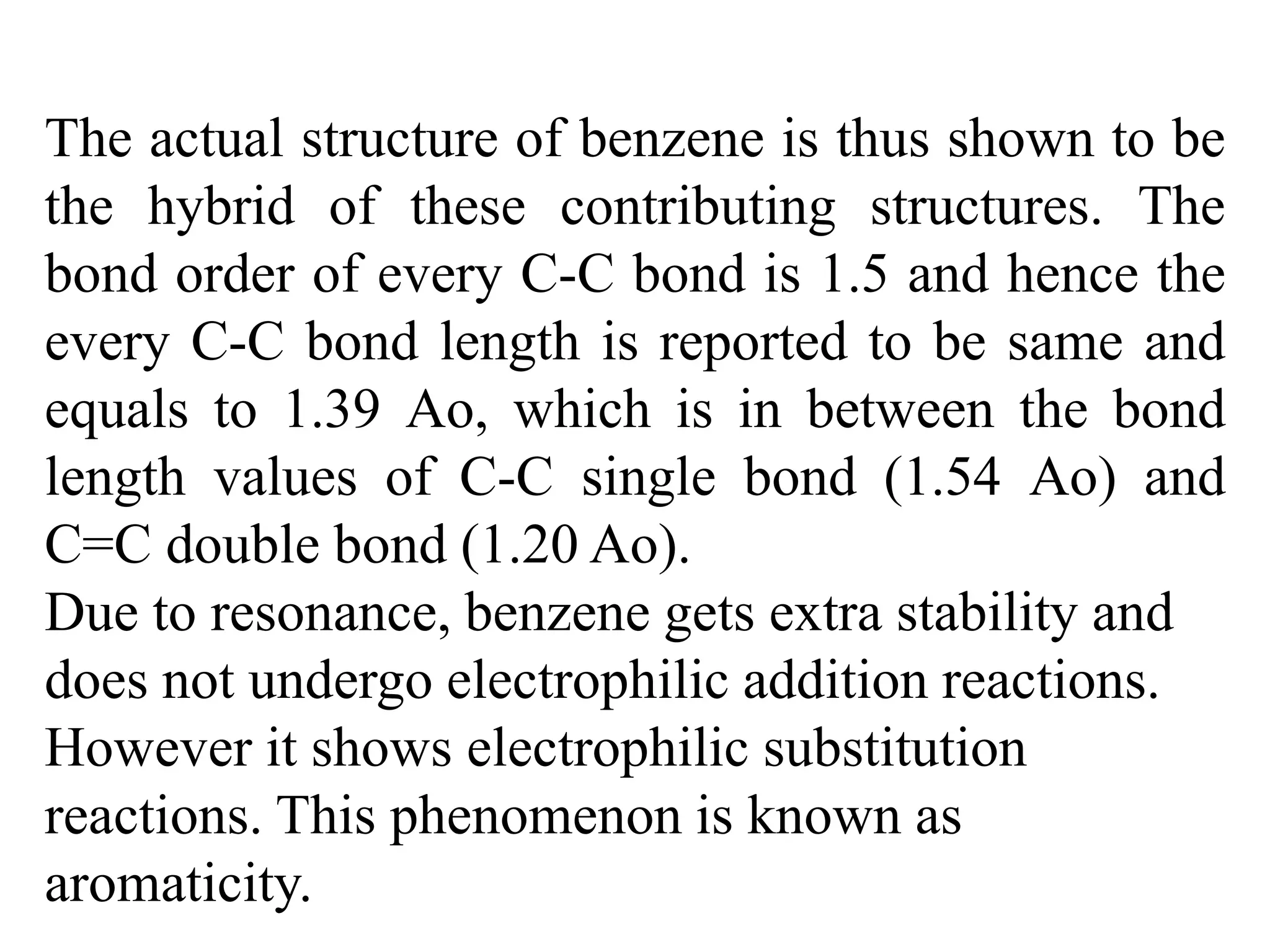
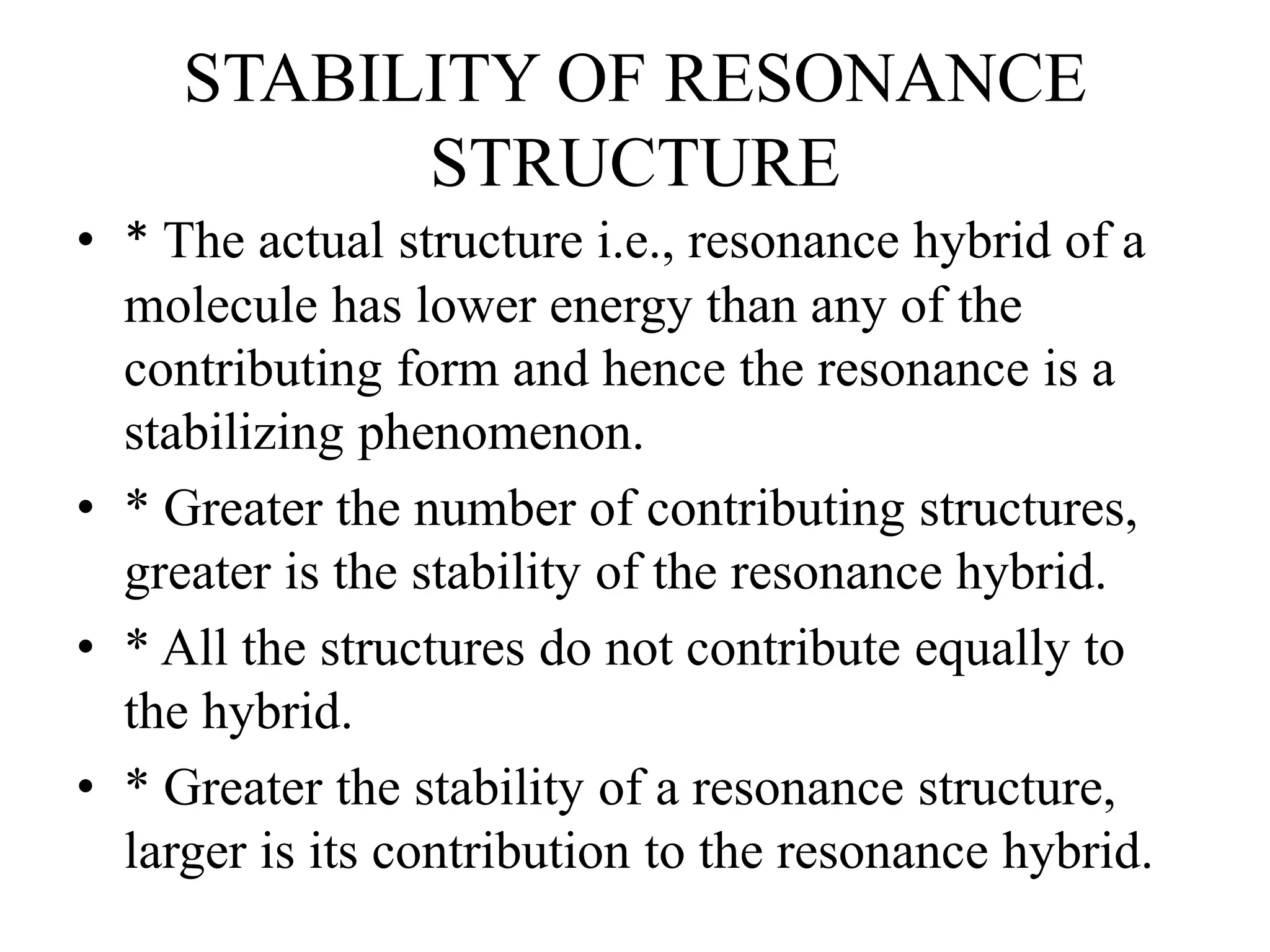
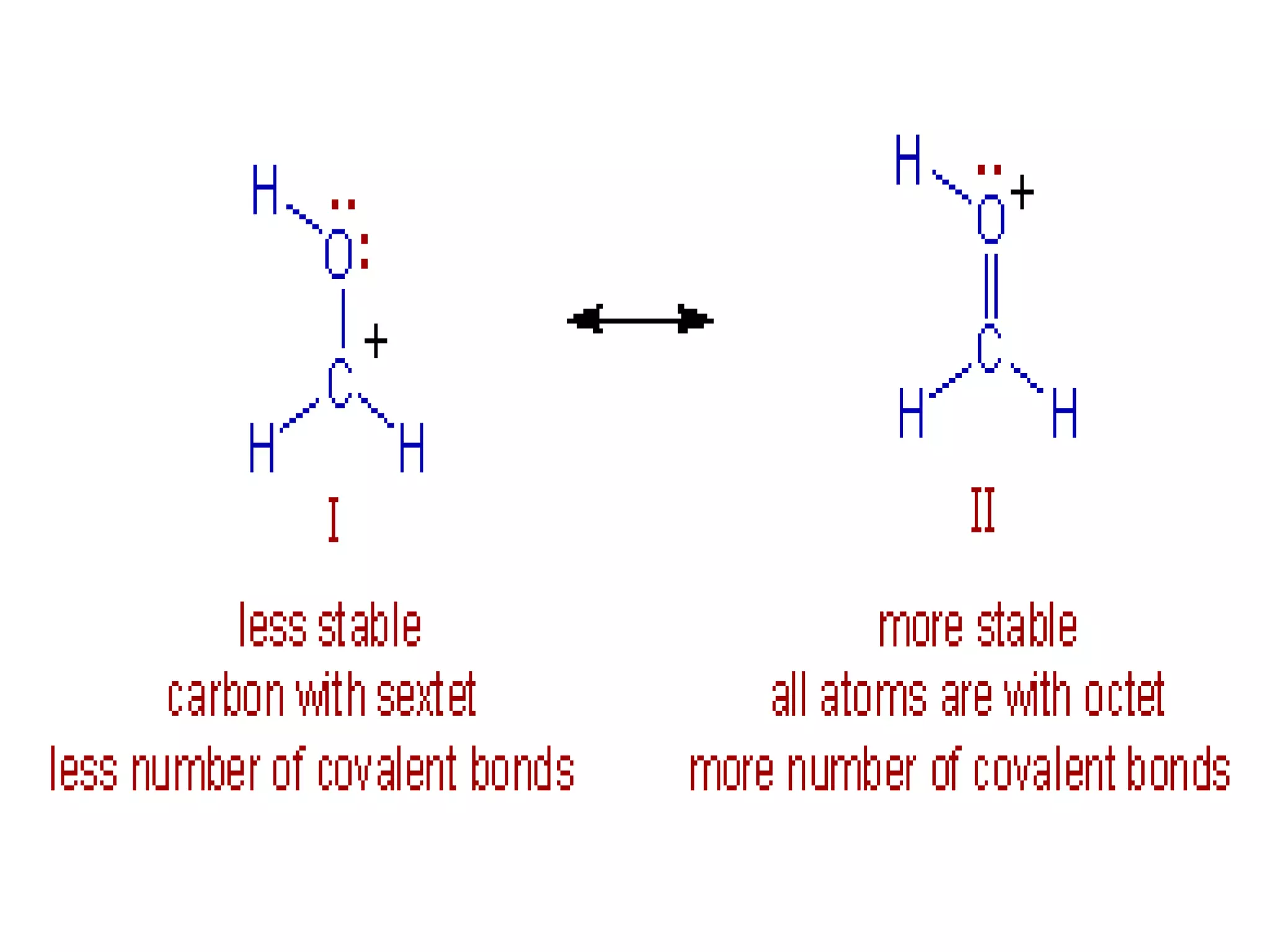
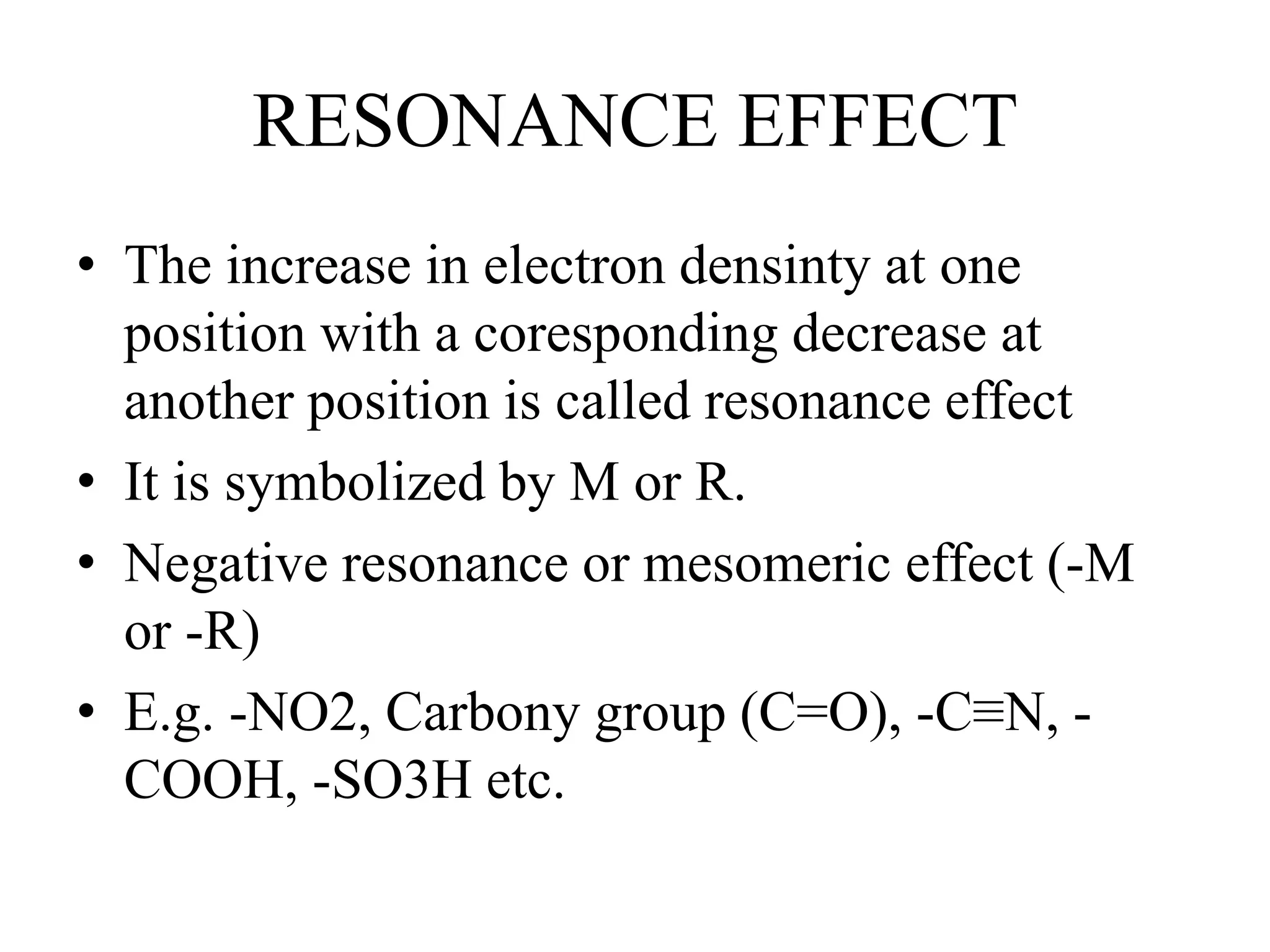
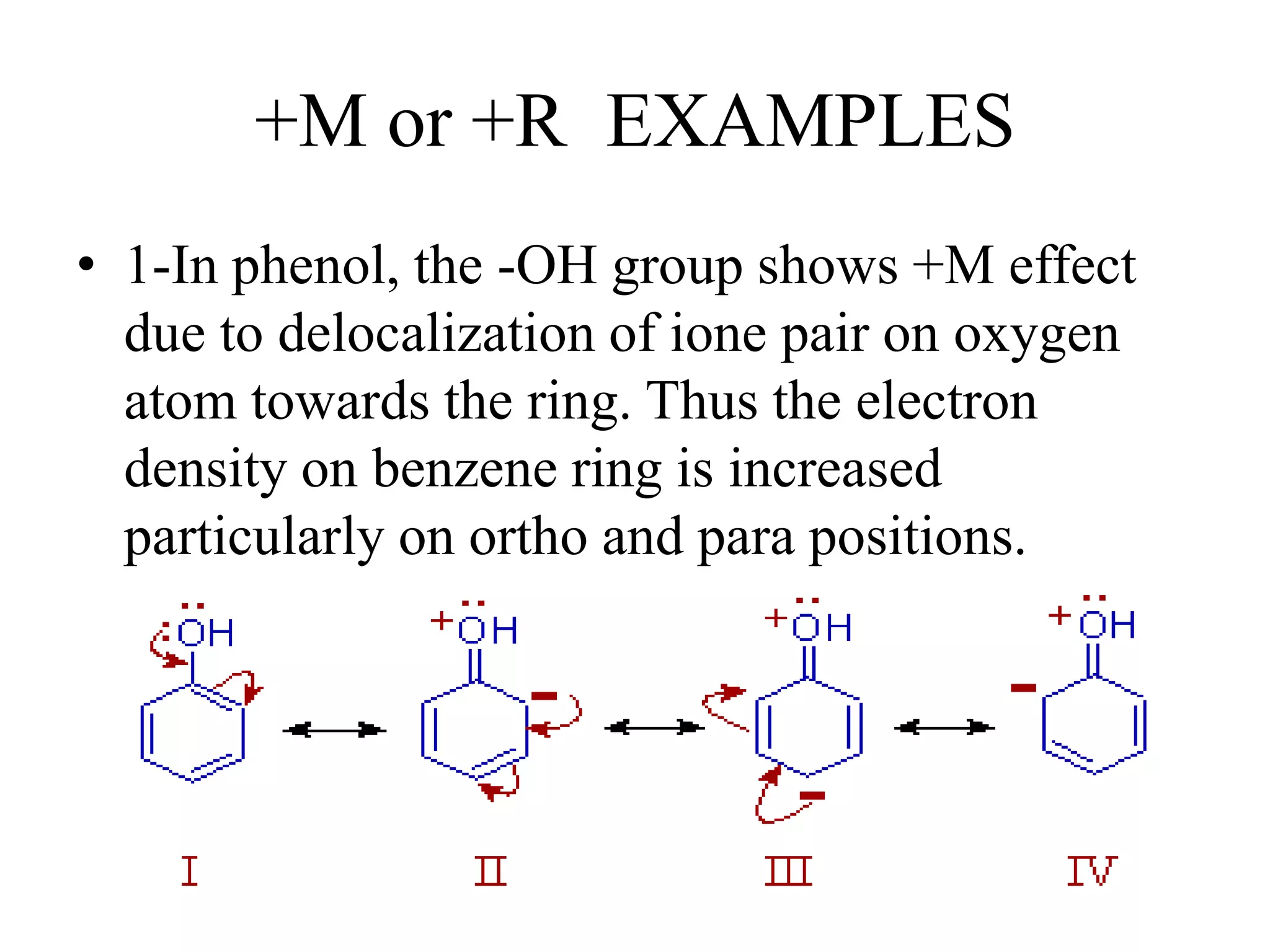
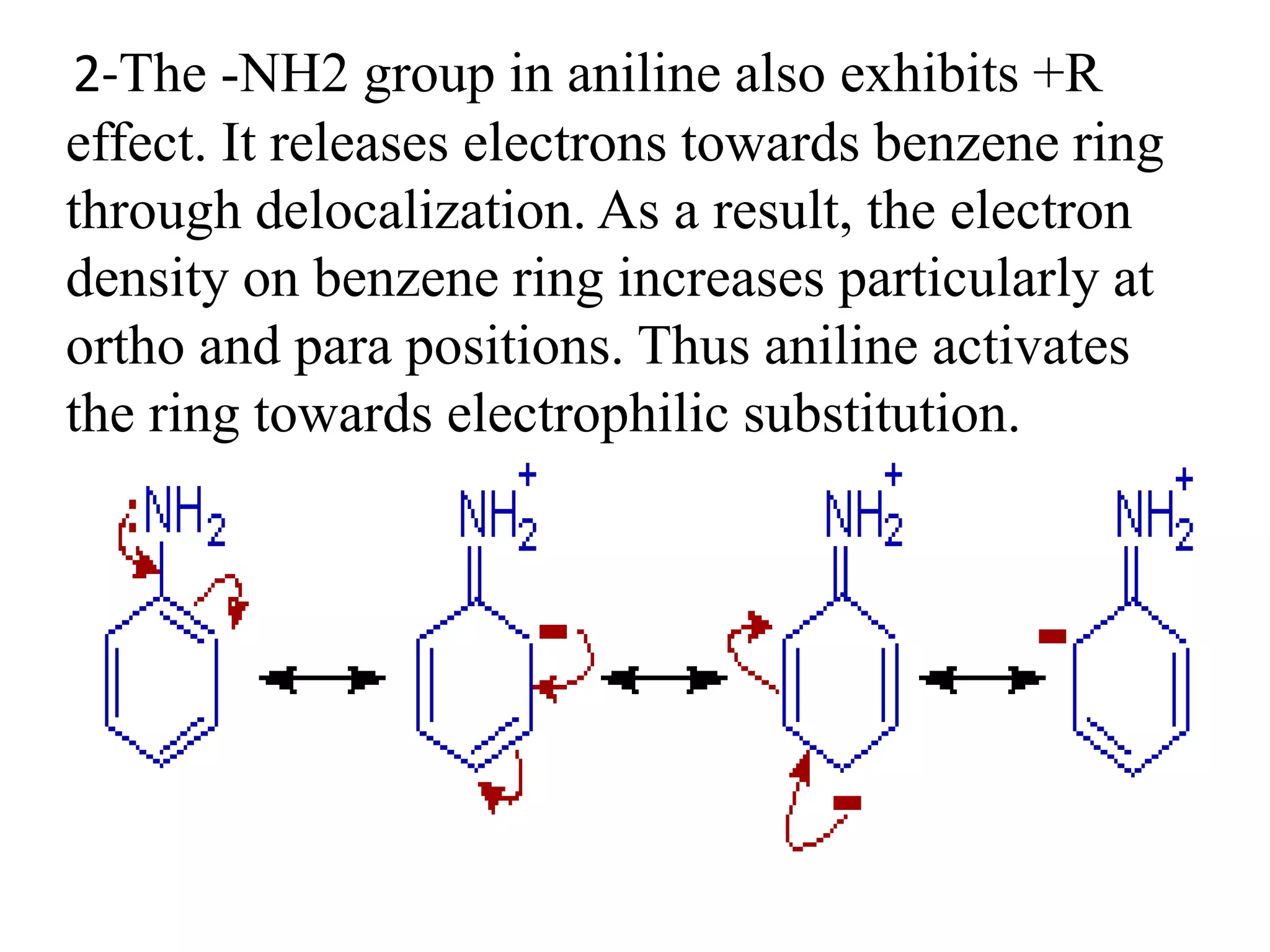
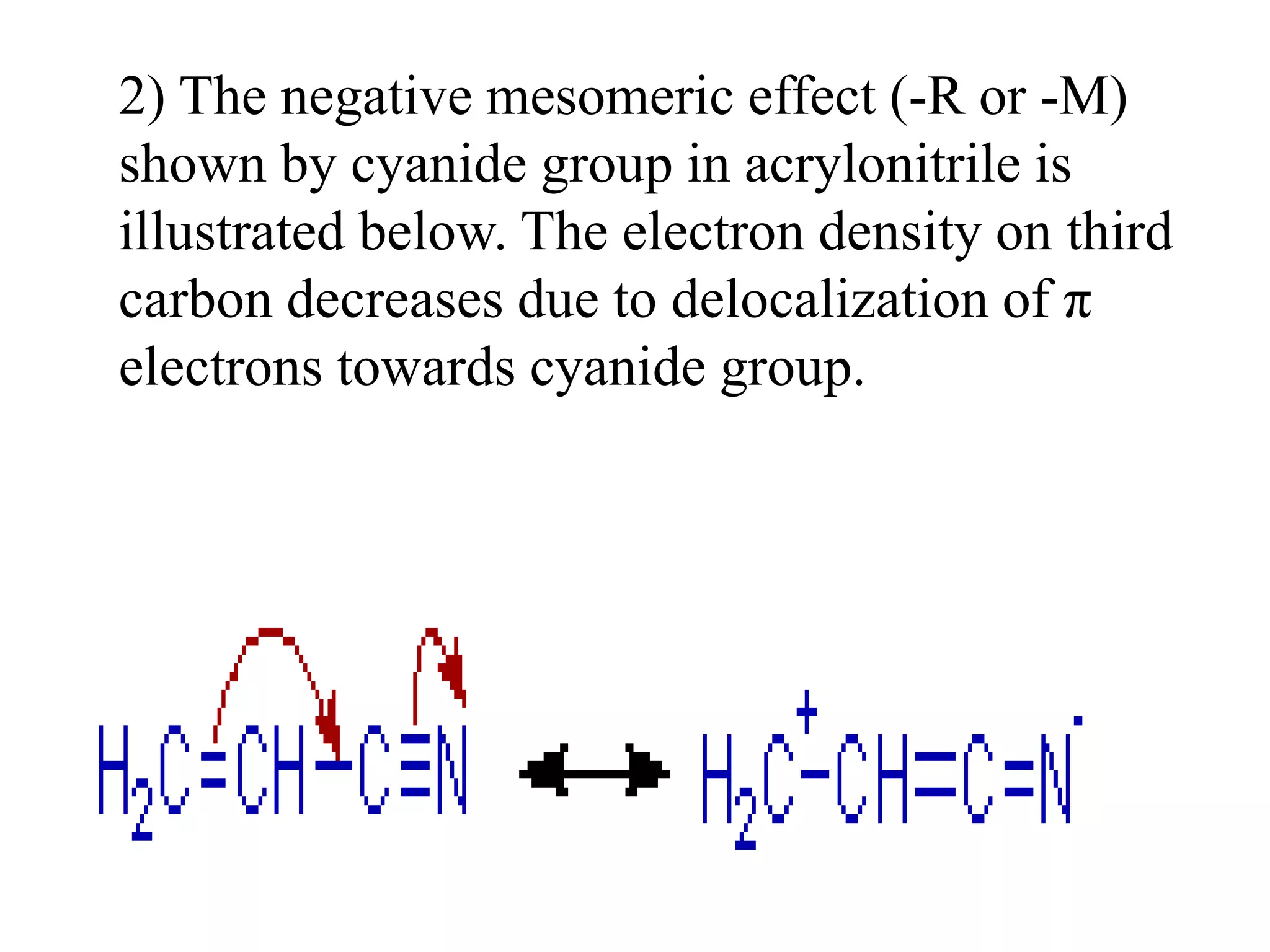
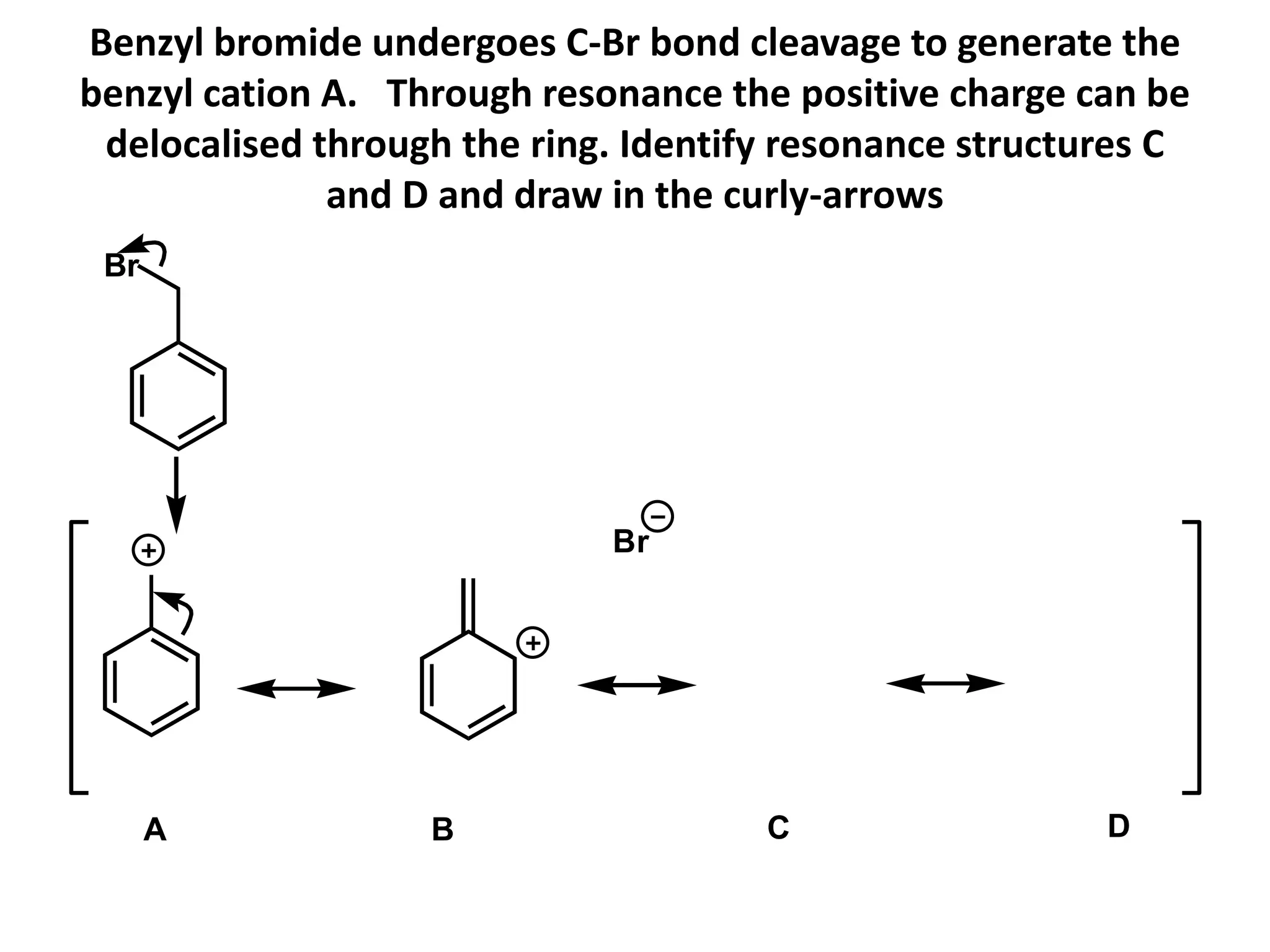
Resonance structures represent different arrangements of electrons in a molecule that have the same positions of nuclei but different bonding patterns. Resonance contributes to the stability of molecules like benzene by delocalizing electrons across multiple equivalent structures. The actual structure of a molecule represented by resonance is a hybrid of the contributing structures, with bond lengths intermediate between single and double bonds. Delocalization of electrons is depicted using curved arrows between resonance structures.