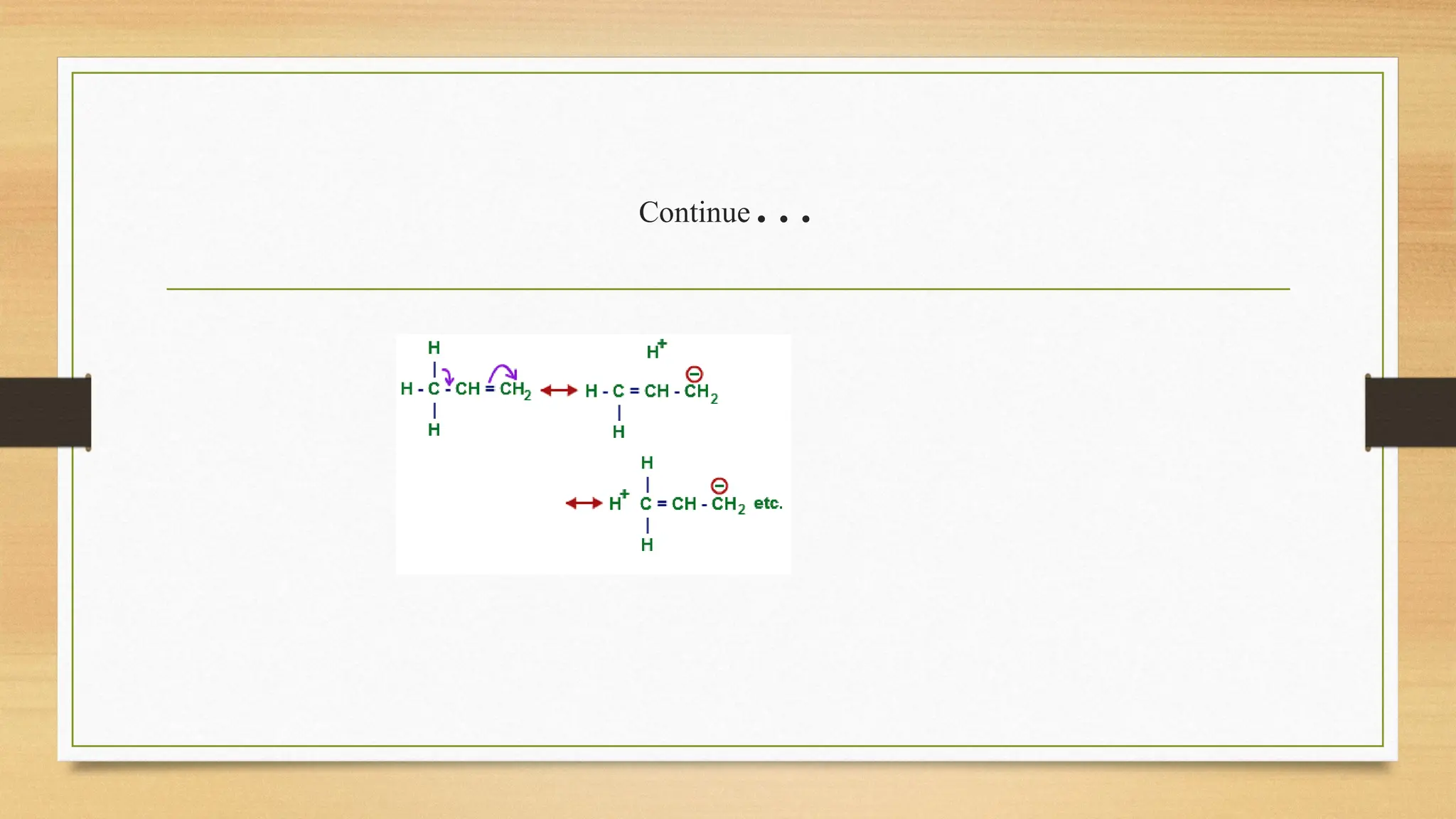
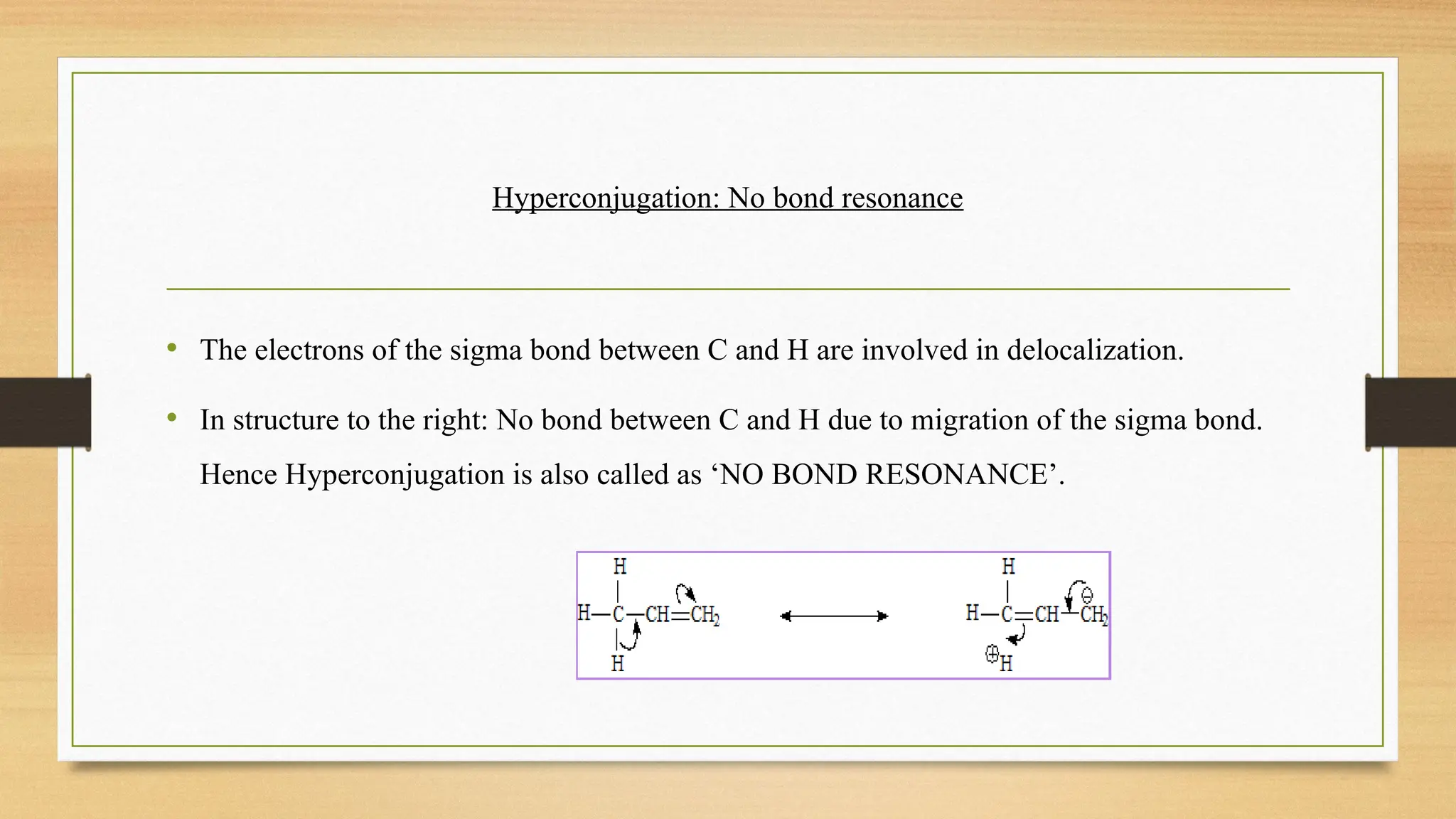
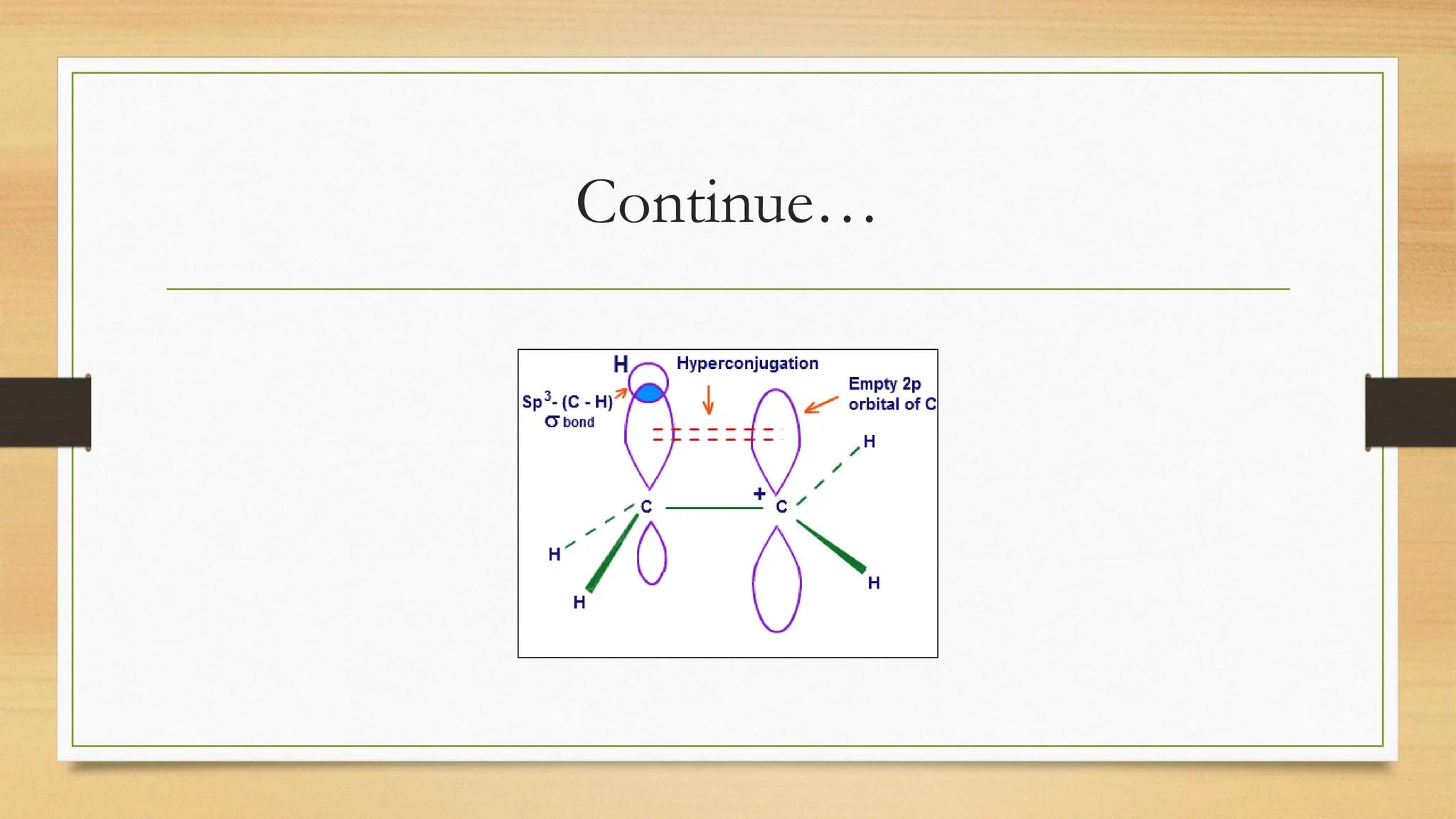
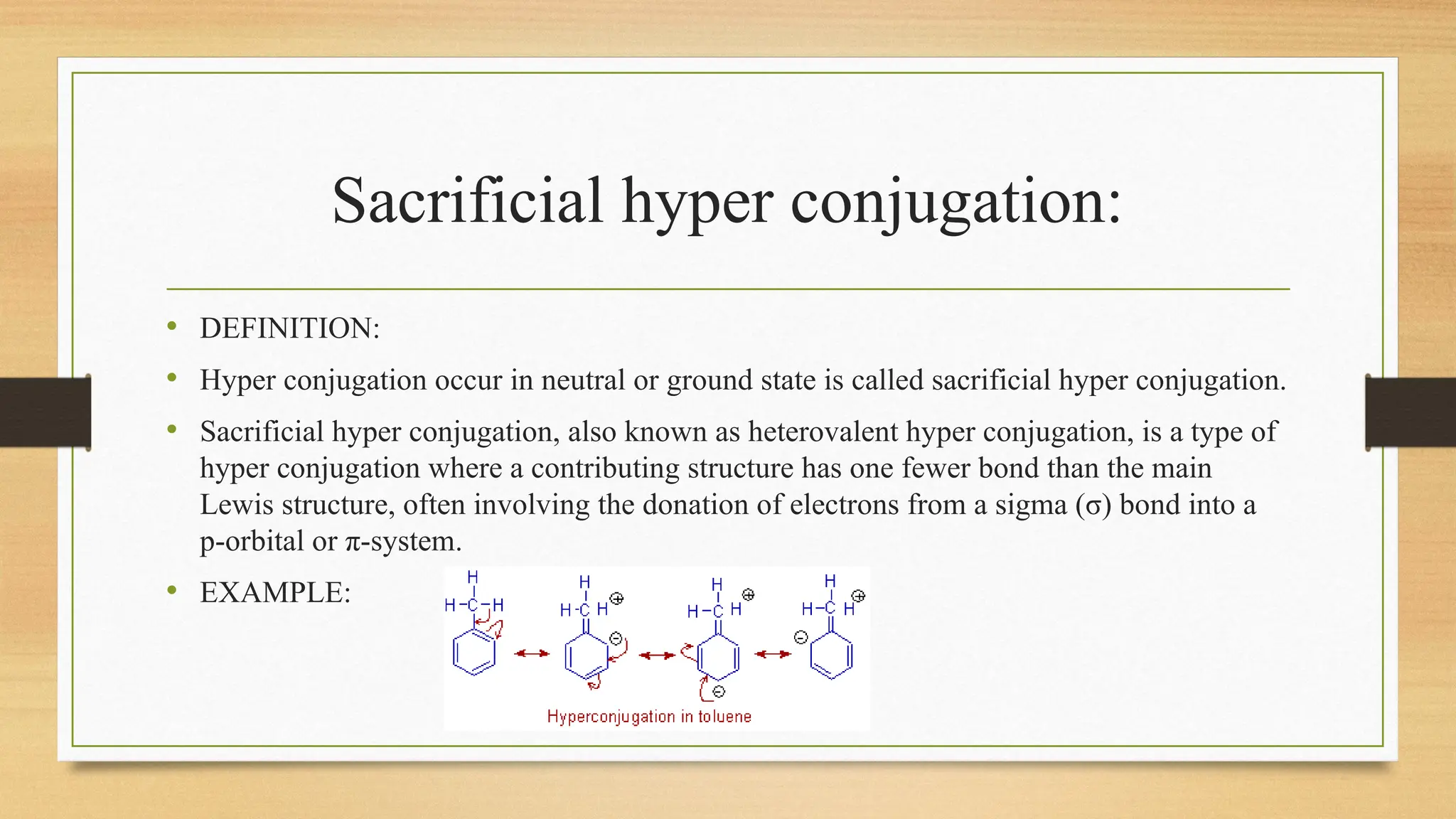
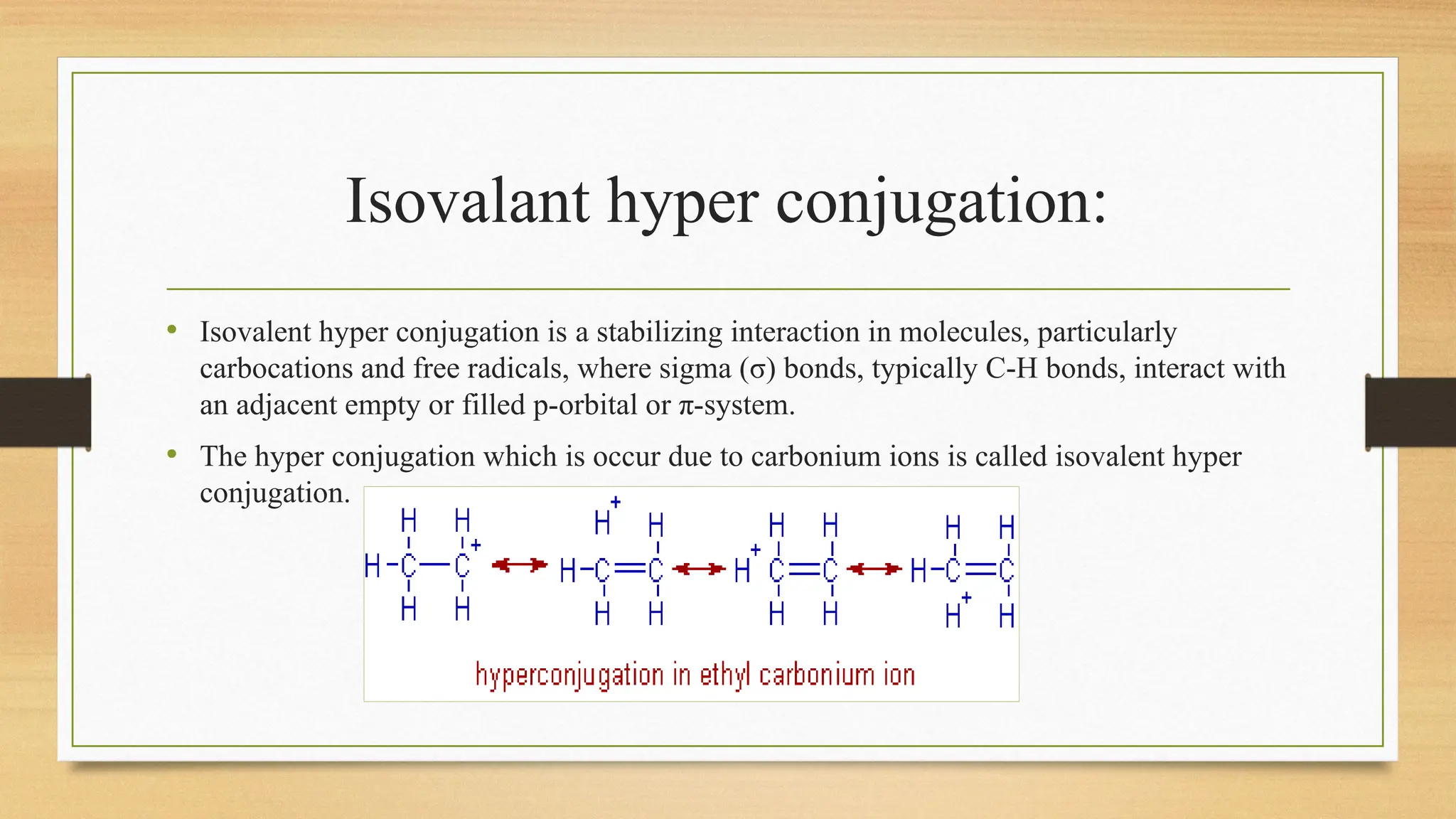
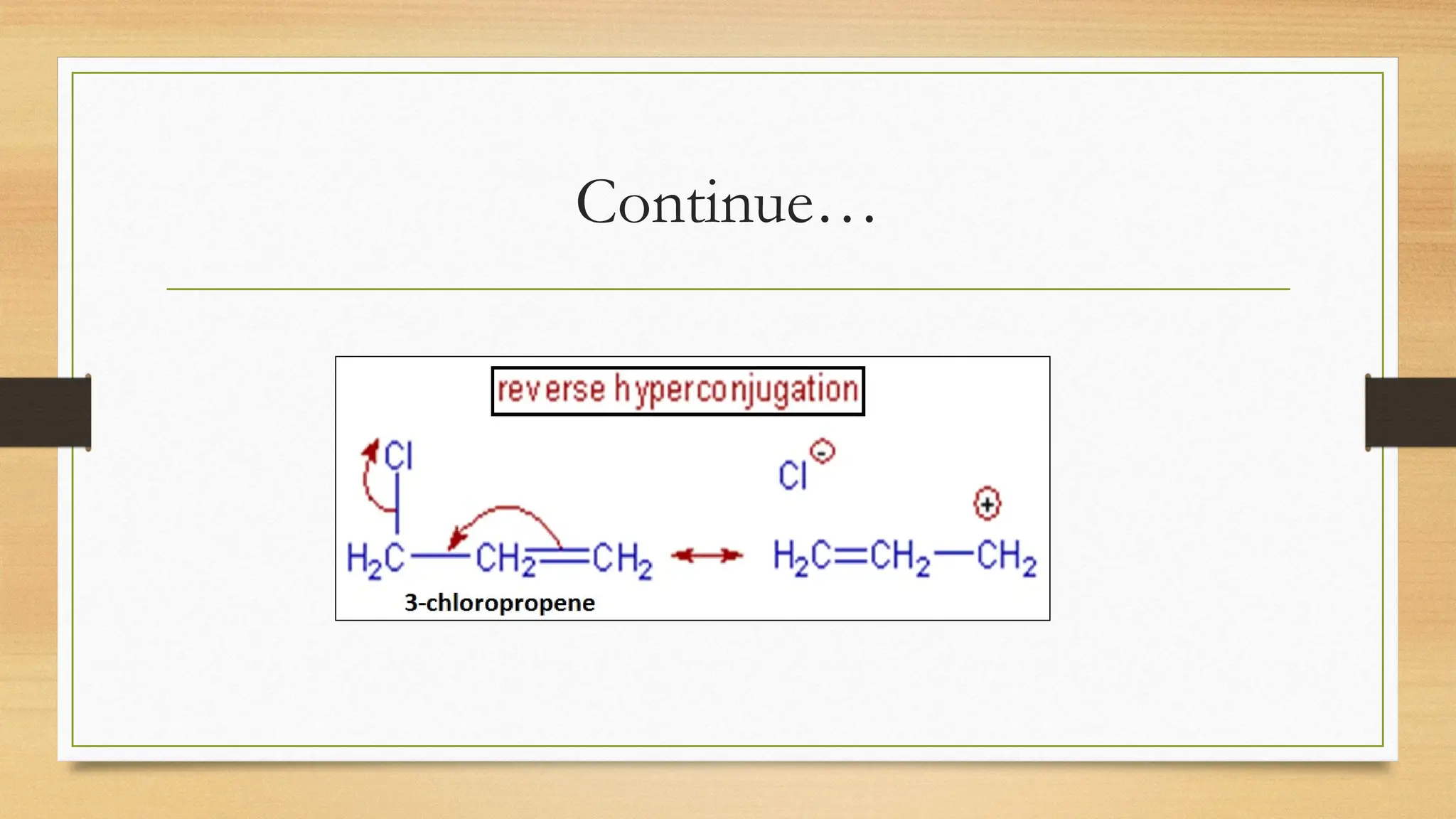
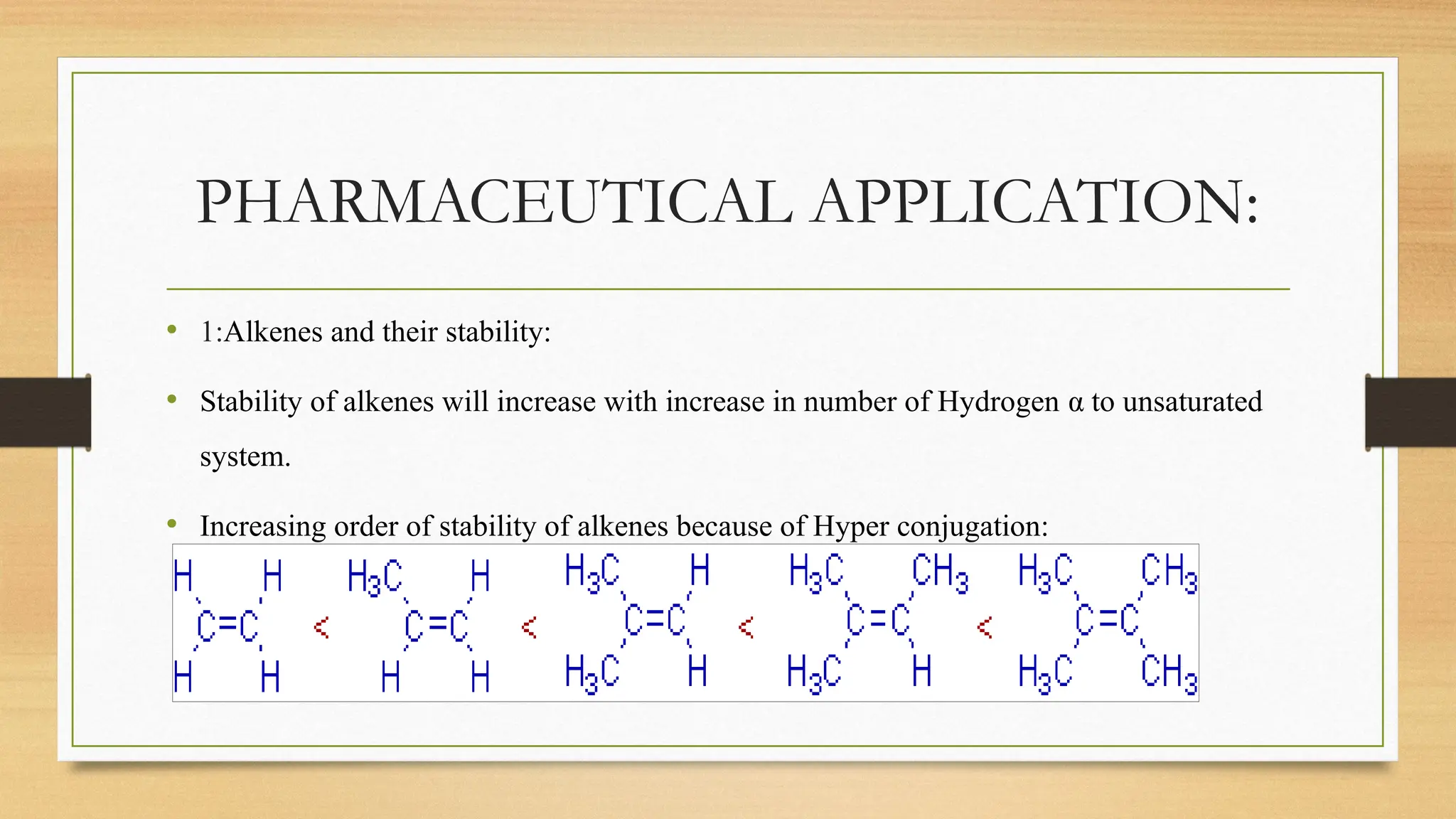
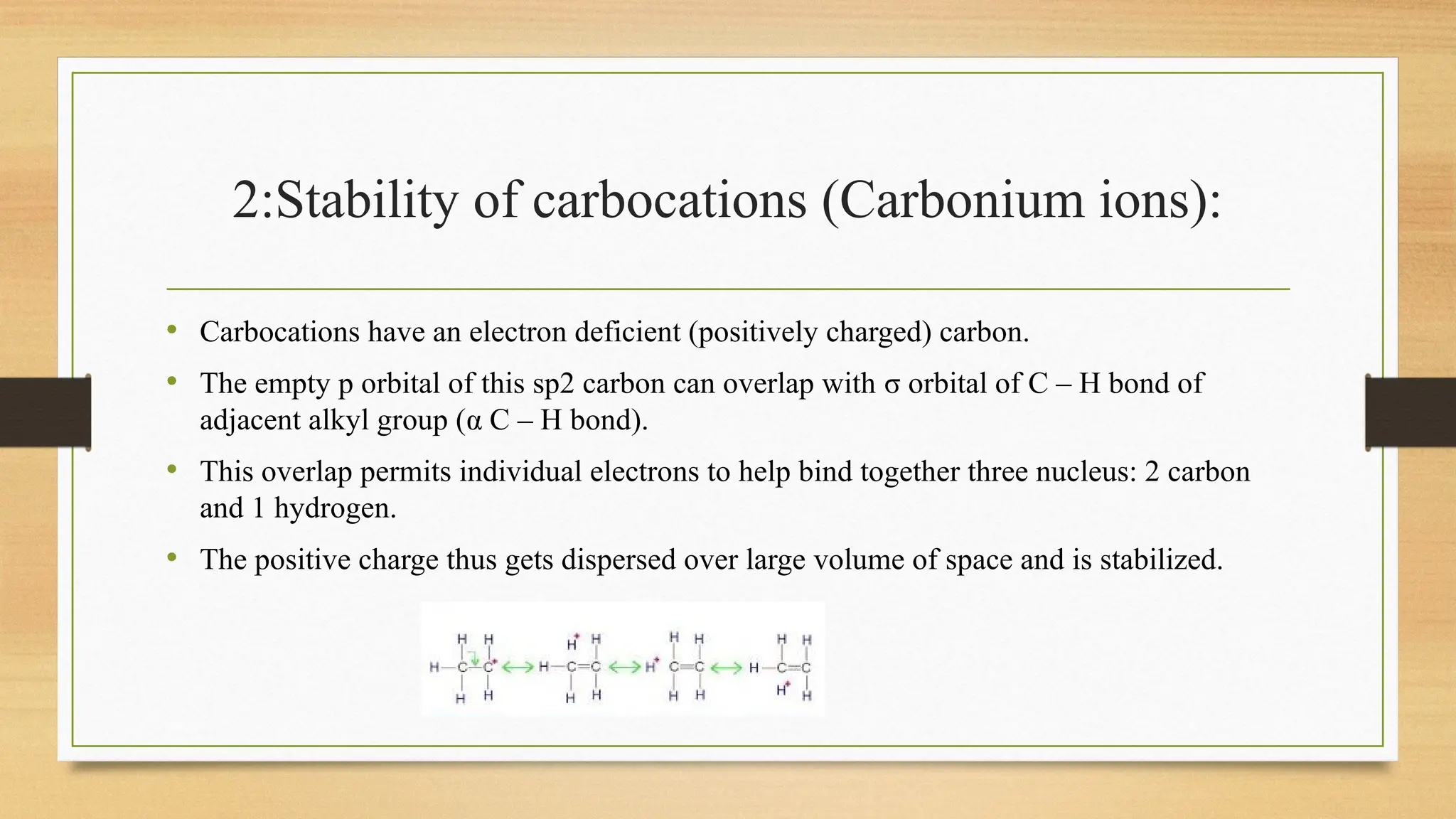
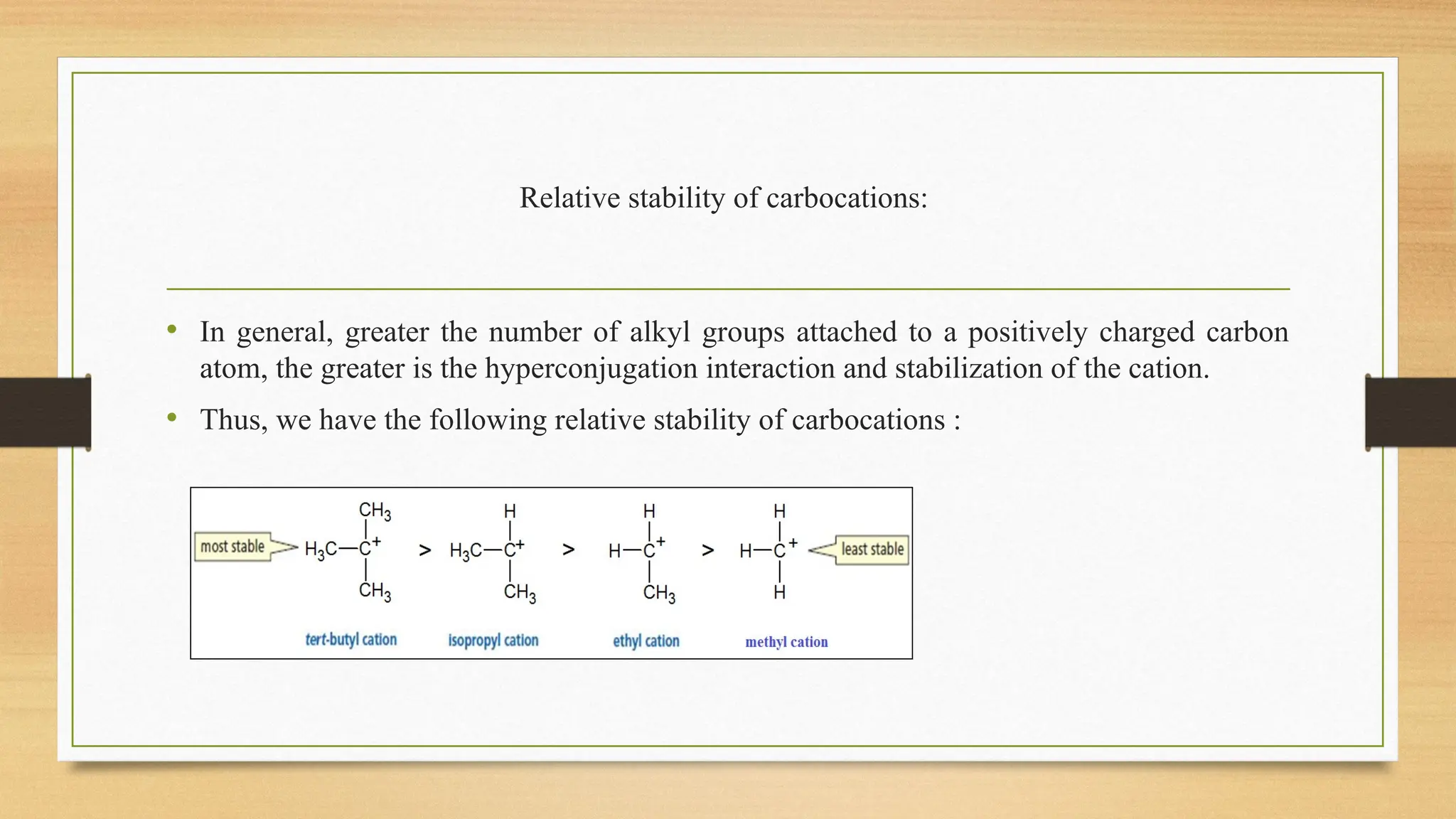
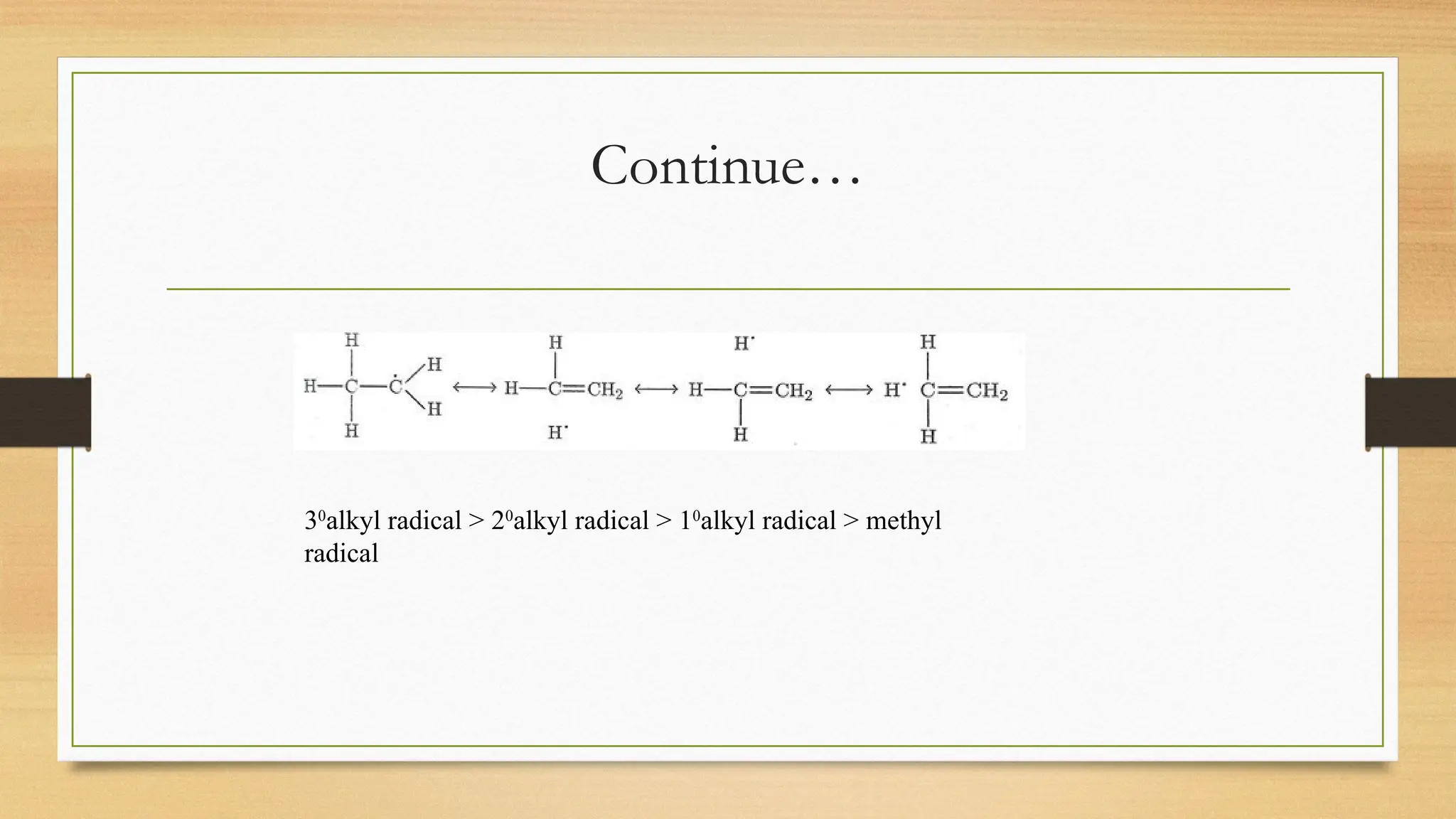
Hyperconjugation is a stabilizing interaction in organic chemistry that occurs when electrons in a sigma (σ) bond (usually C–H or C–C) interact with an adjacent empty or partially filled p-orbital or a π-orbital to increase the stability of the molecule.
🔹 Definition:
Hyperconjugation is the delocalization of electrons from a C–H or C–C sigma bond to an adjacent empty p-orbital or π-orbital, leading to molecular stability.