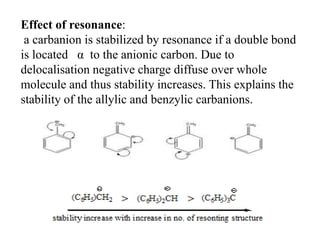
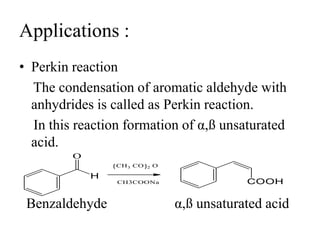
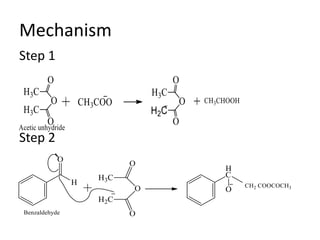
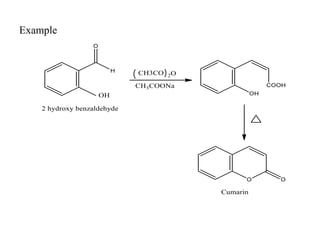
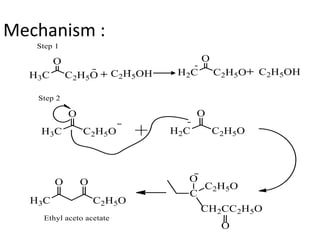
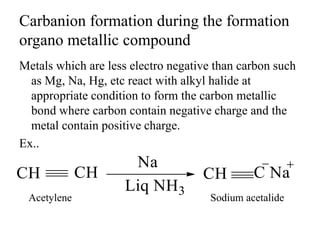
Carbanions are carbon atoms with a negative charge that are formed through various mechanisms. They can be classified based on their formation method such as through heterocyclic cleavage, proton abstraction using a base, decarboxylation, addition of a nucleophile to an alkene, or formation of an organometallic compound. Carbanion stability depends on factors like the electronegativity of the carbon, inductive effects, resonance effects, and attachment to sulfur or phosphorus. Aromatic carbanions and those with electron-withdrawing groups are particularly stable due to resonance delocalization. Carbanions have applications in reactions like the Perkin reaction, Claisen condensation, benzoin condensation,










![Inductive effect :
Stability of alkyl carbanions can be explained by
inductive effect. Greater the number of alkyl group [+
I effect] attached to the carbon atom bearing
negative charge, lesser is the stability. Because there
inductive effect increase negative charge density on
the carbon.
Primary Secondary Tertiary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/carbanions-181206094435/85/Carbanions-12-320.jpg)