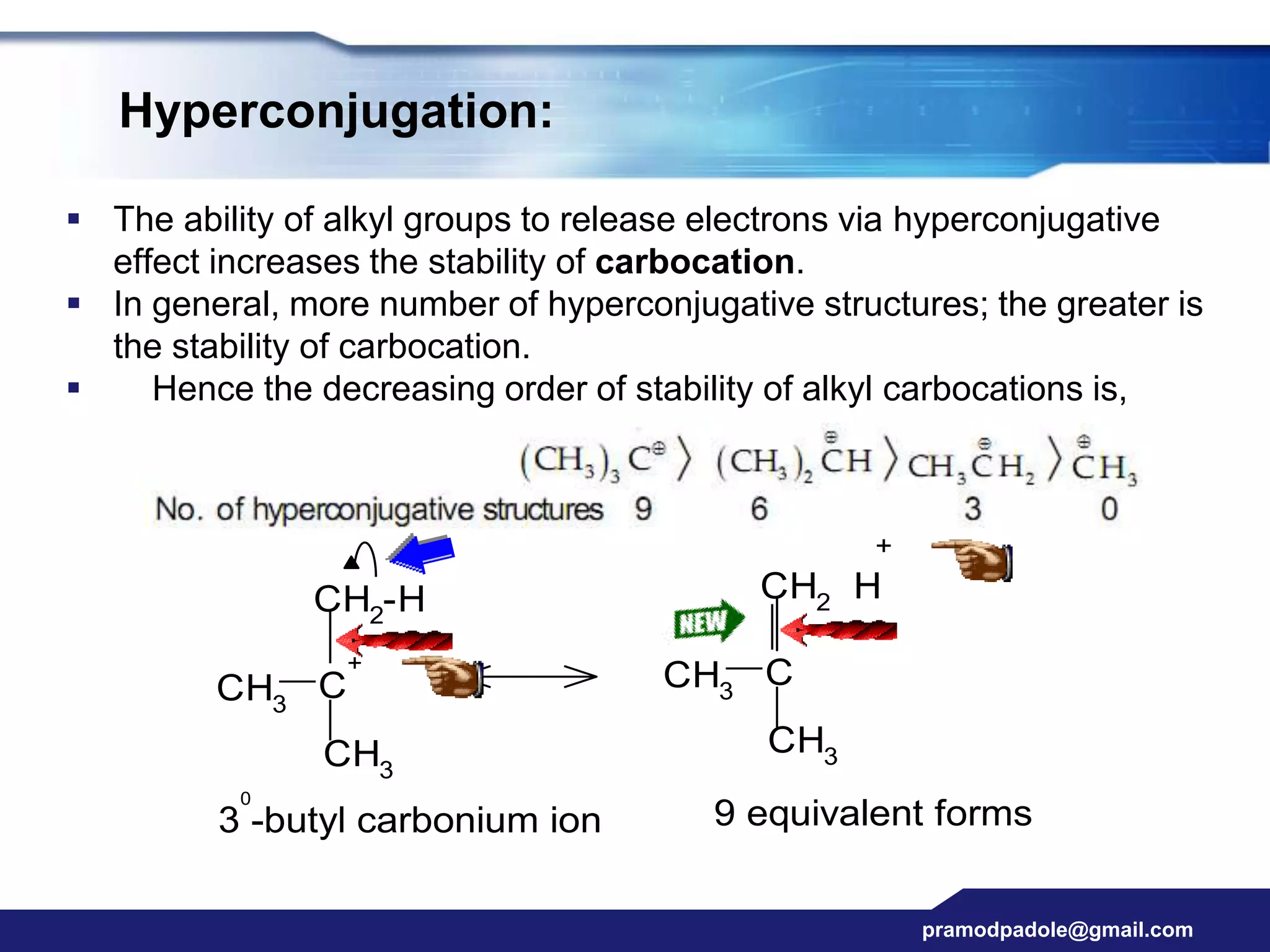
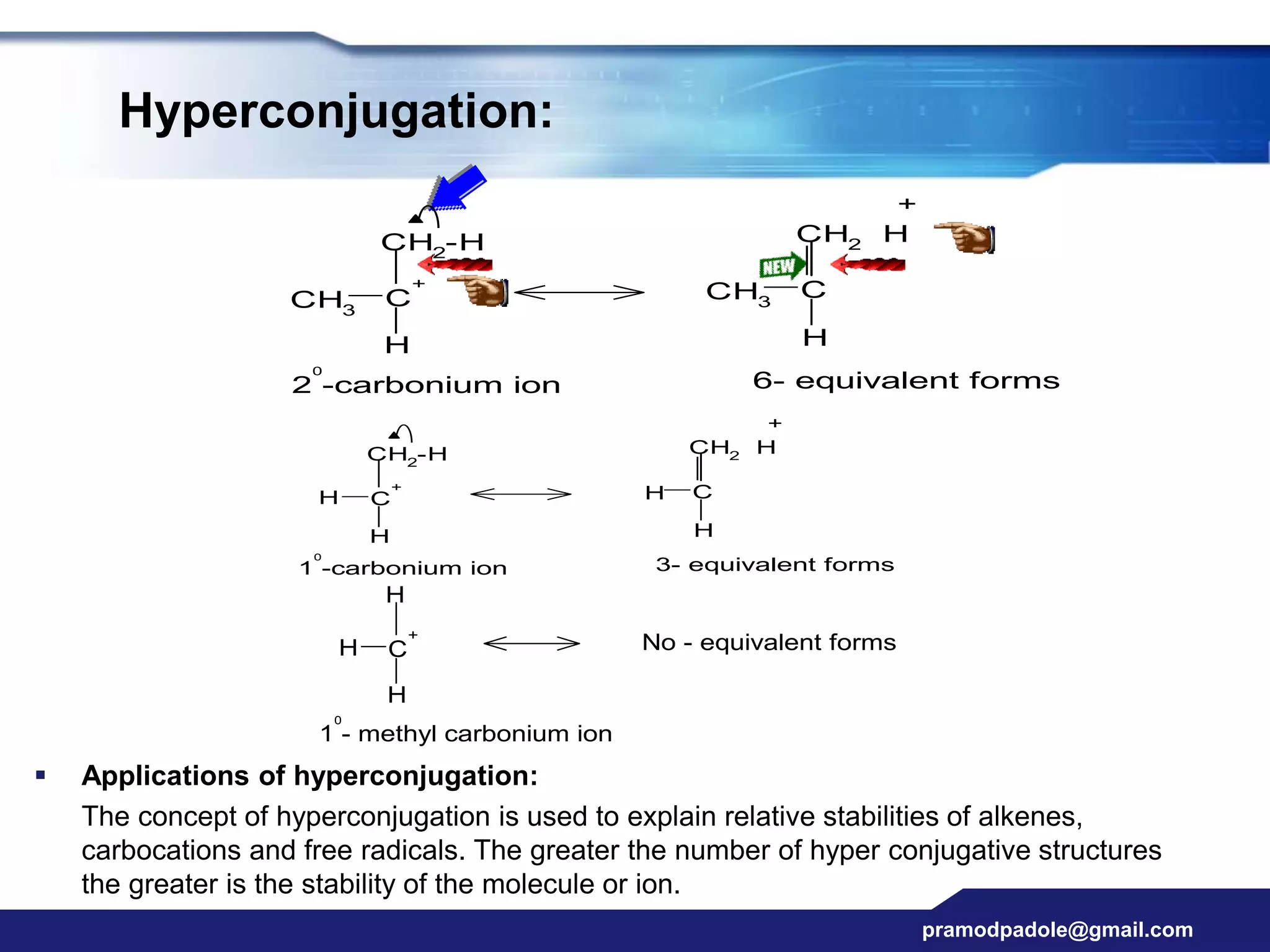
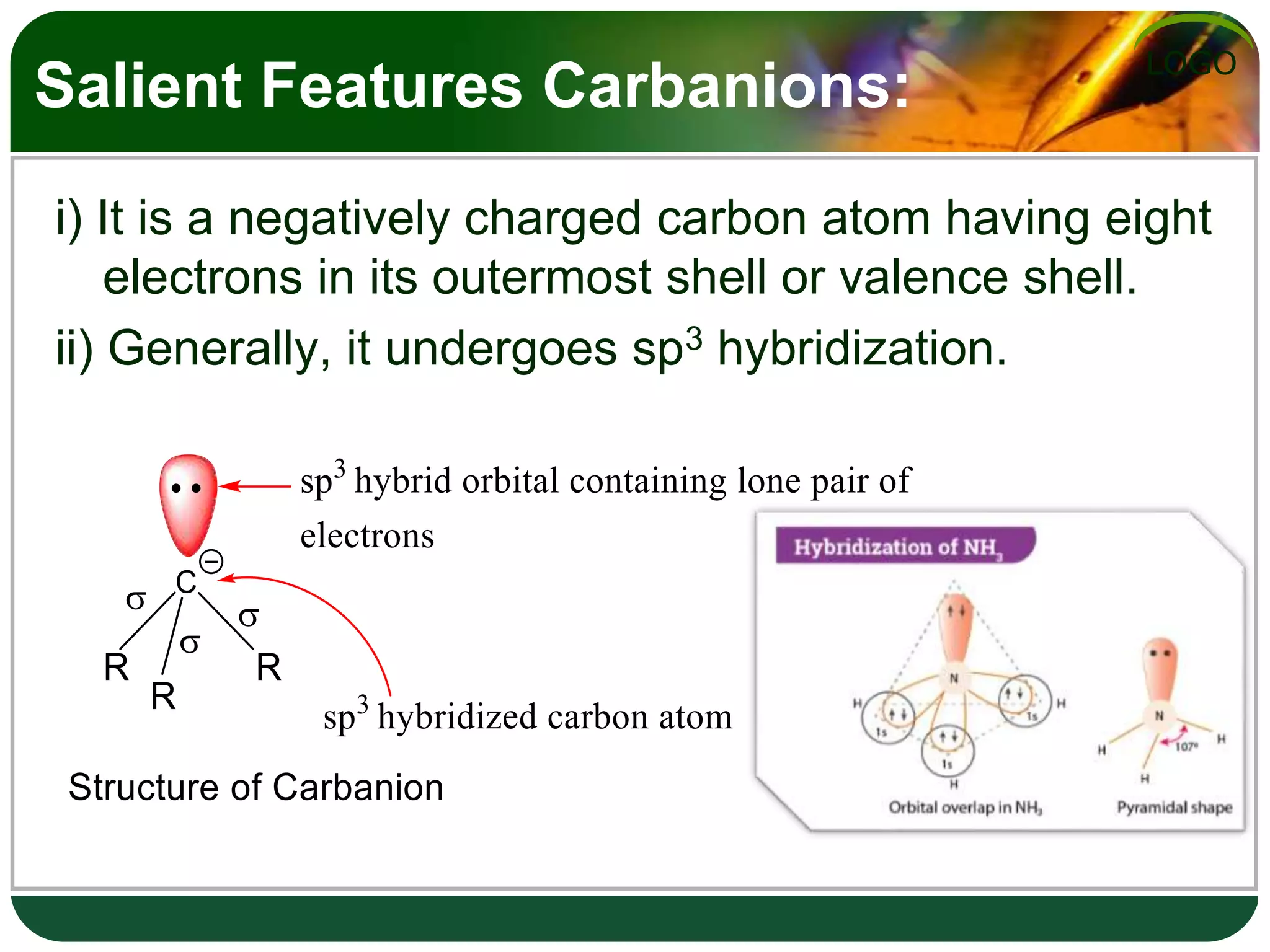
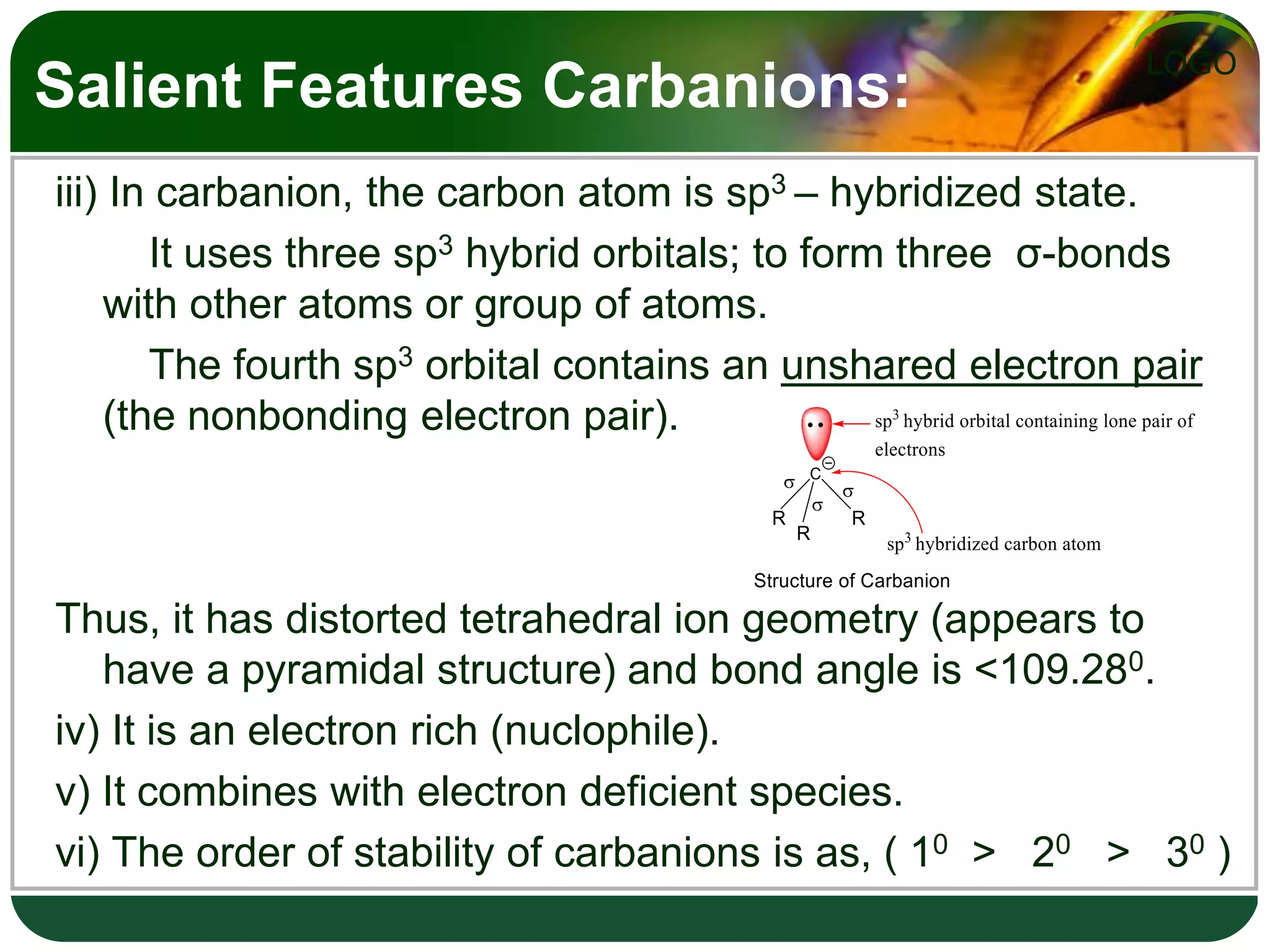
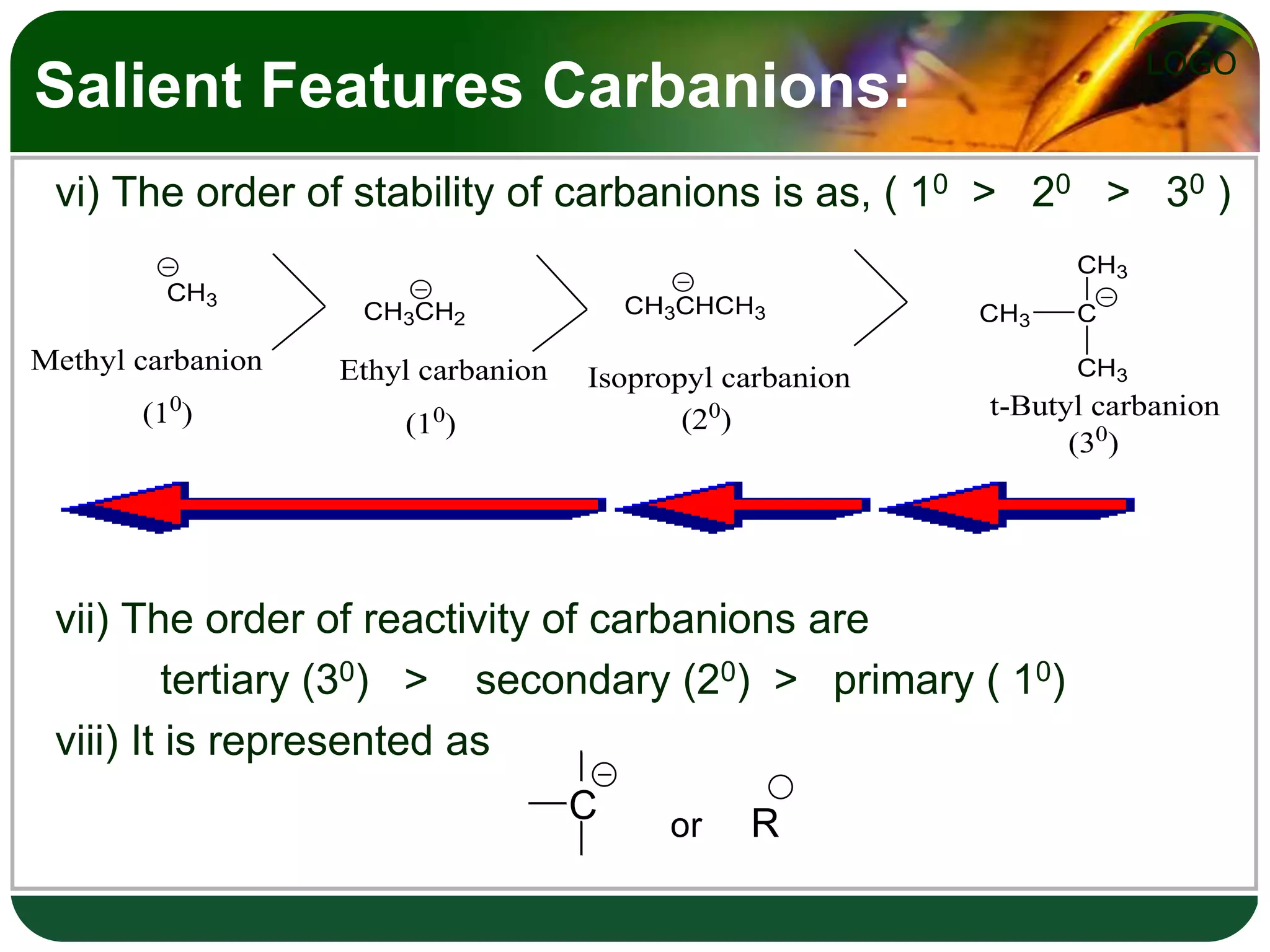
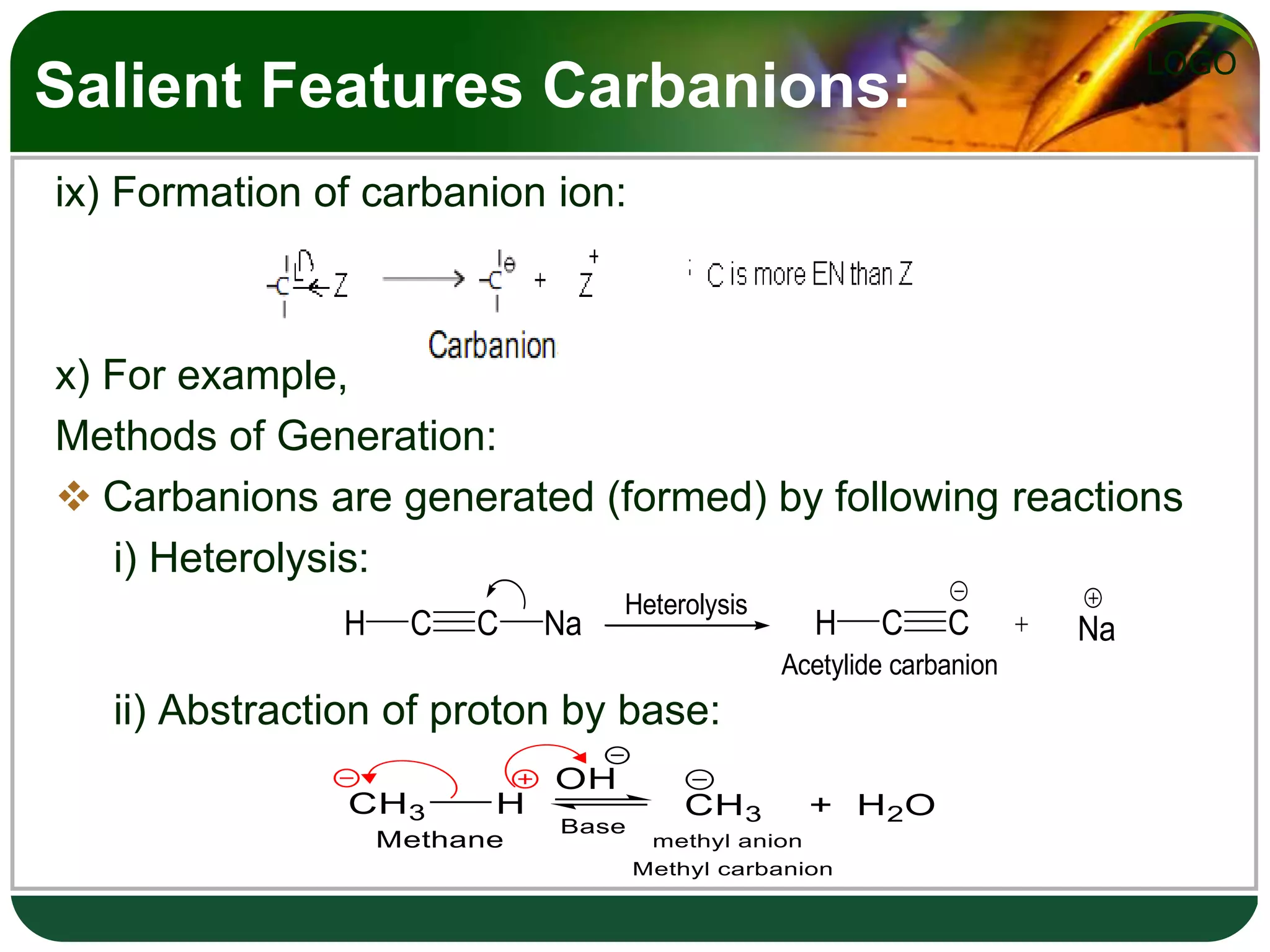
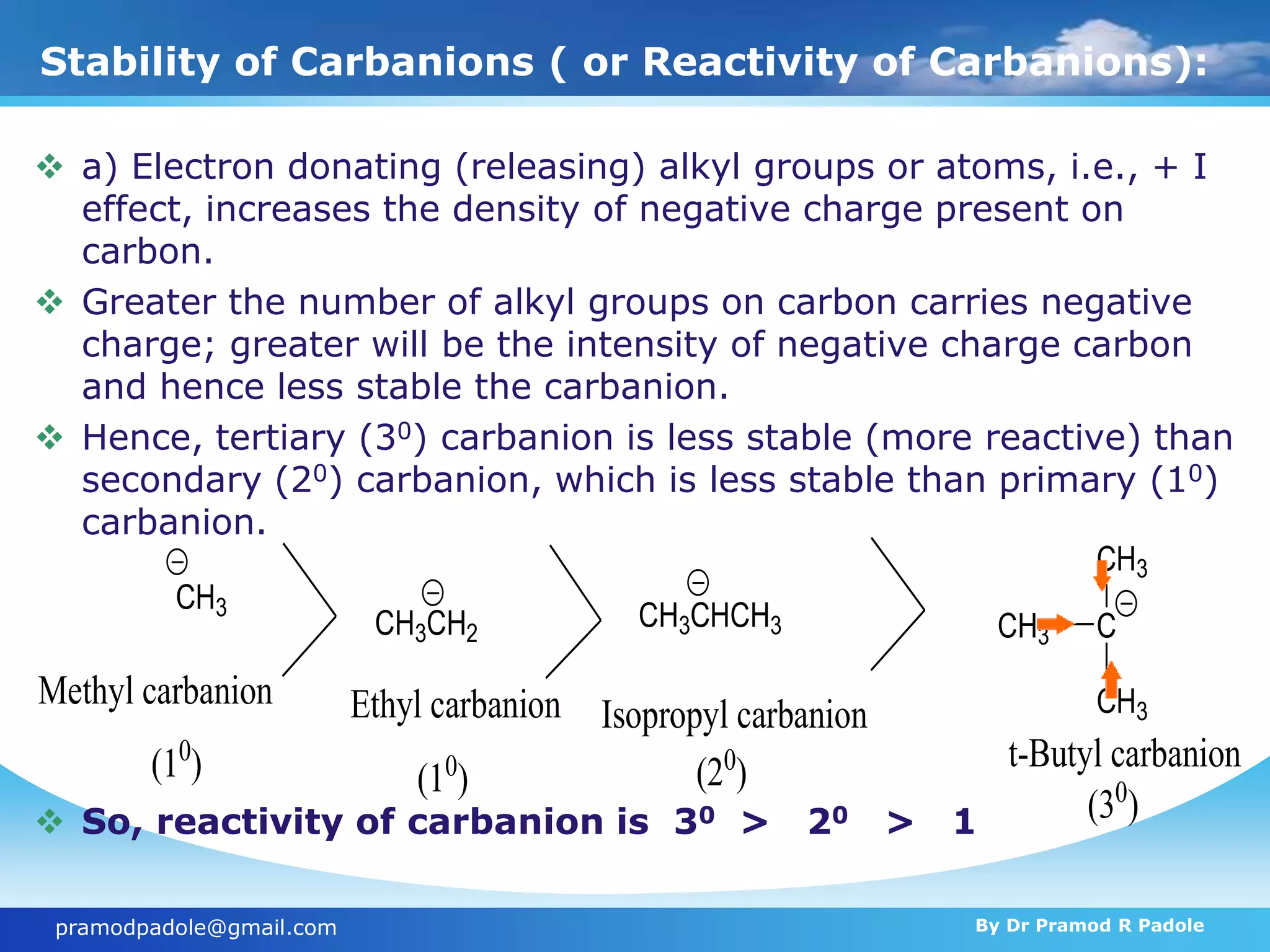
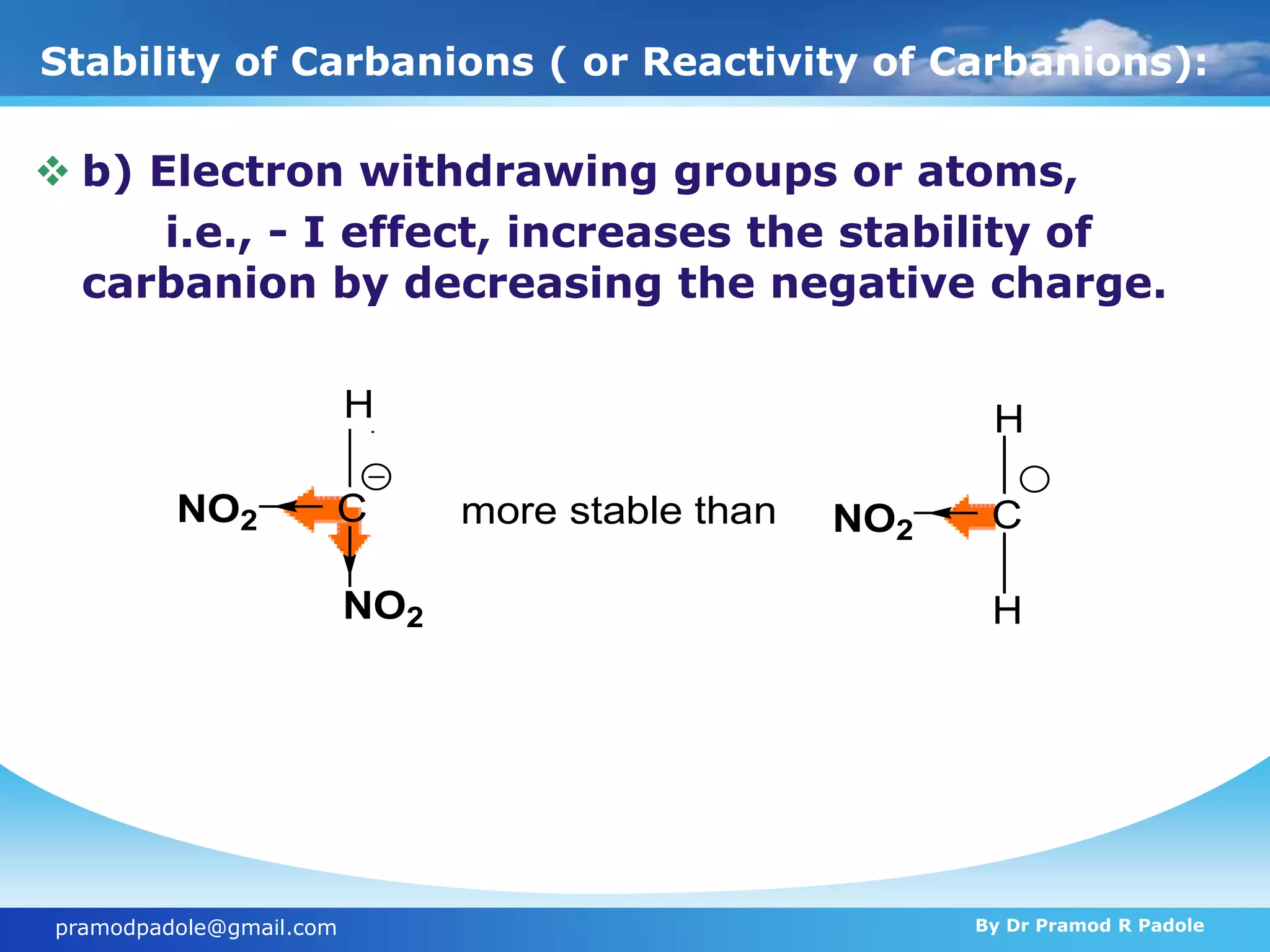
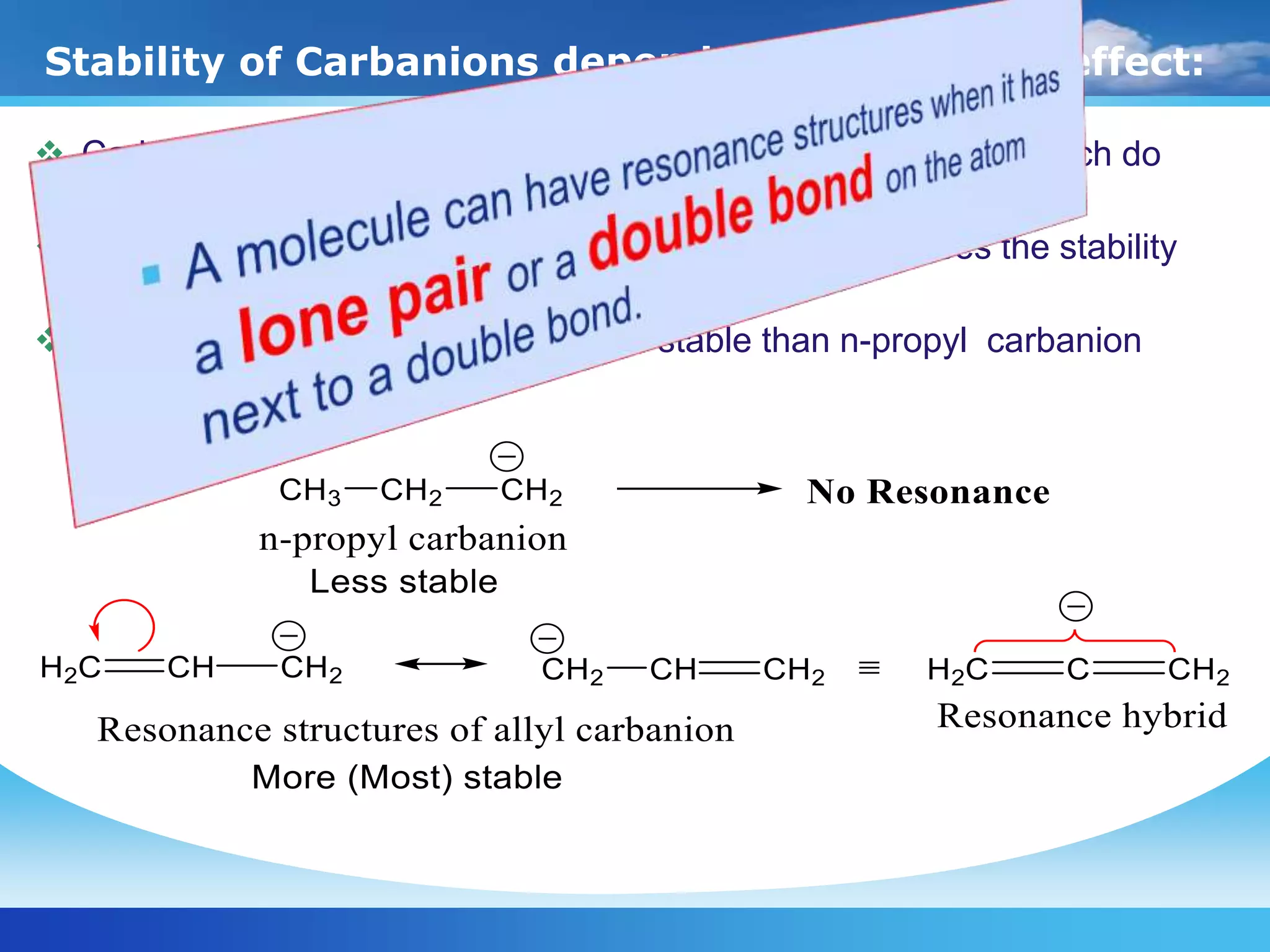
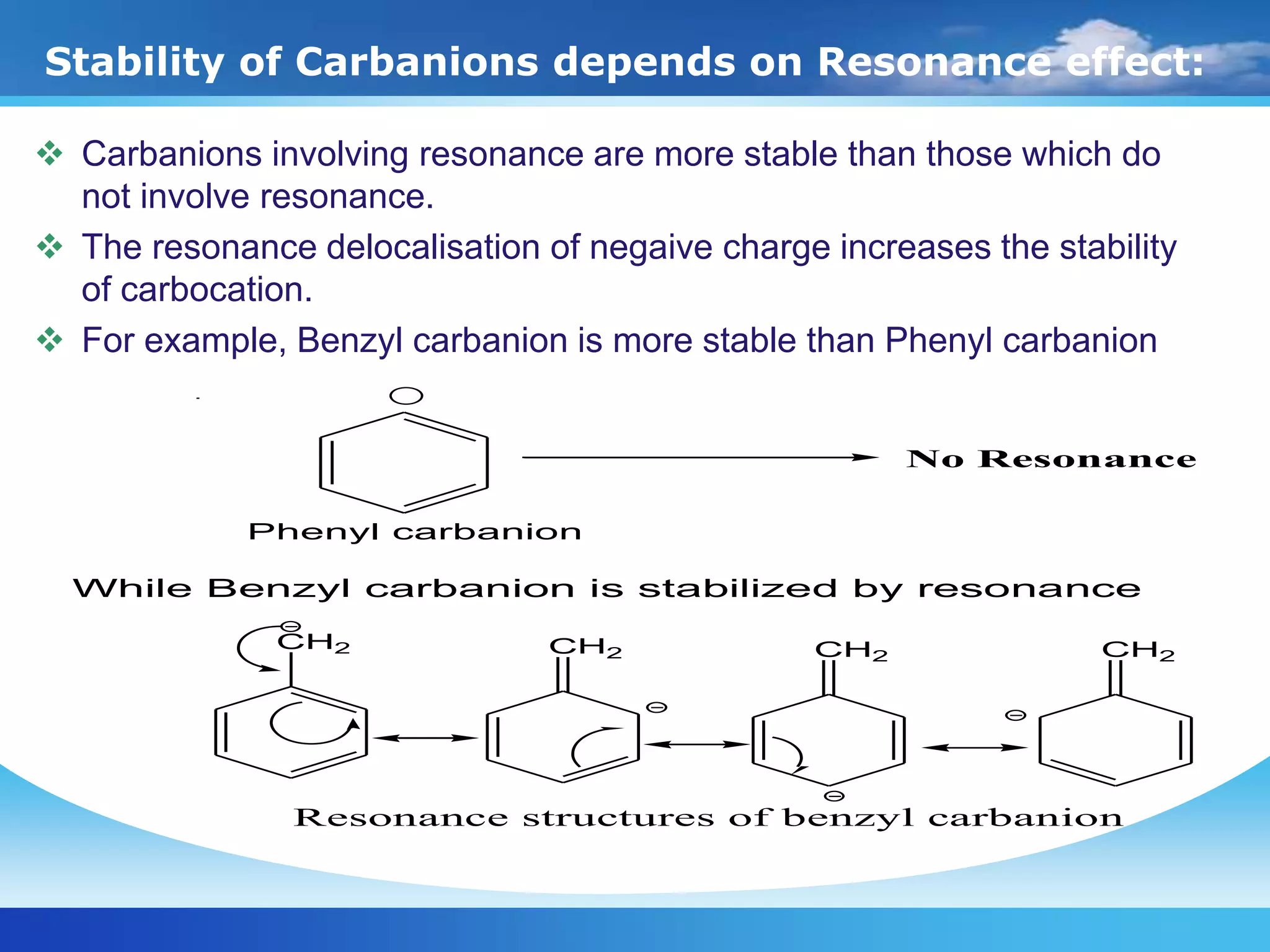
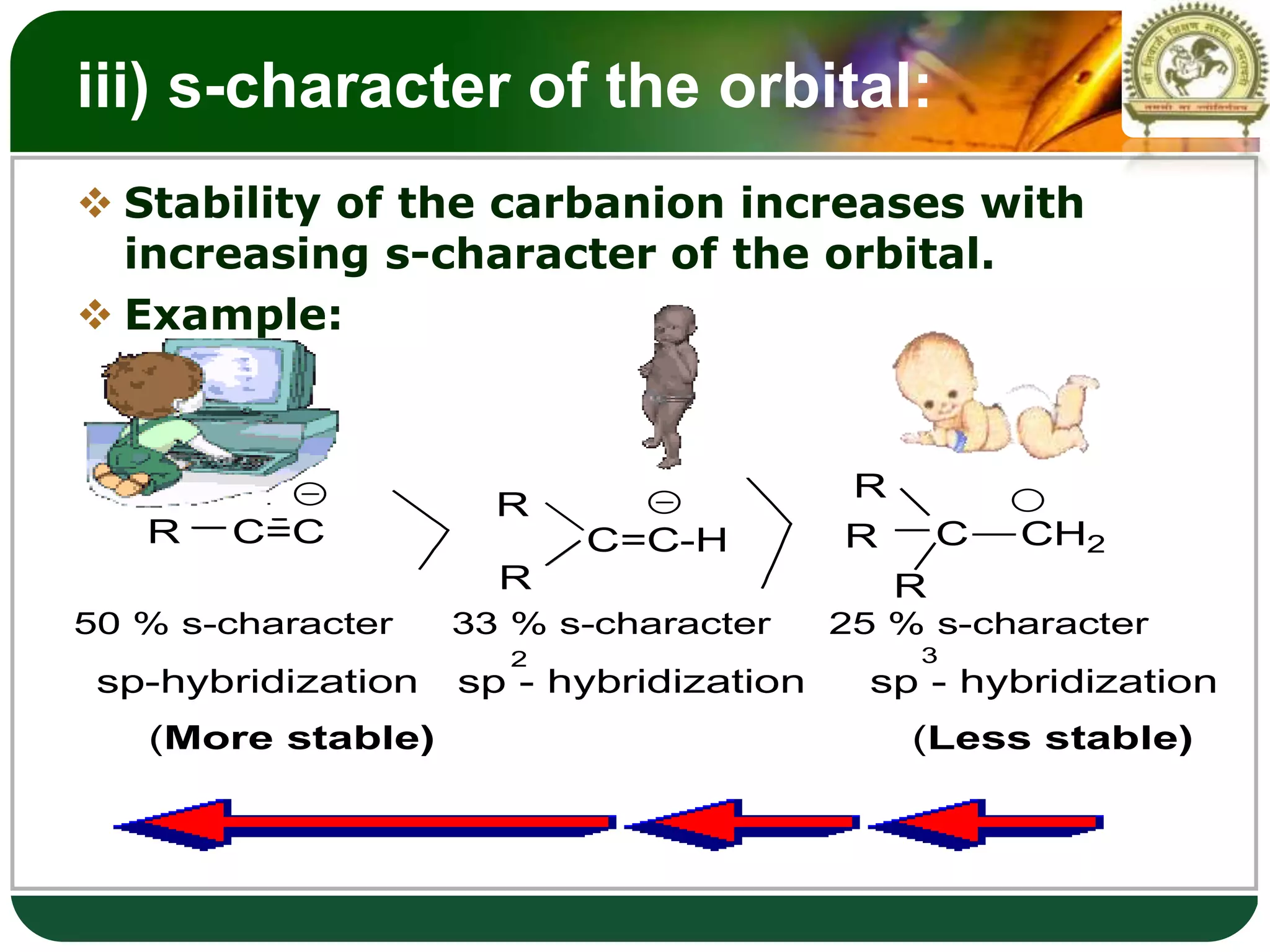
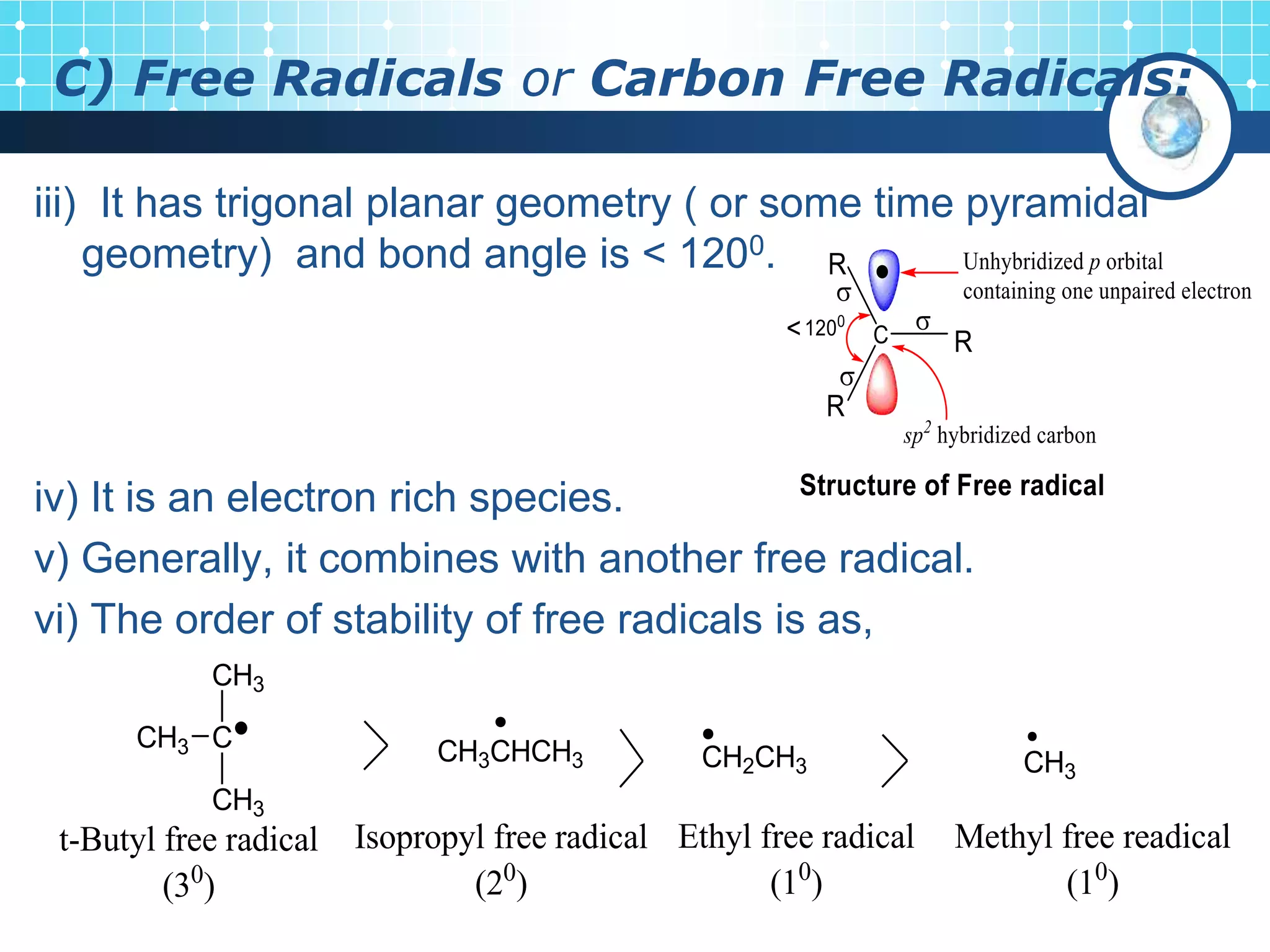
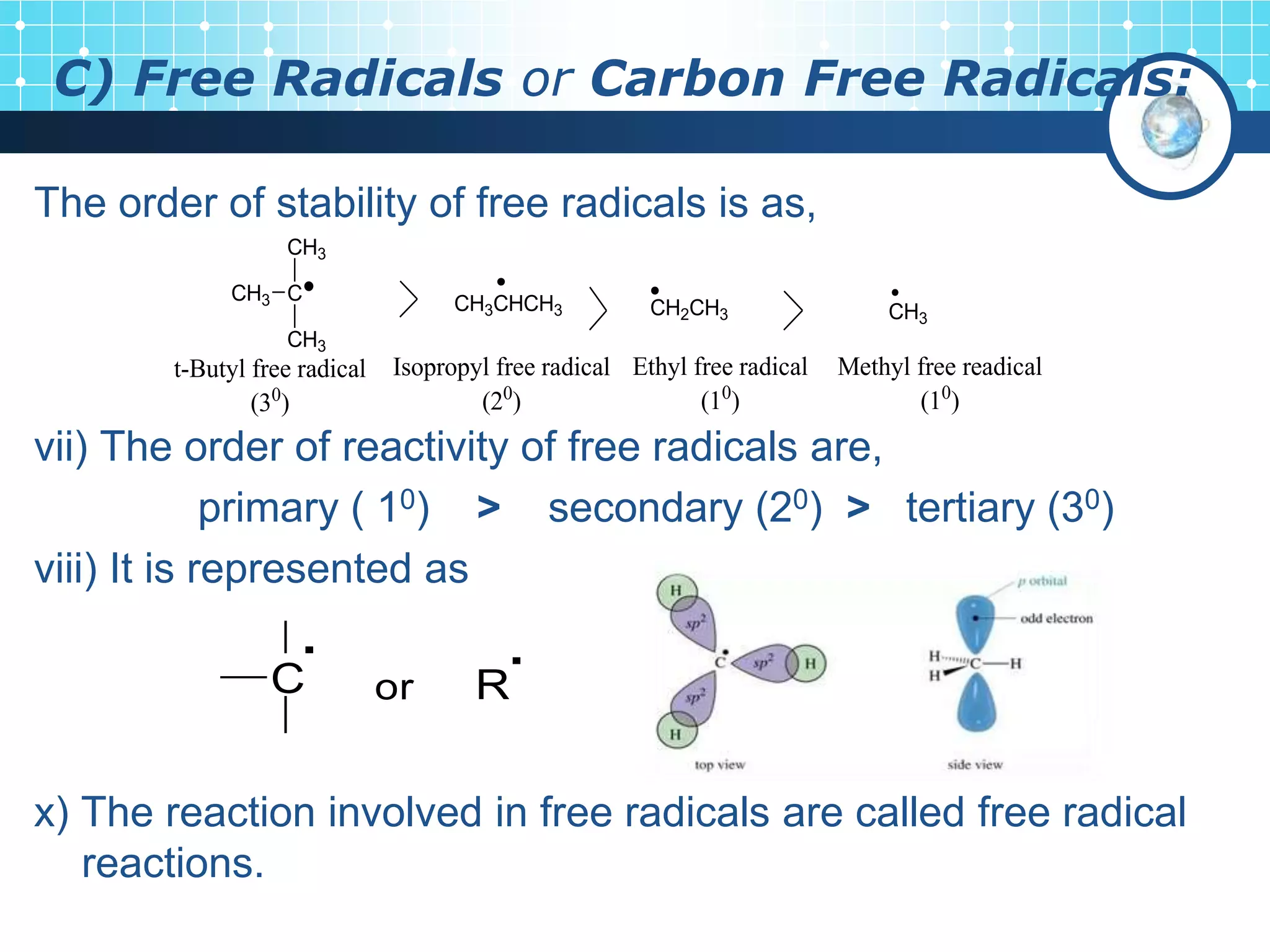
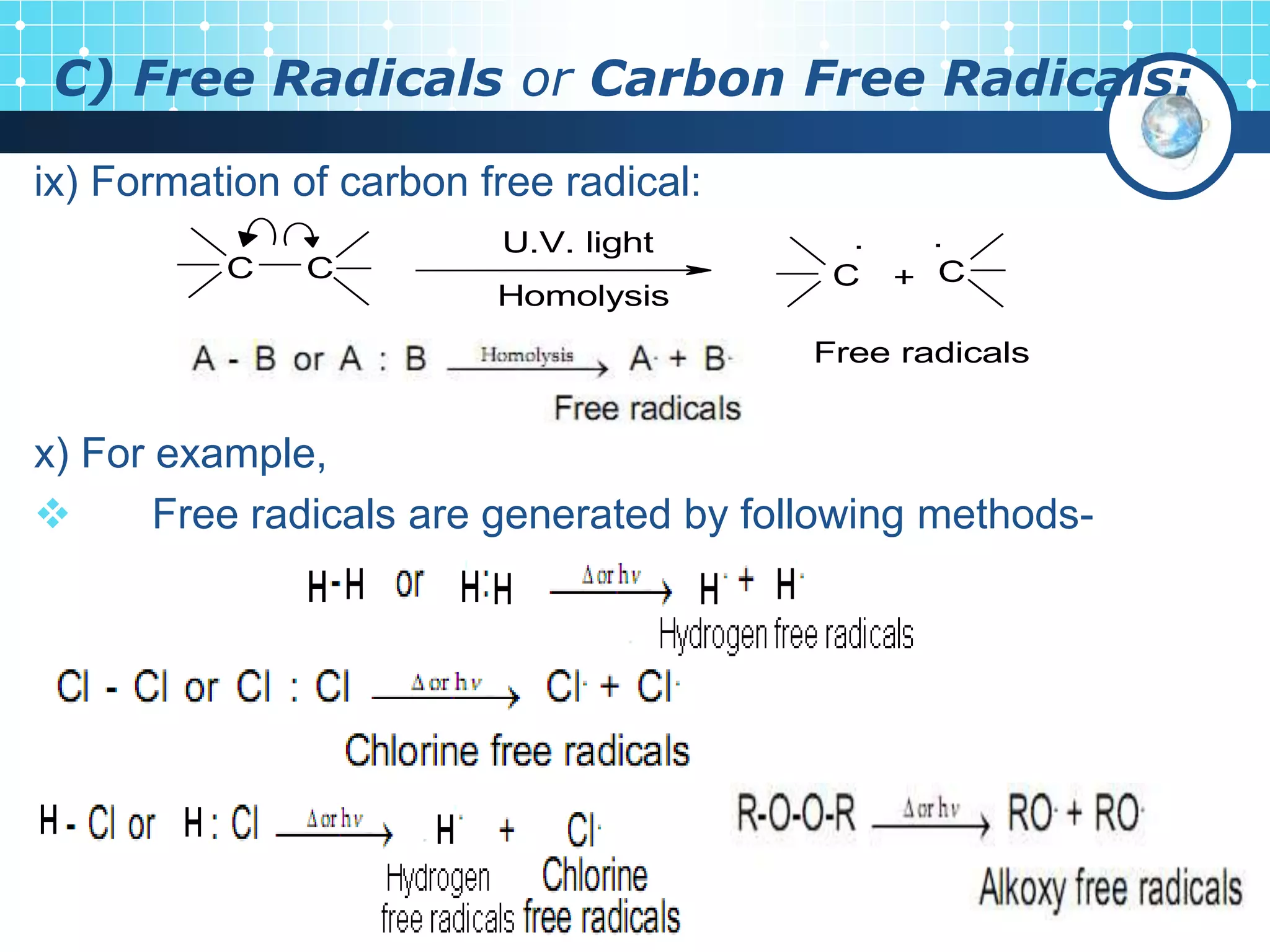
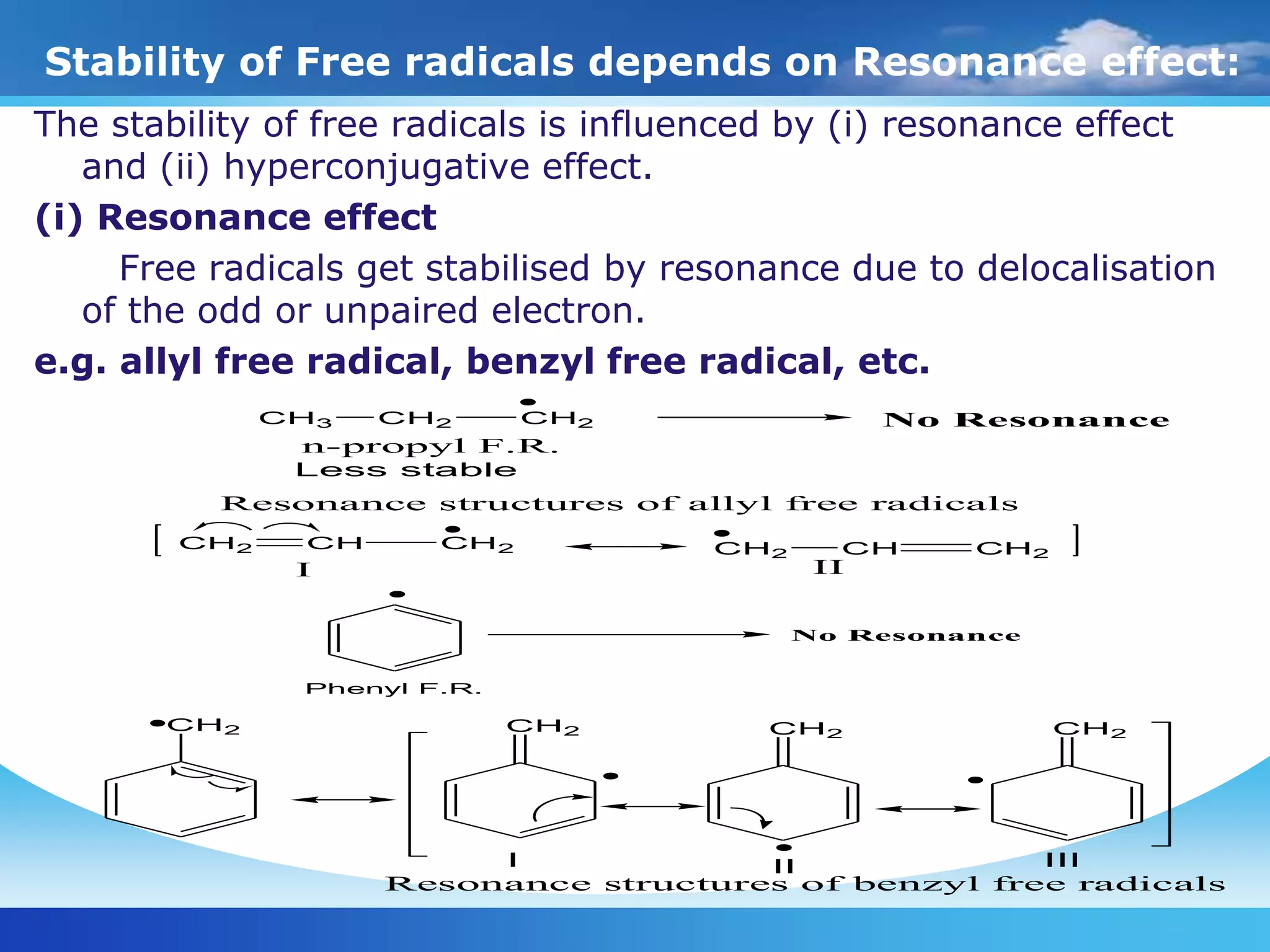
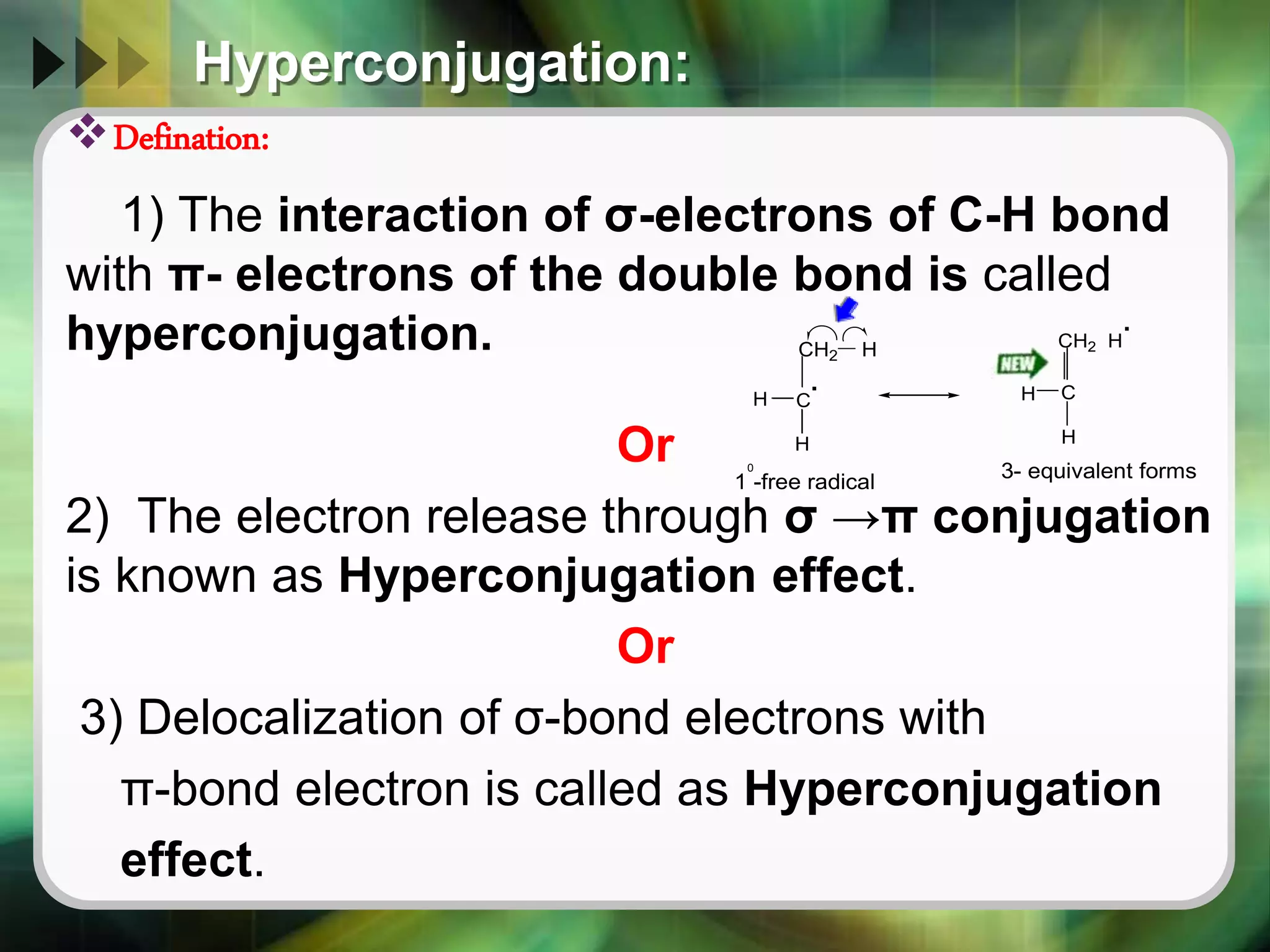
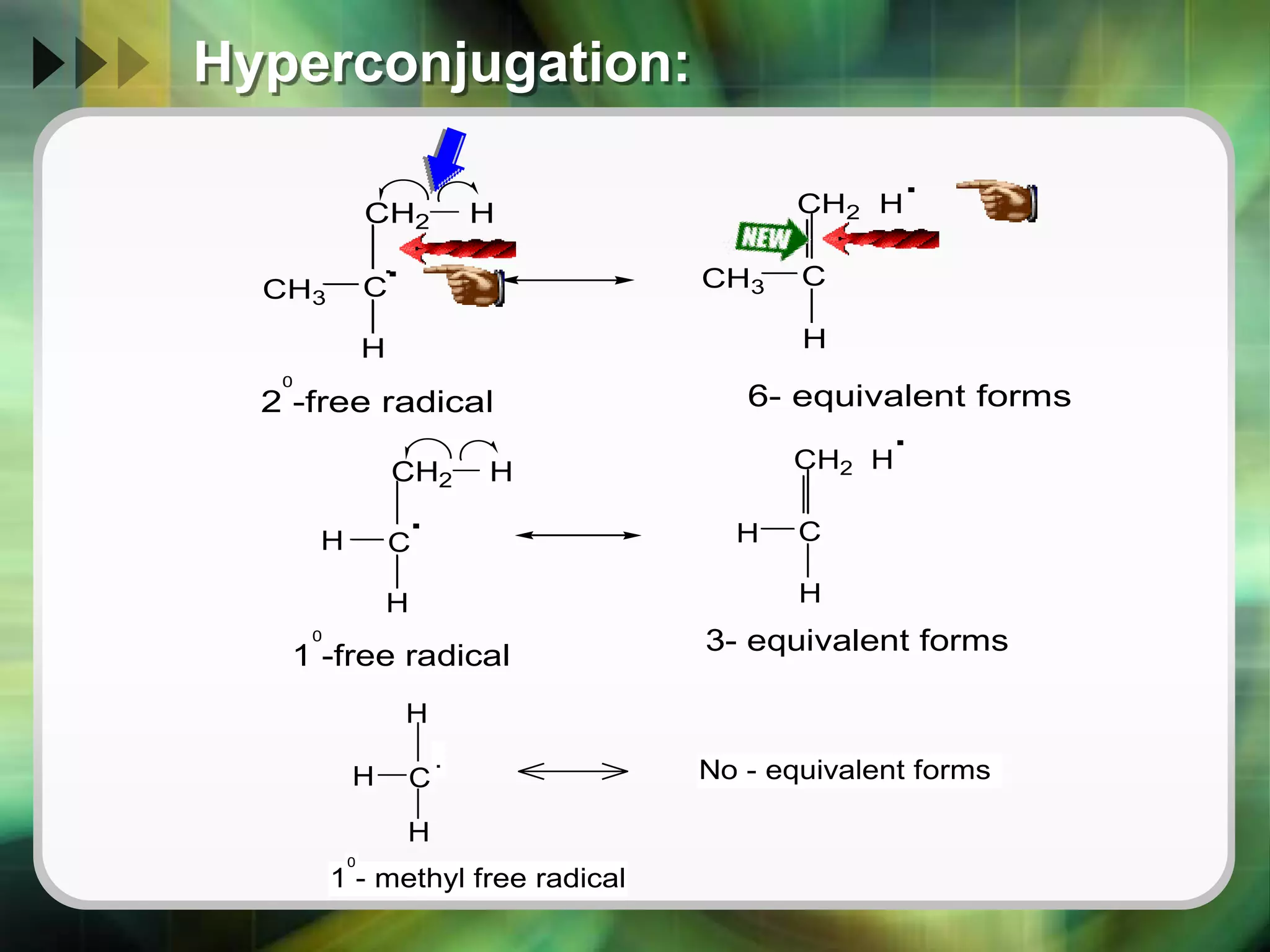
The document discusses various reactive intermediates in organic chemistry, focusing on carbocations and carbanions. It defines carbocations as organic ions with a positively charged carbon atom and carbanions as organic ions with a negatively charged carbon atom. It describes their structures, methods of generation, stability orders, and factors affecting stability such as inductive and resonance effects. Carbocations are more stable with electron-donating groups or resonance, while carbanions are more stable with electron-withdrawing groups or resonance. The document also provides examples and practice questions related to these reactive intermediates.