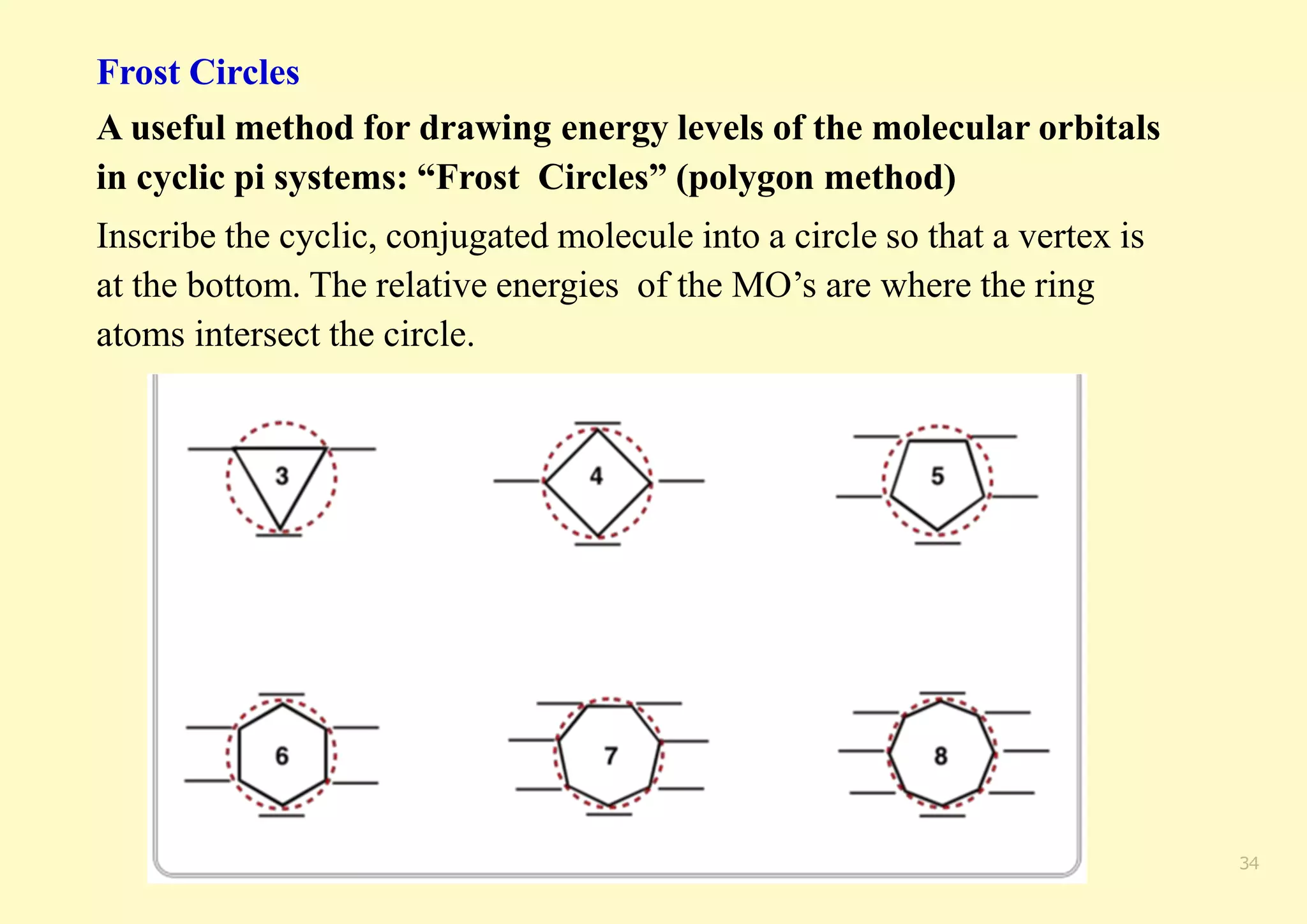
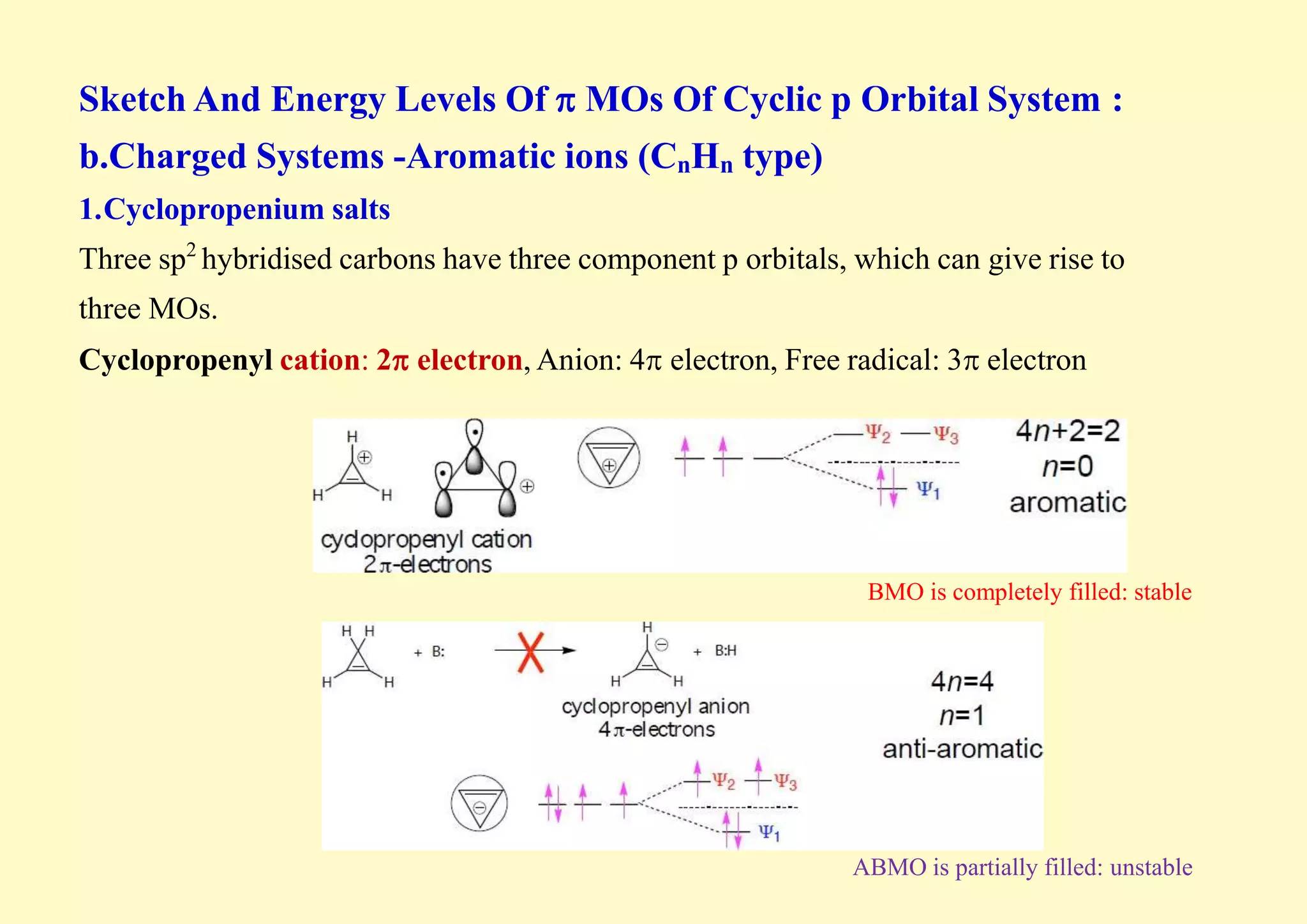
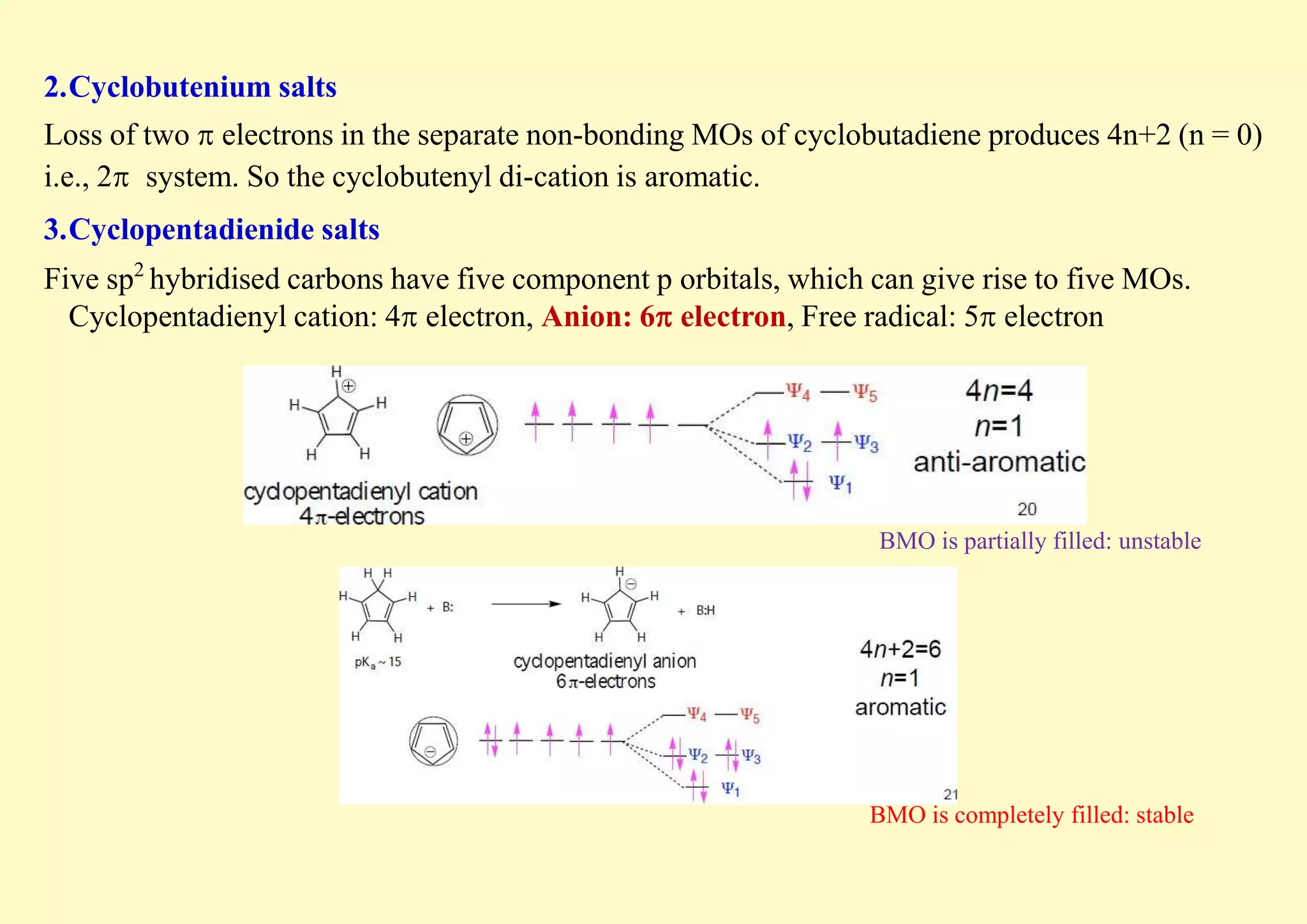
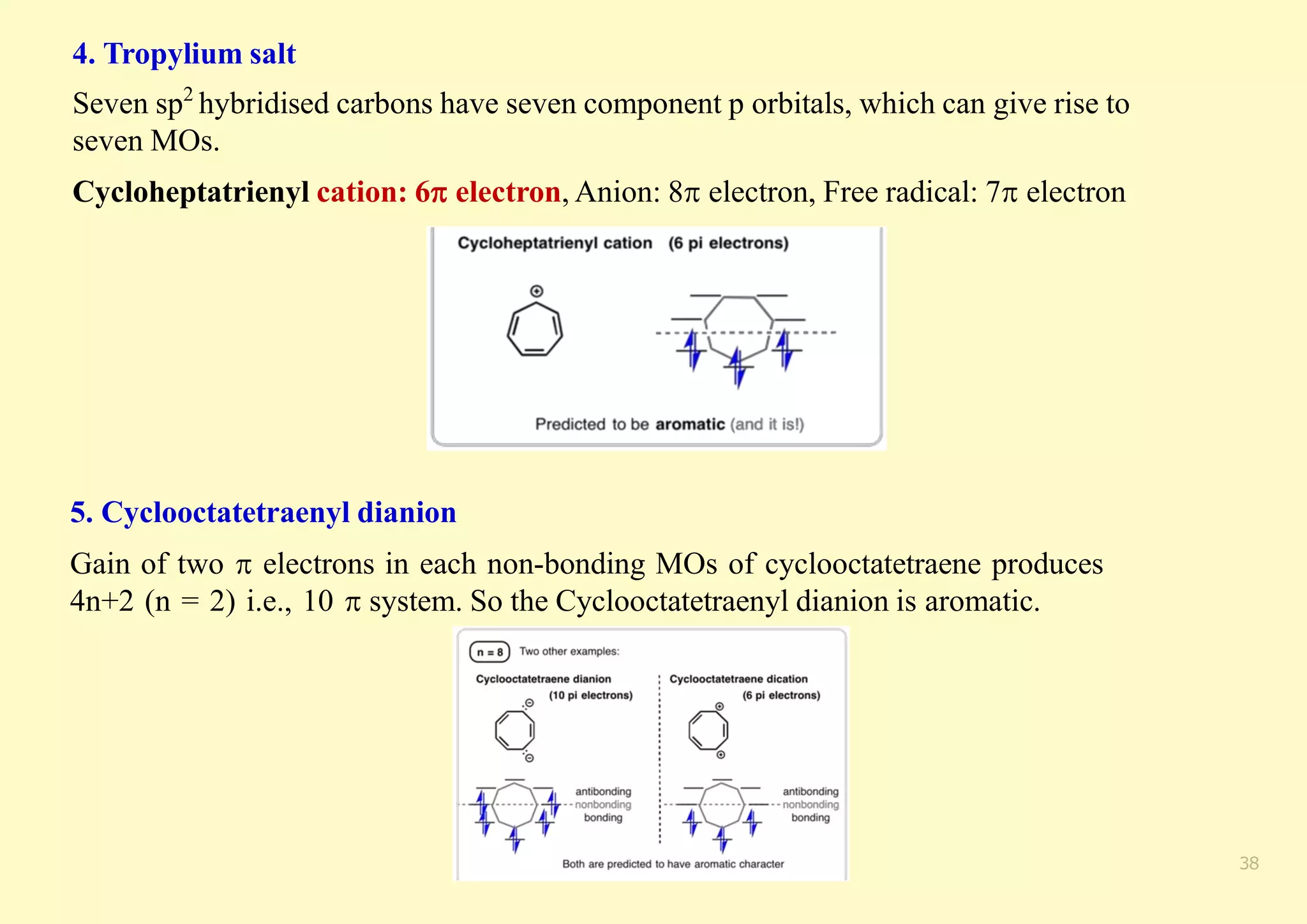
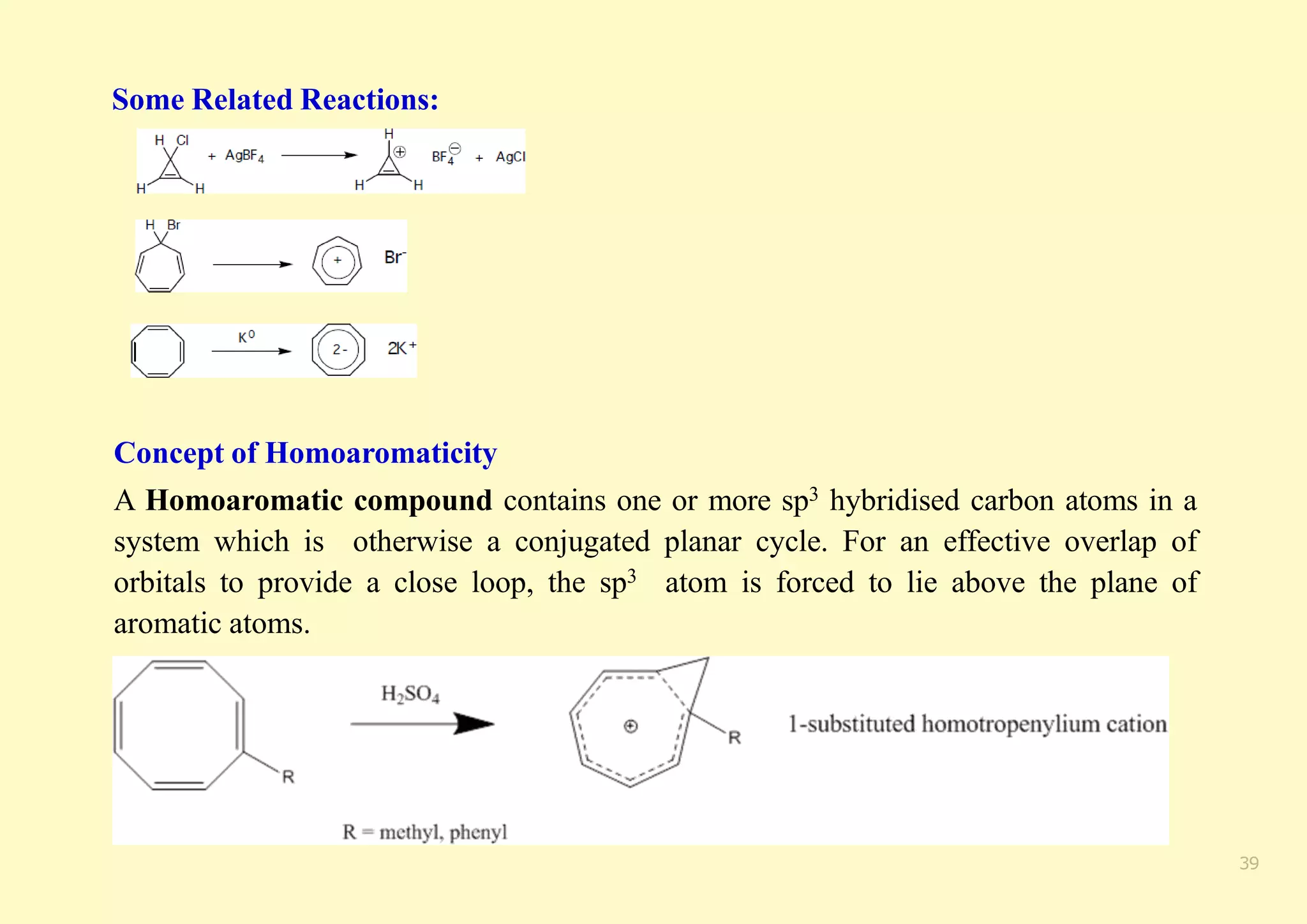
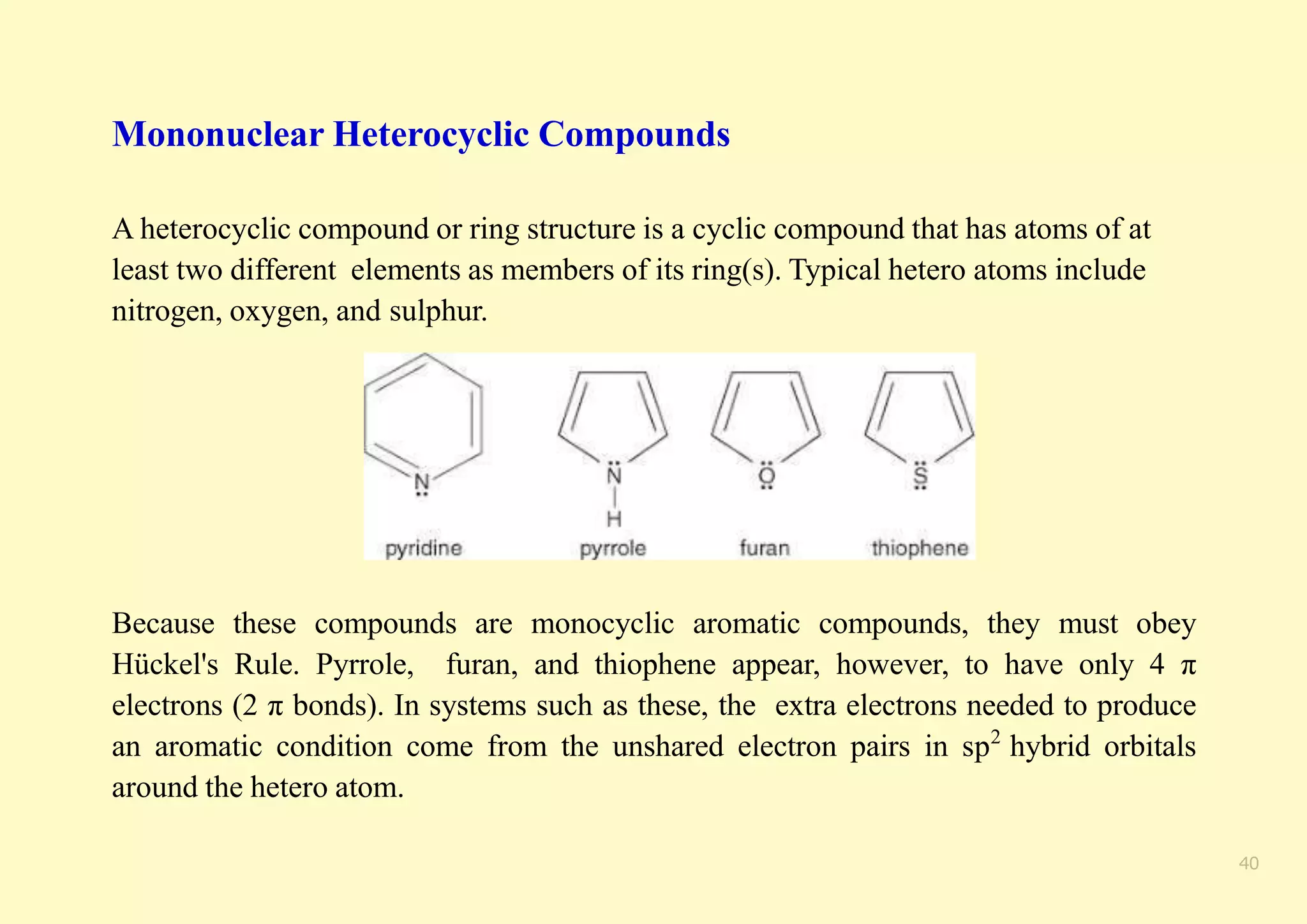
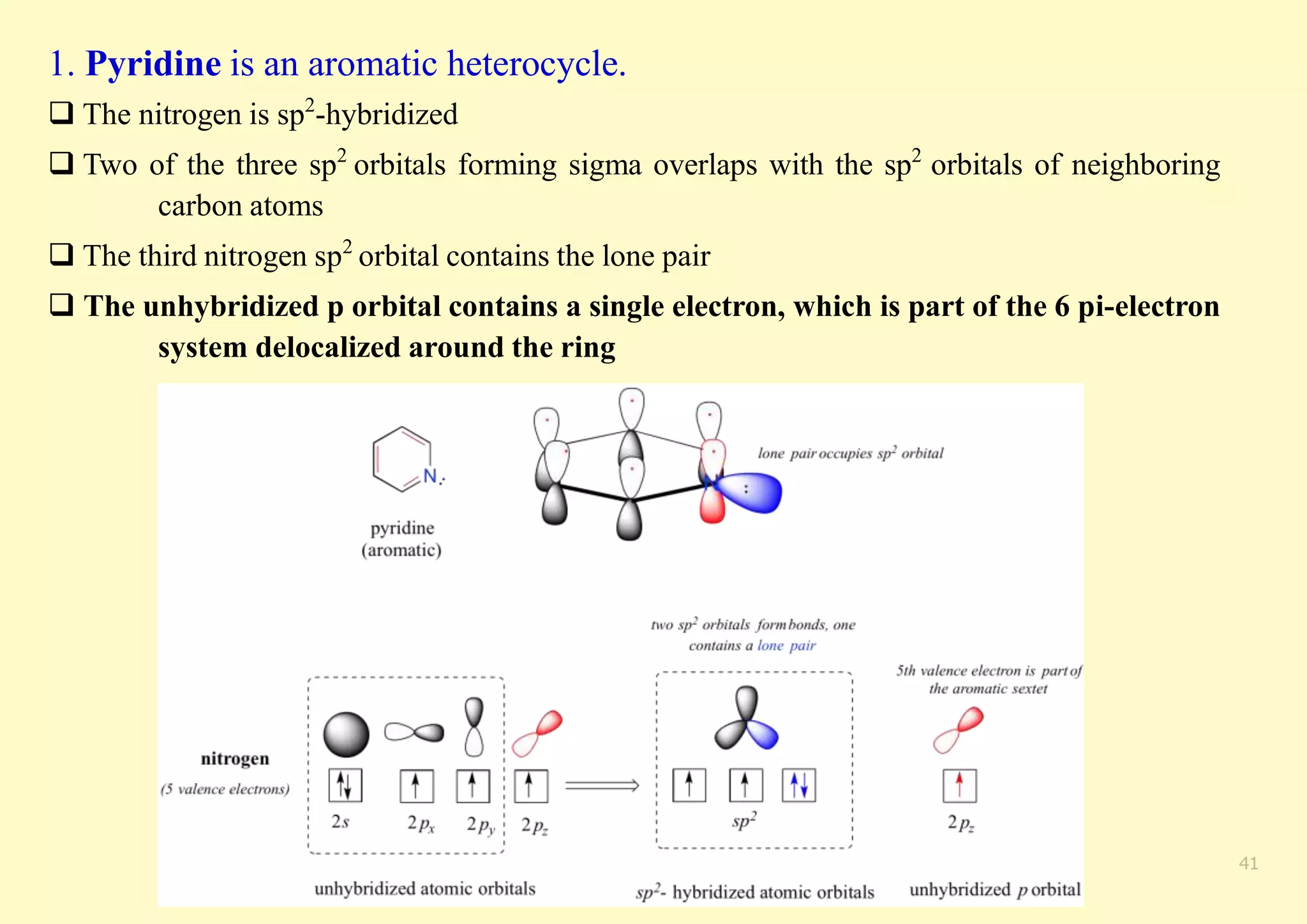
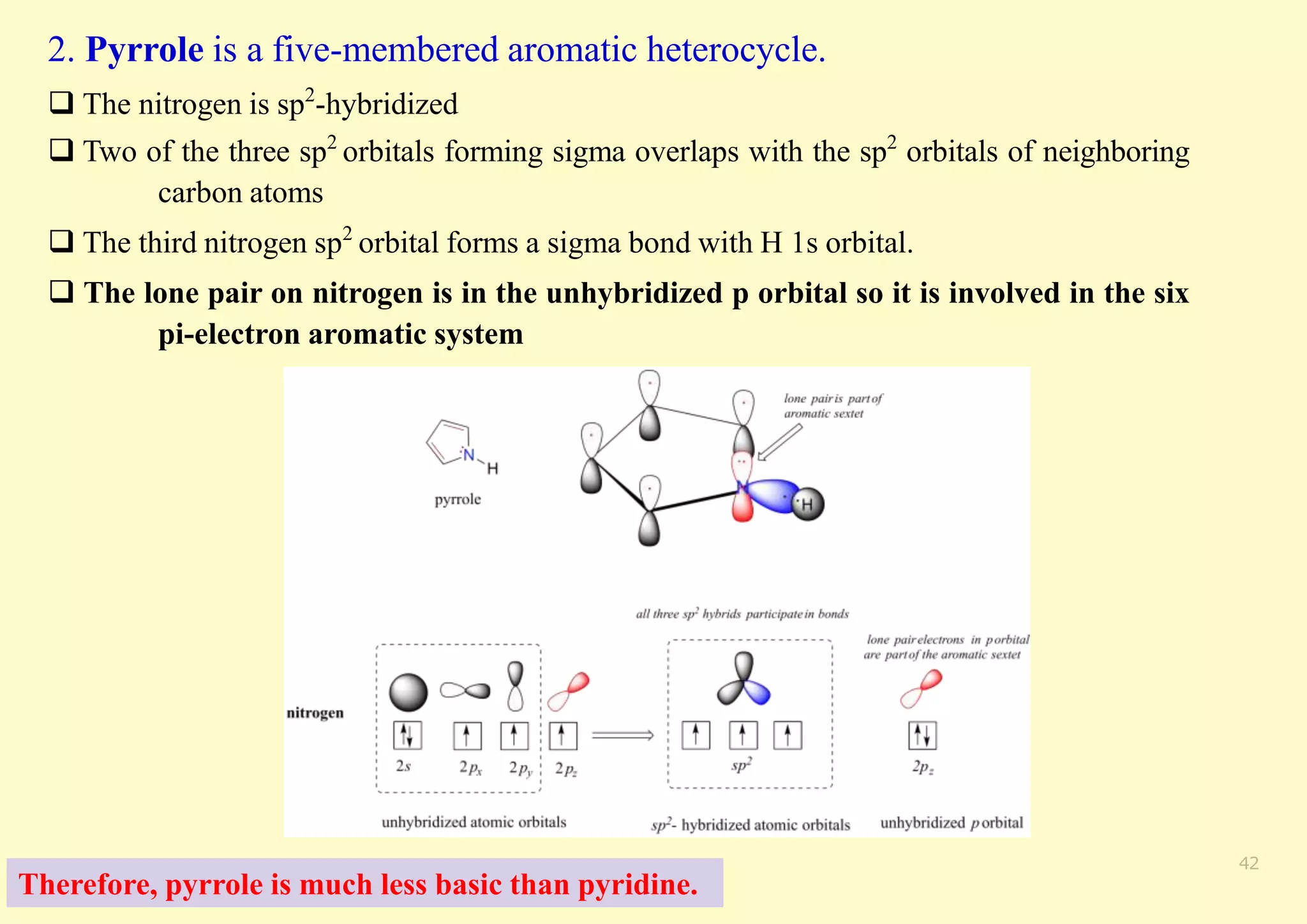
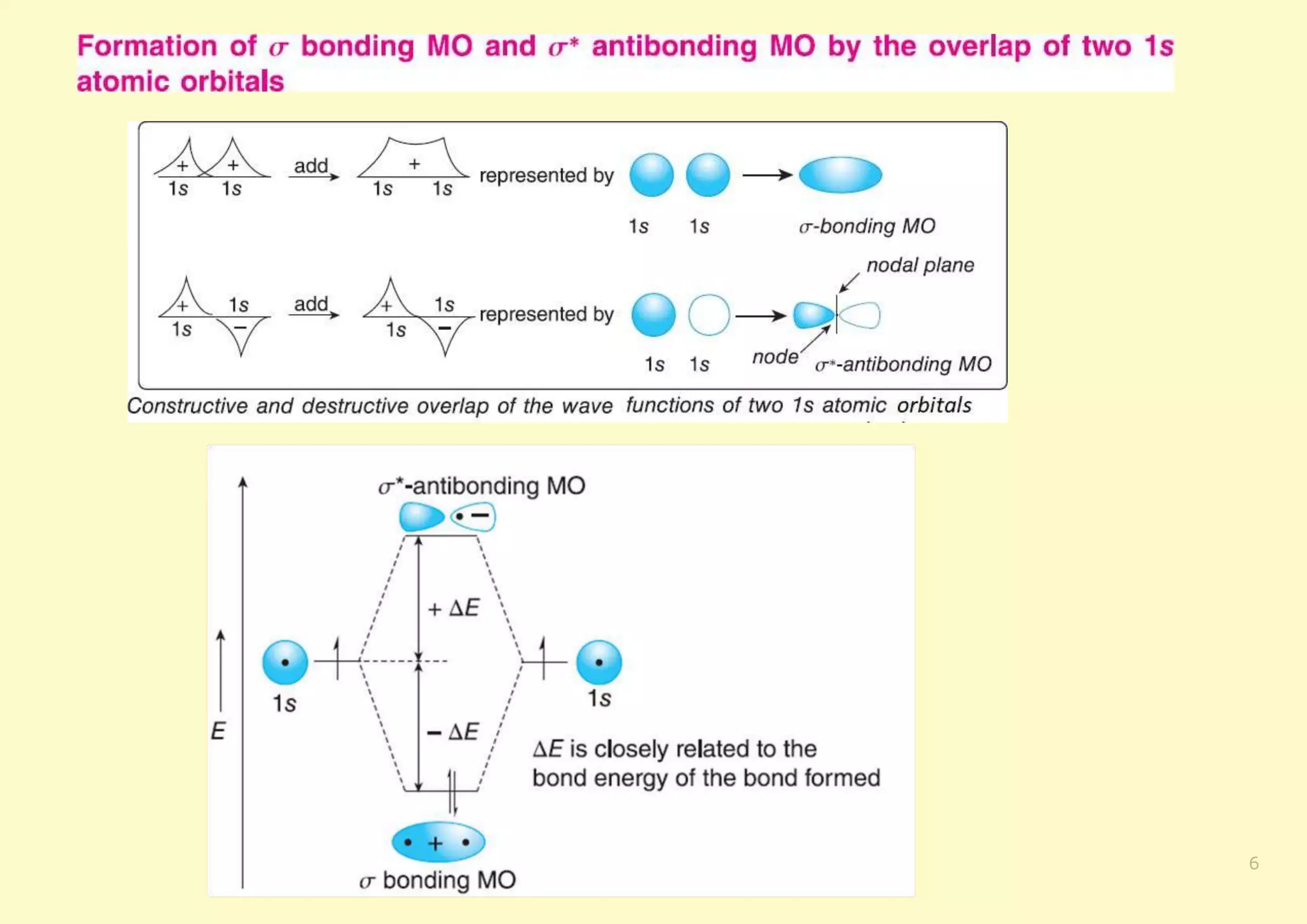
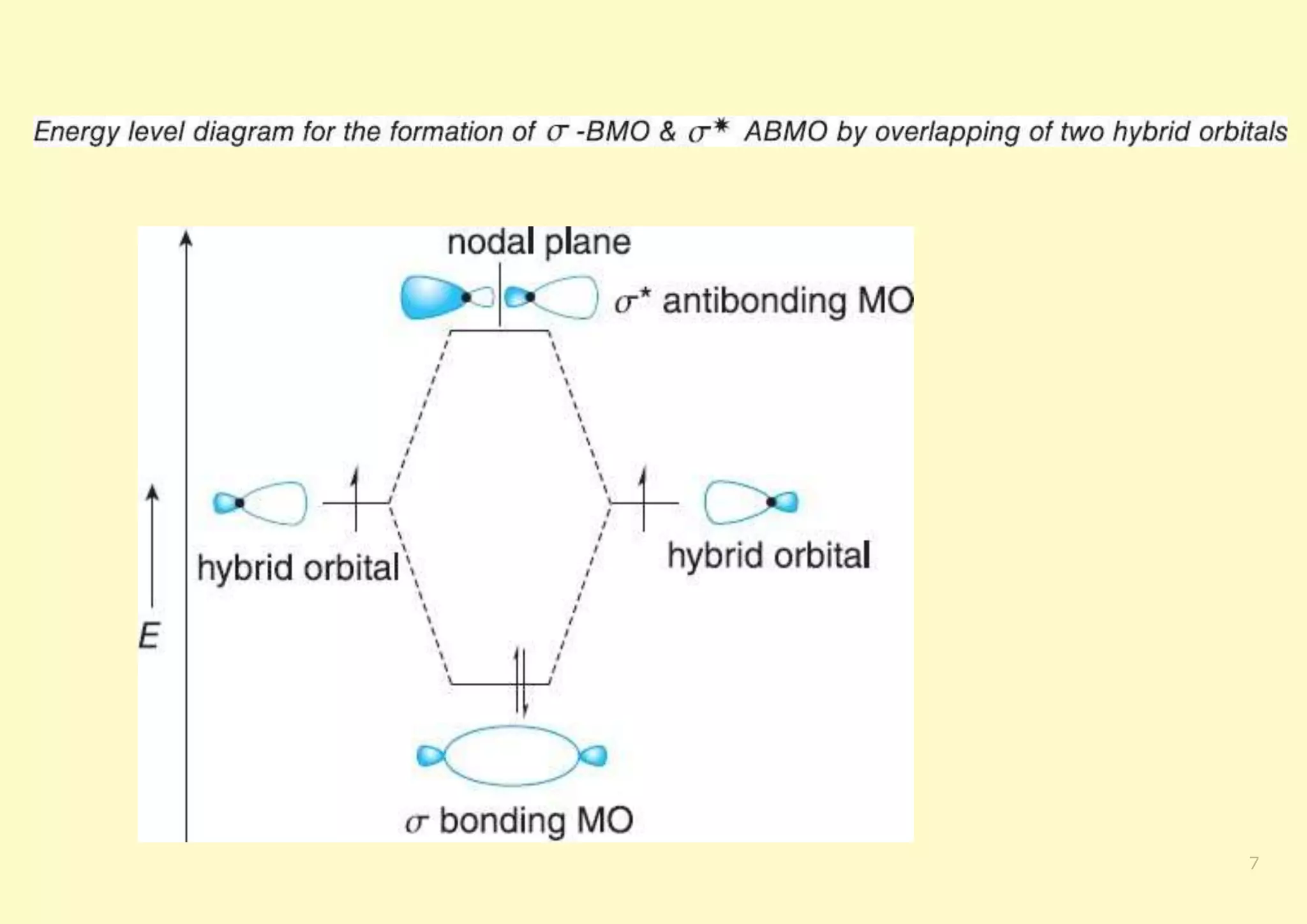
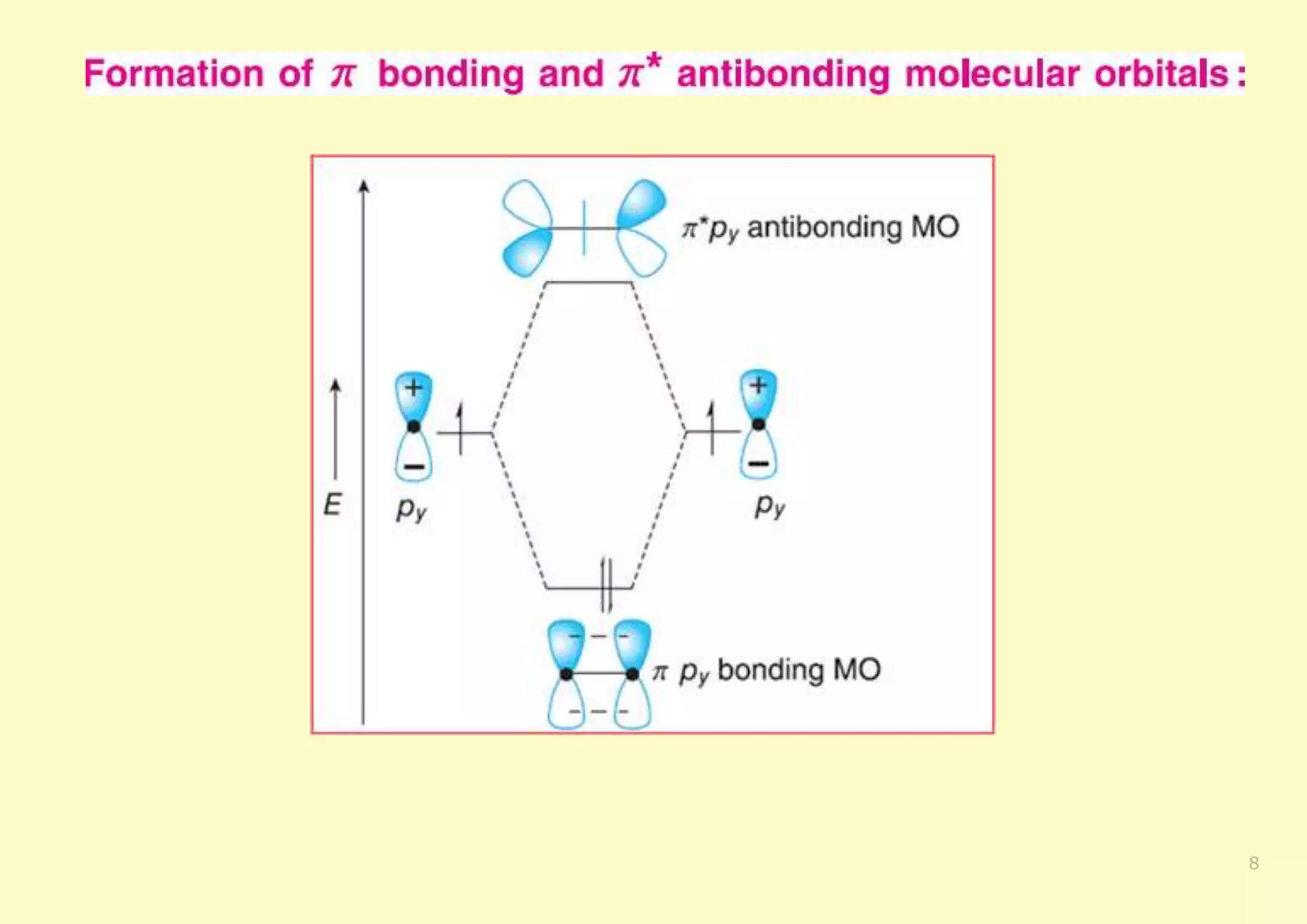
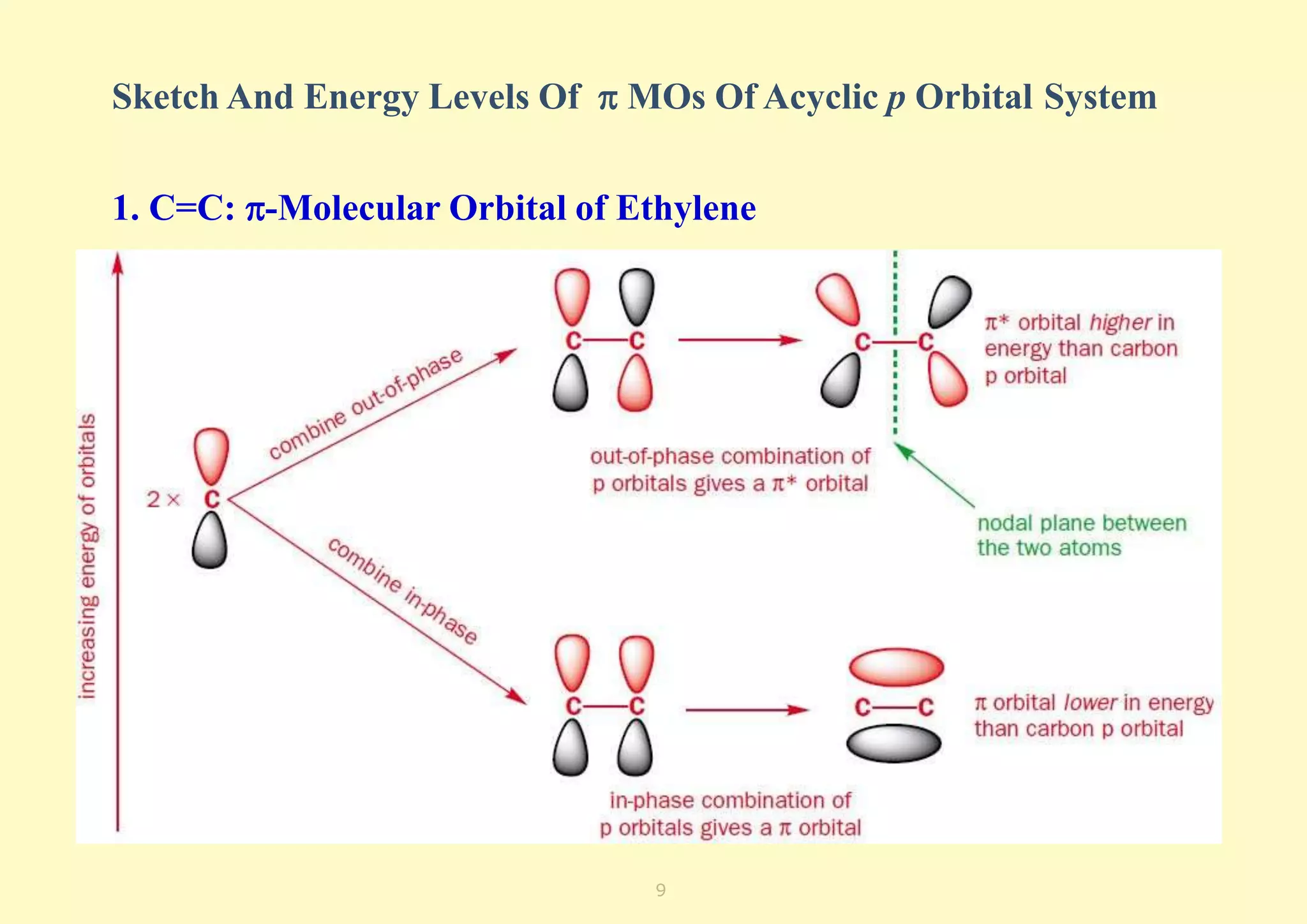
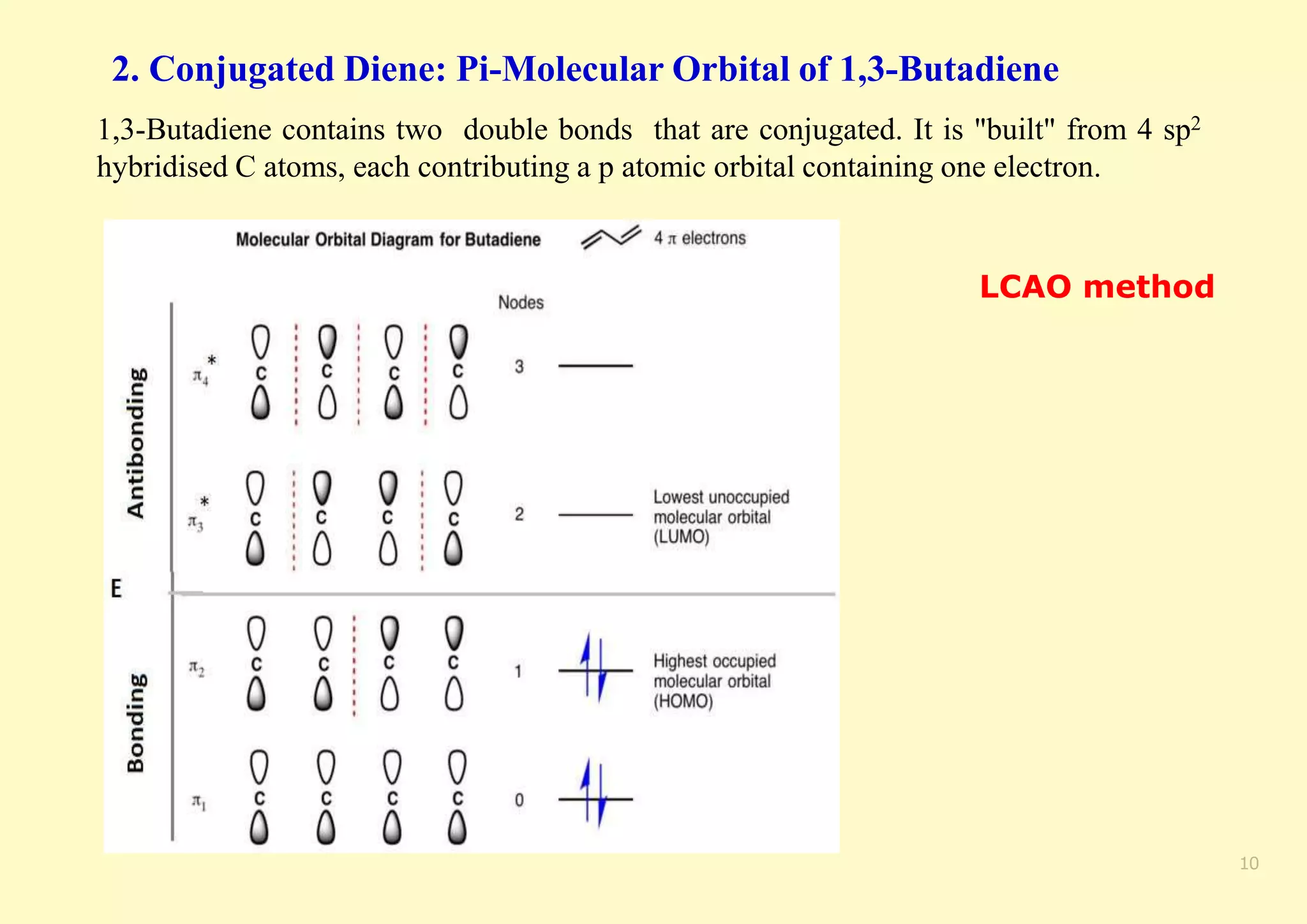
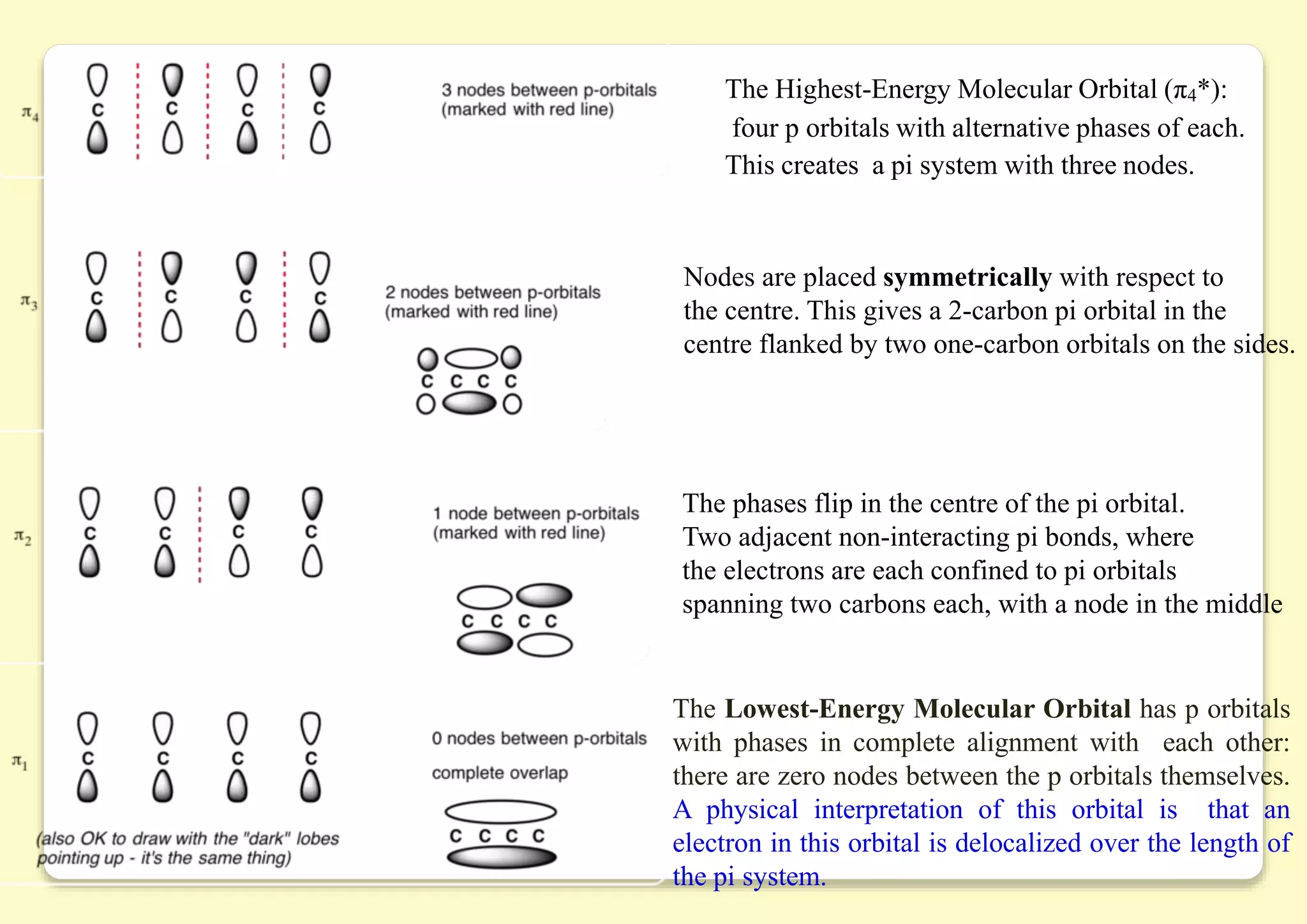
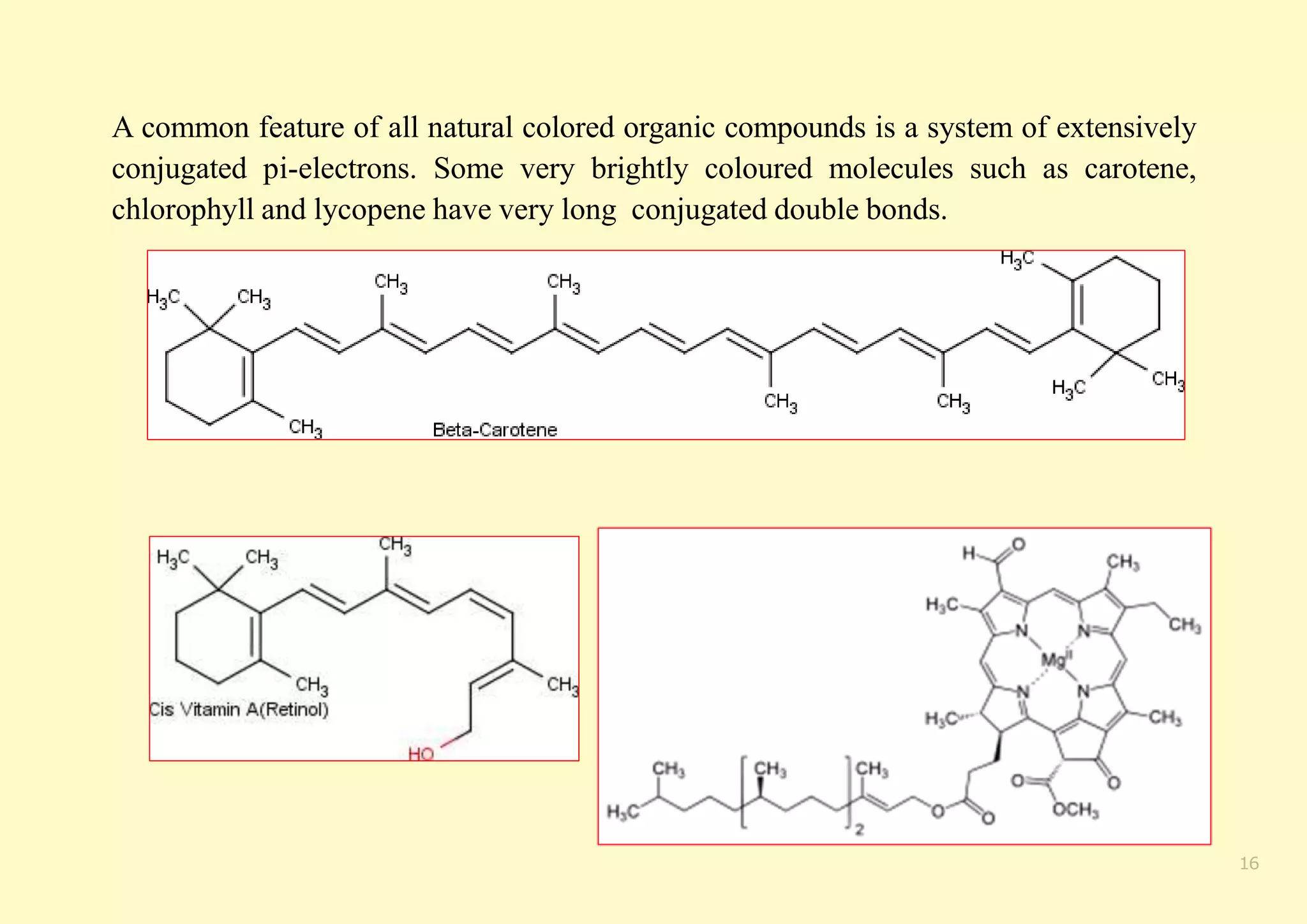
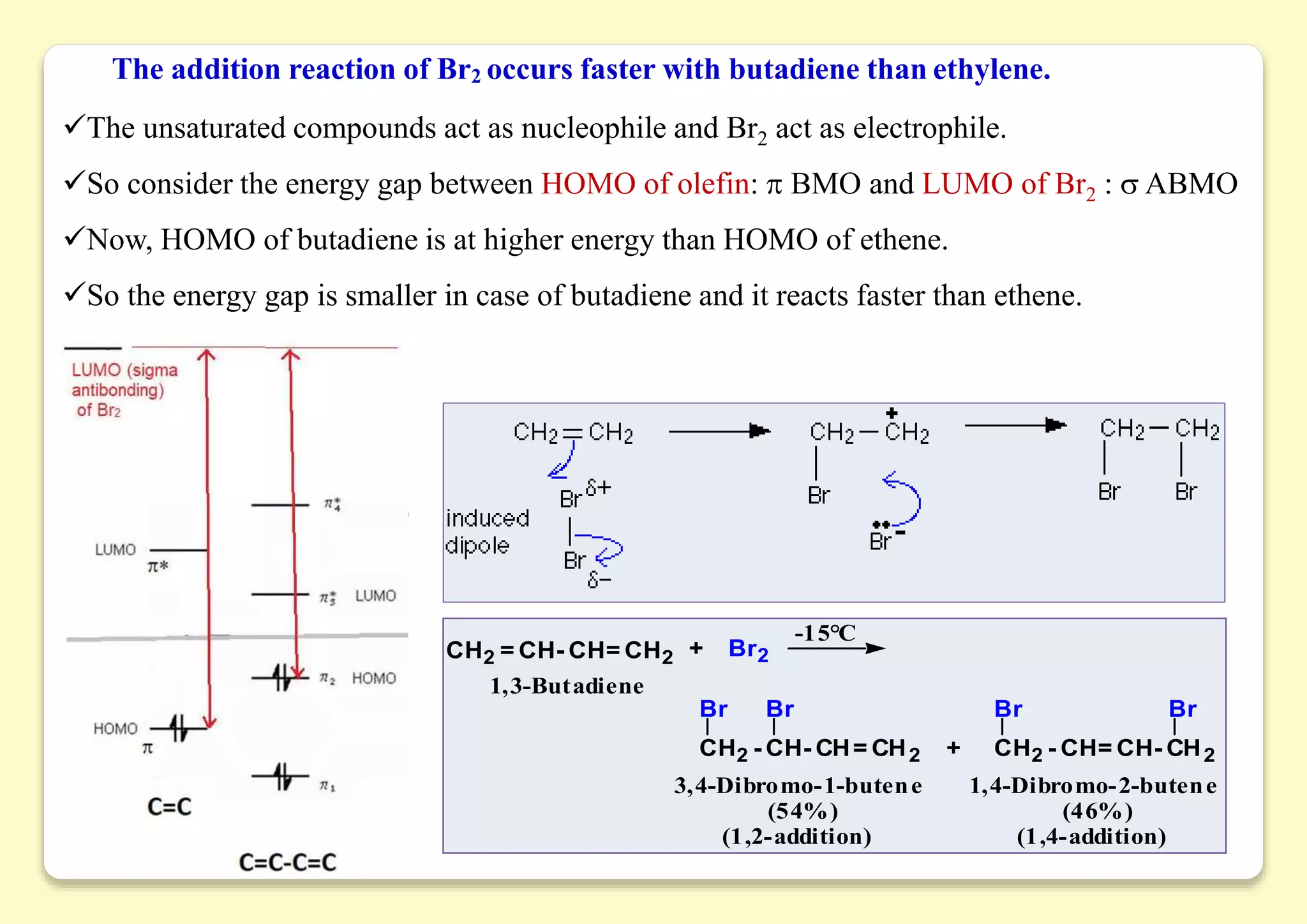
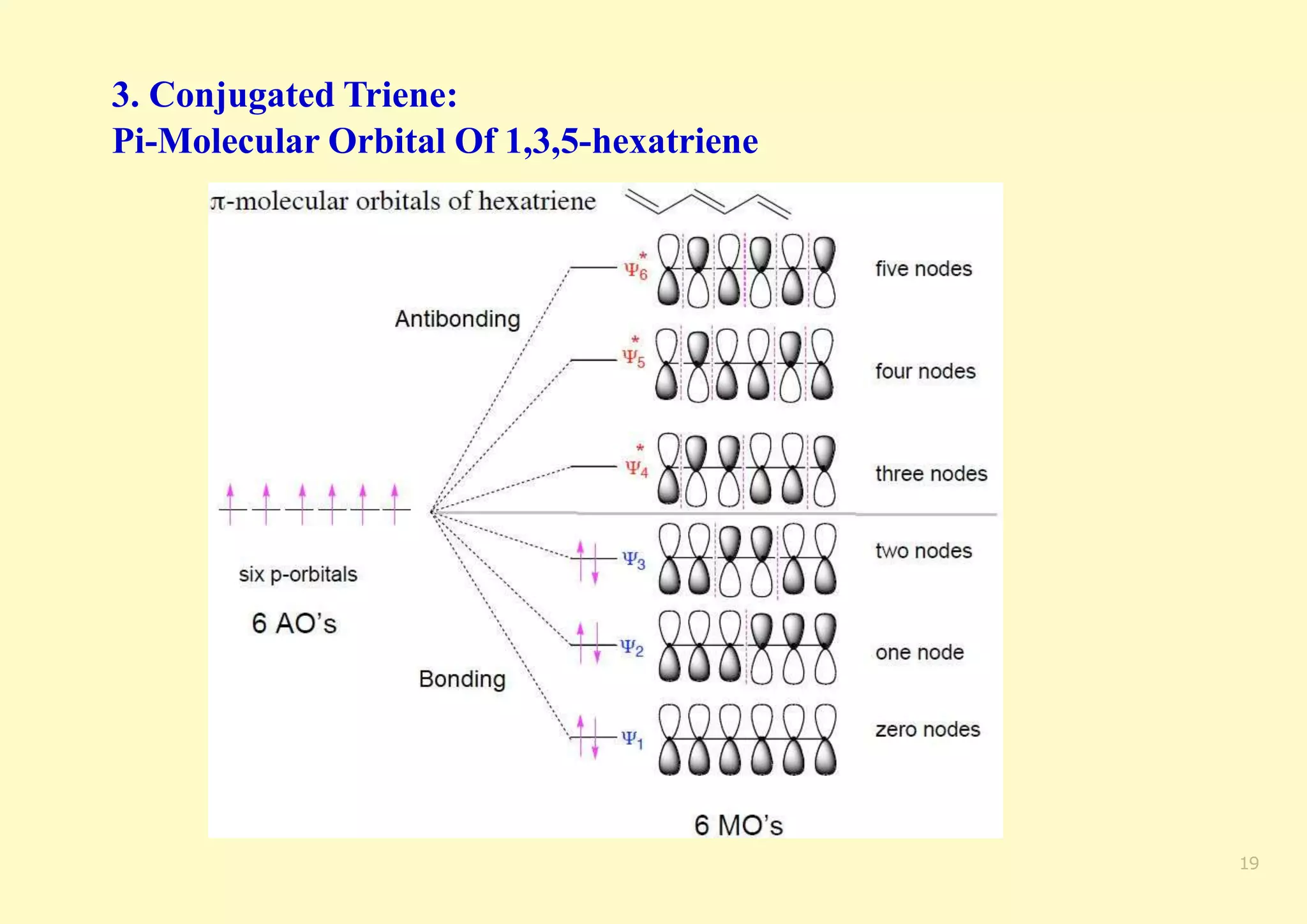
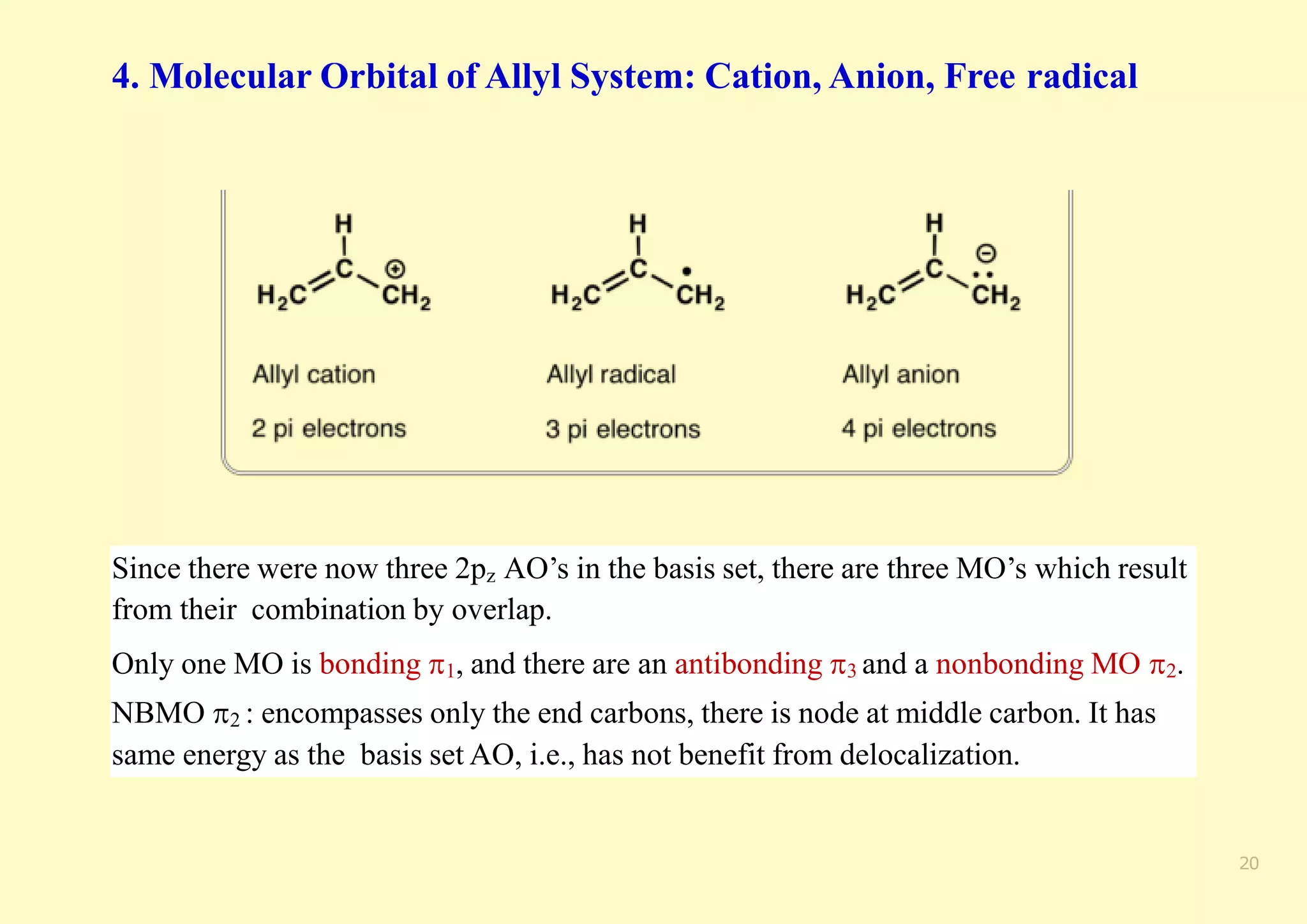
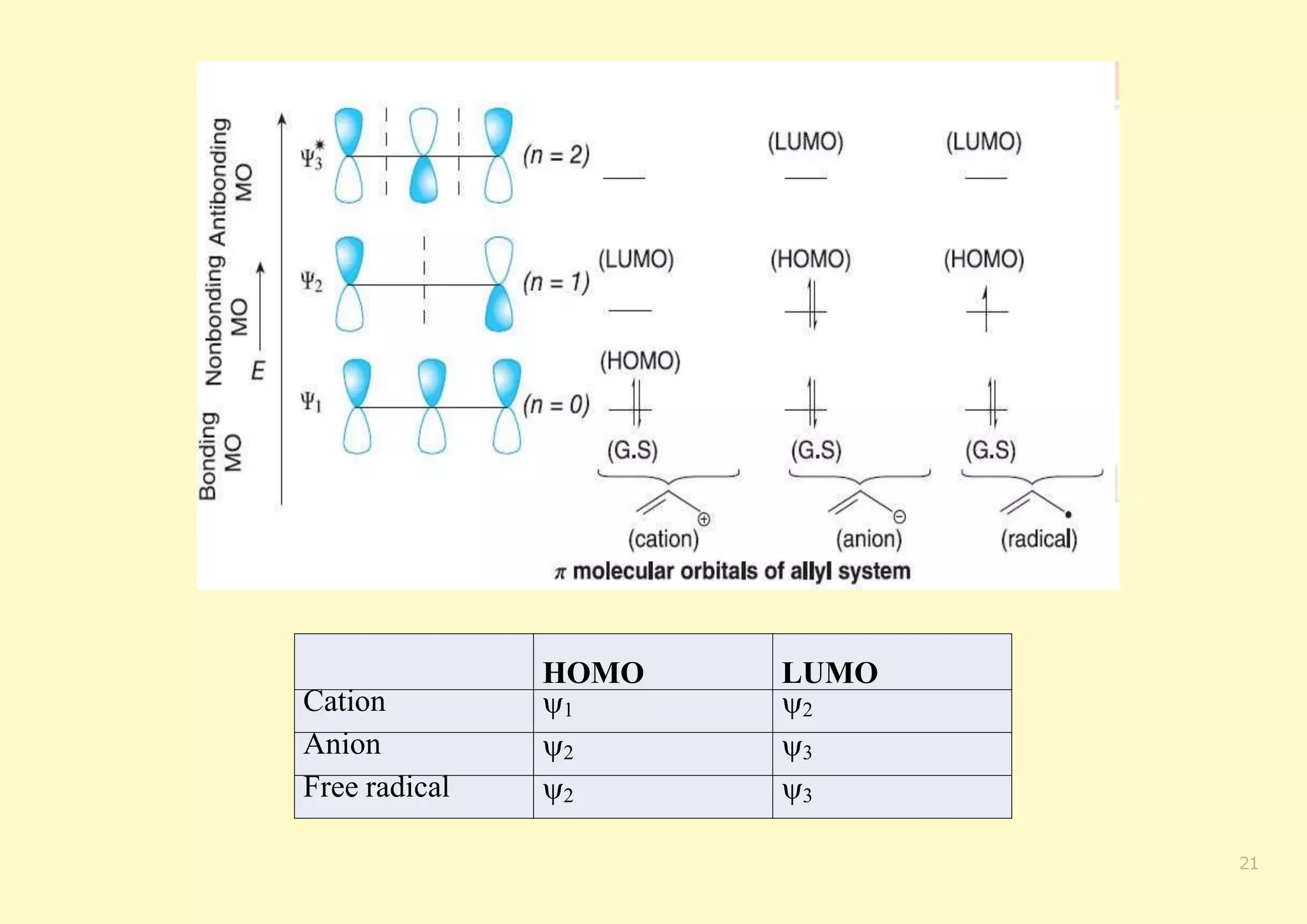
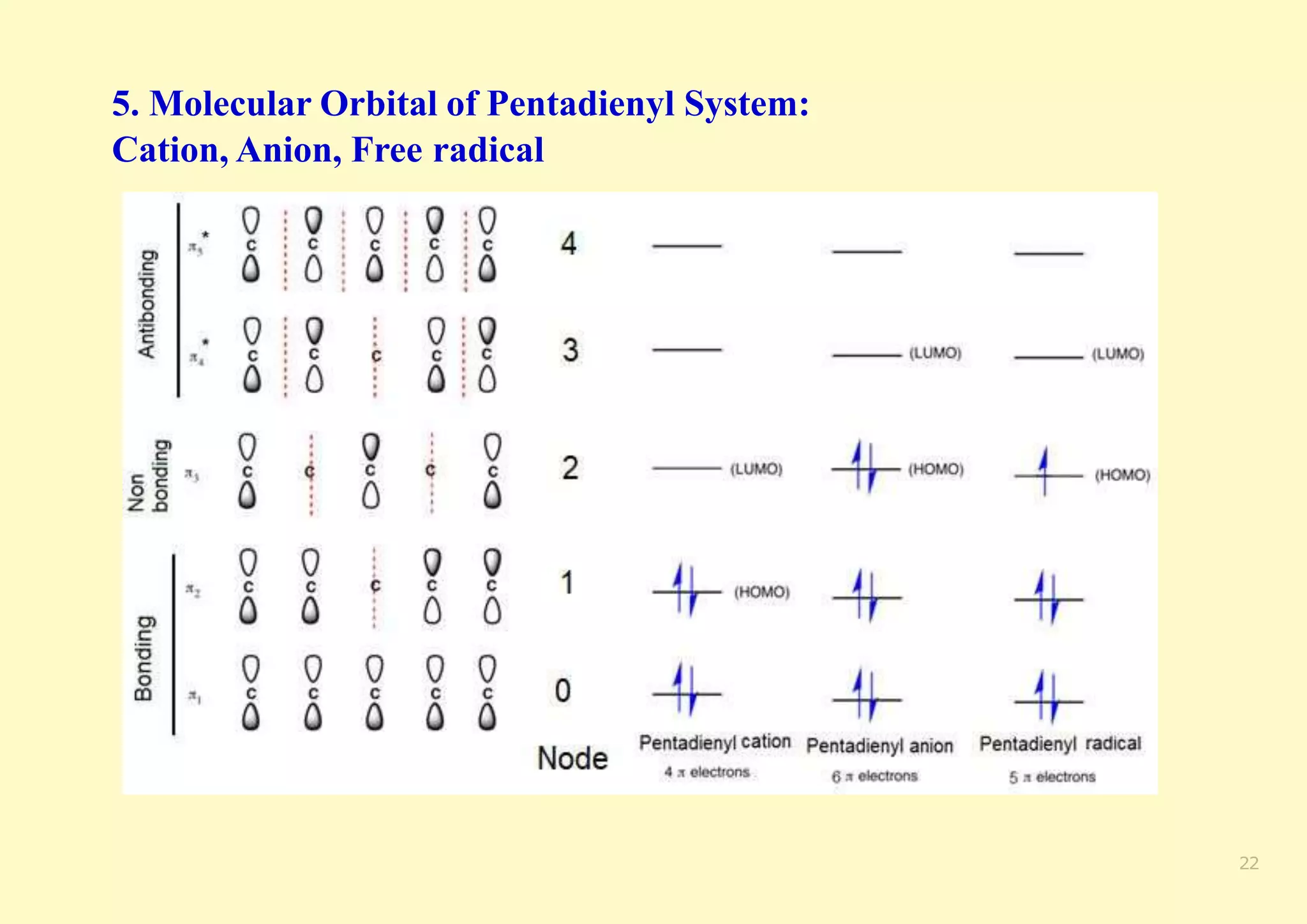
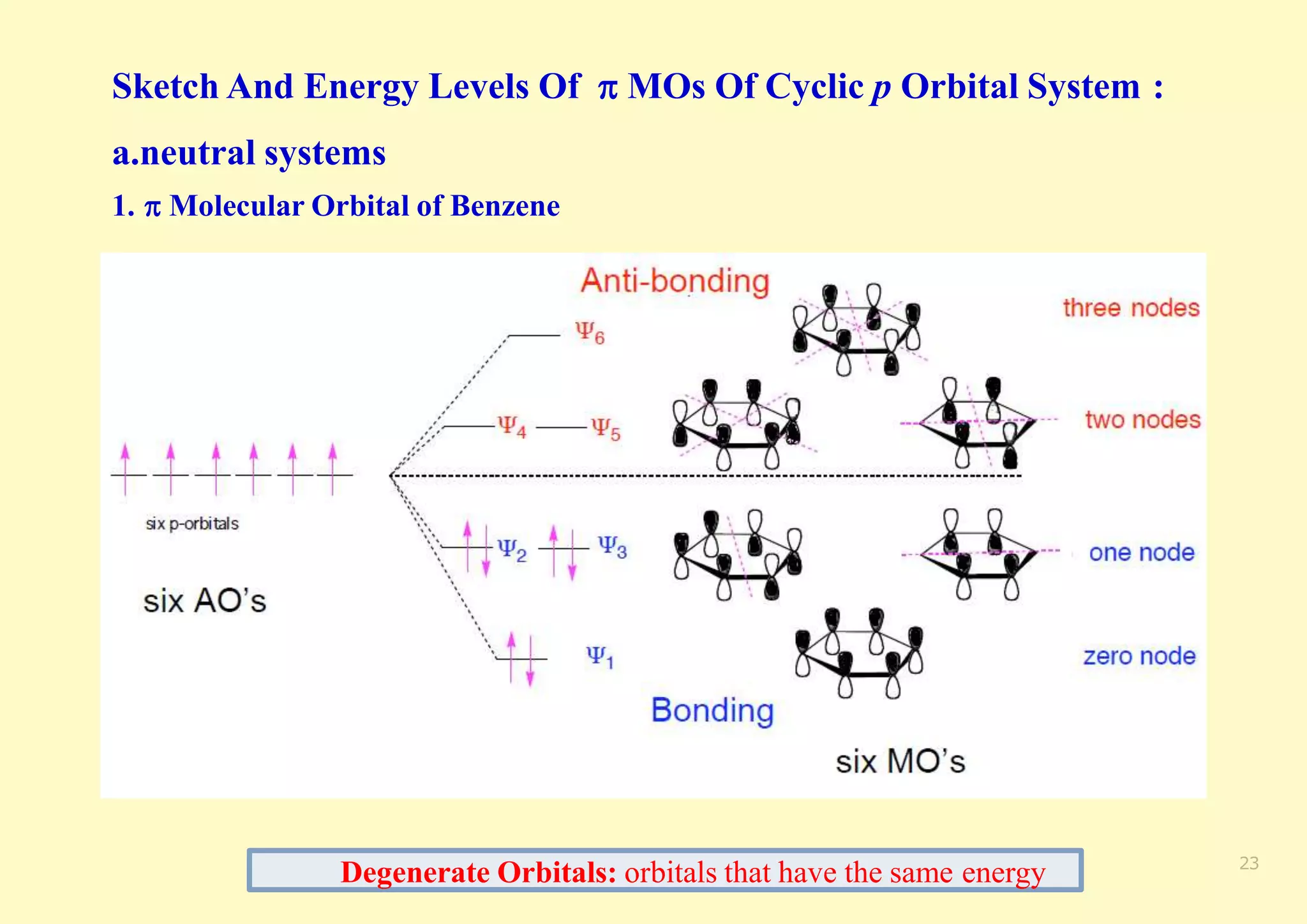
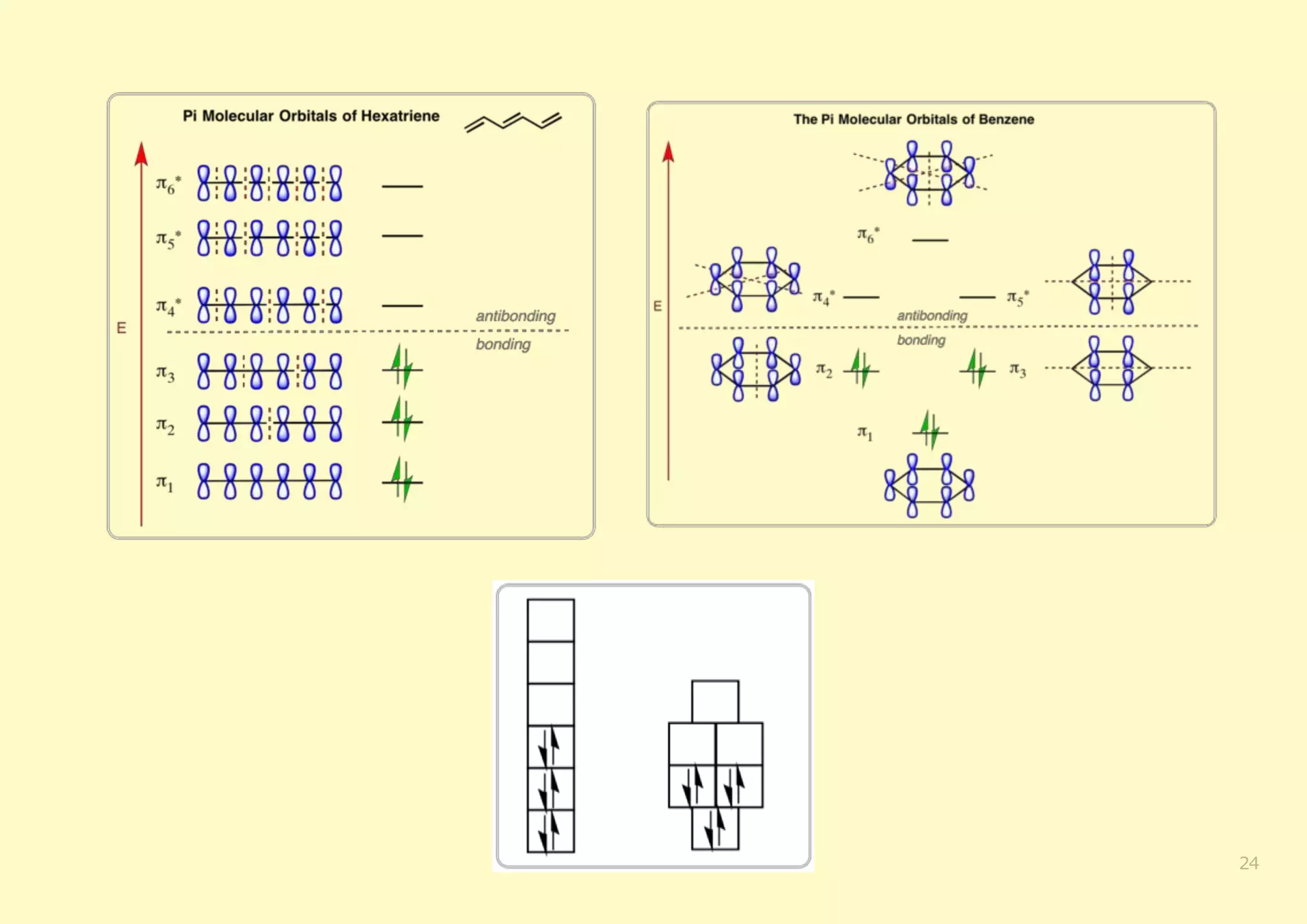
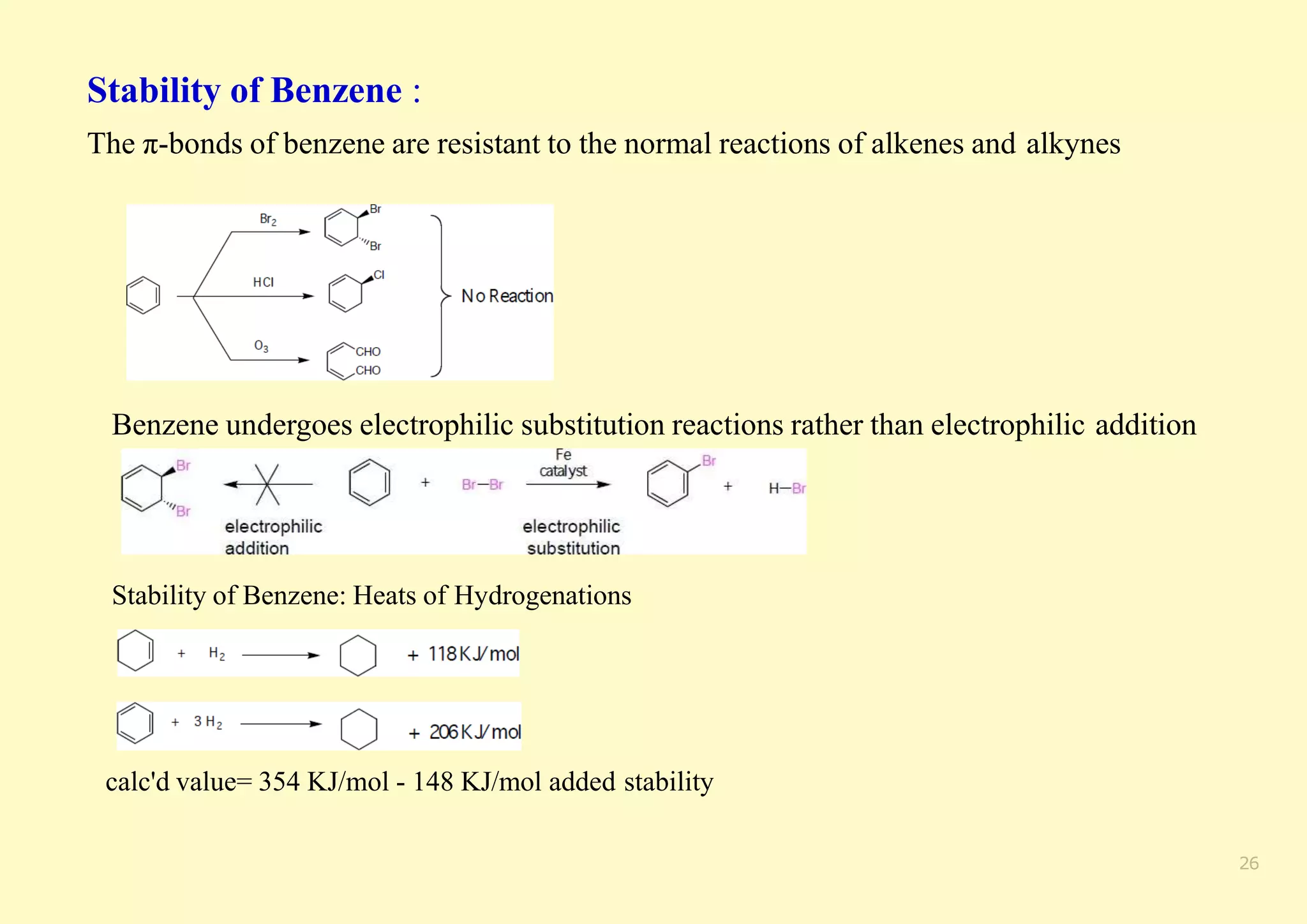
The document provides an overview of molecular orbital theory, focusing on the energy levels of π molecular orbitals in various conjugated systems, particularly ethylene and butadiene. It discusses the stability and reactivity differences between aromatic and antiaromatic compounds, explaining mechanisms like electrophilic substitution and the significance of the HOMO-LUMO gap. Additionally, it highlights specific examples such as benzene, cyclobutadiene, and heterocyclic compounds like pyrrole and pyridine in the context of their aromatic properties.



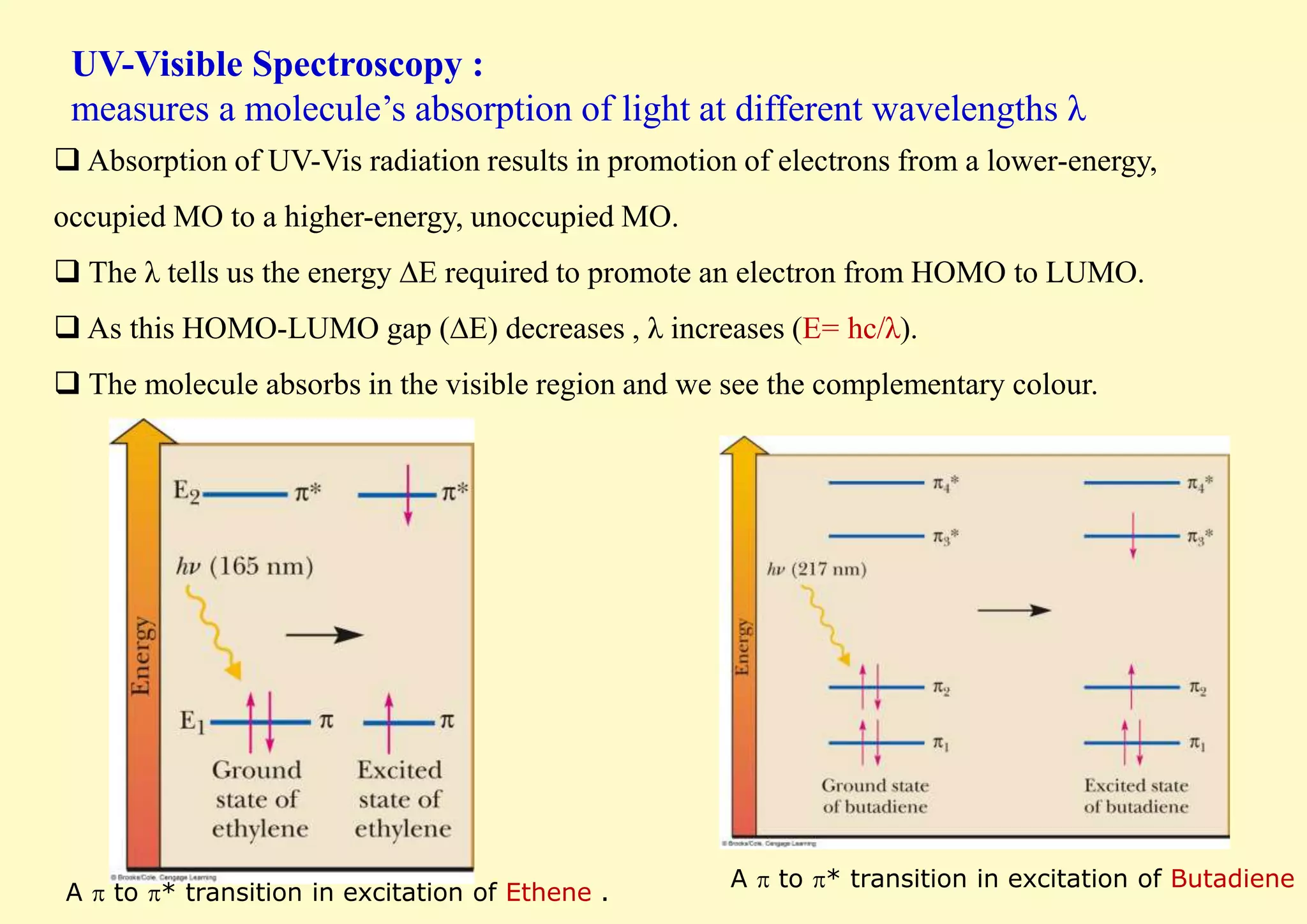
![In general, as conjugated pi systems become larger, the energy gap for a π - π*
transition becomes increasingly narrow, and the wavelength of light absorbed
correspondingly becomes longer (E= hc/λ).
In other words, excitation of an electron from HOMO to LUMO (i.e. absorbing a
photon, which gives rise to the colour of the molecule) takes less energy as the number
of double bonds increases.
15
724 (173)
552 (132)
448 (107)
385 (92)
290
268
217
165
m ax
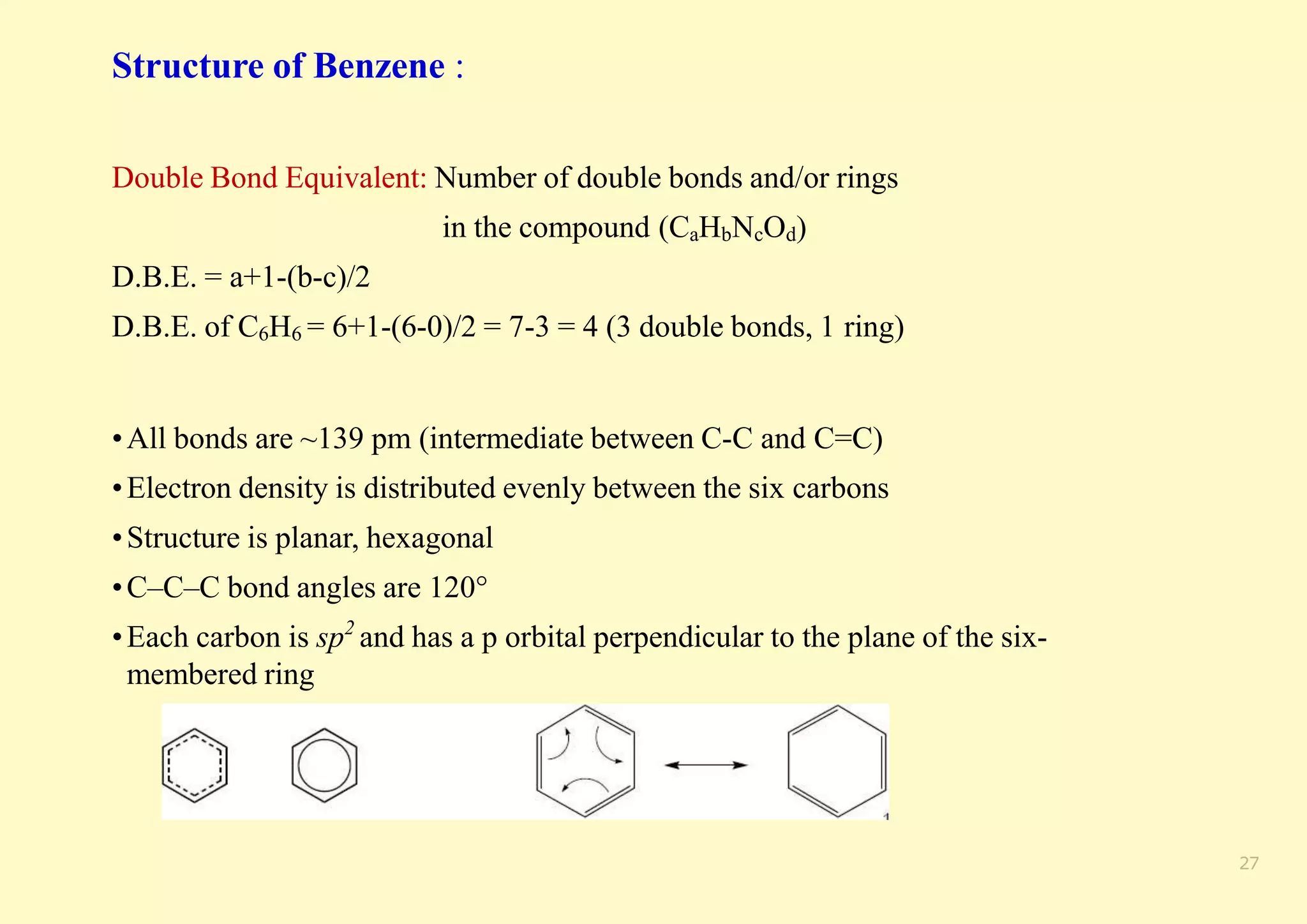
Structural Formula
Name
(3E,5E)-1,3,5,7-Octatetraene
(3E)-1,3,5-Hexatriene
1,3-Butadiene
Ethylene
(nm)
Energy
[kJ (kcal)/mol]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheoryconjugatedmolecules-210507092815/75/Molecular-orbital-theory-conjugated-molecules-15-2048.jpg)




![Annulenes
Annulenes are completely conjugated monocyclic hydrocarbons. They have the general
formula CnHn (when n is an even number) or CnHn+1 (when n is an odd number). The
IUPAC naming conventions are that annulenes with 7 or more carbon atoms are named
as [n]annulene, where n is the number of carbon atoms in their ring, though sometimes
the smaller annulenes are referred to using the same notation, and benzene is
sometimes referred to simply as annulene
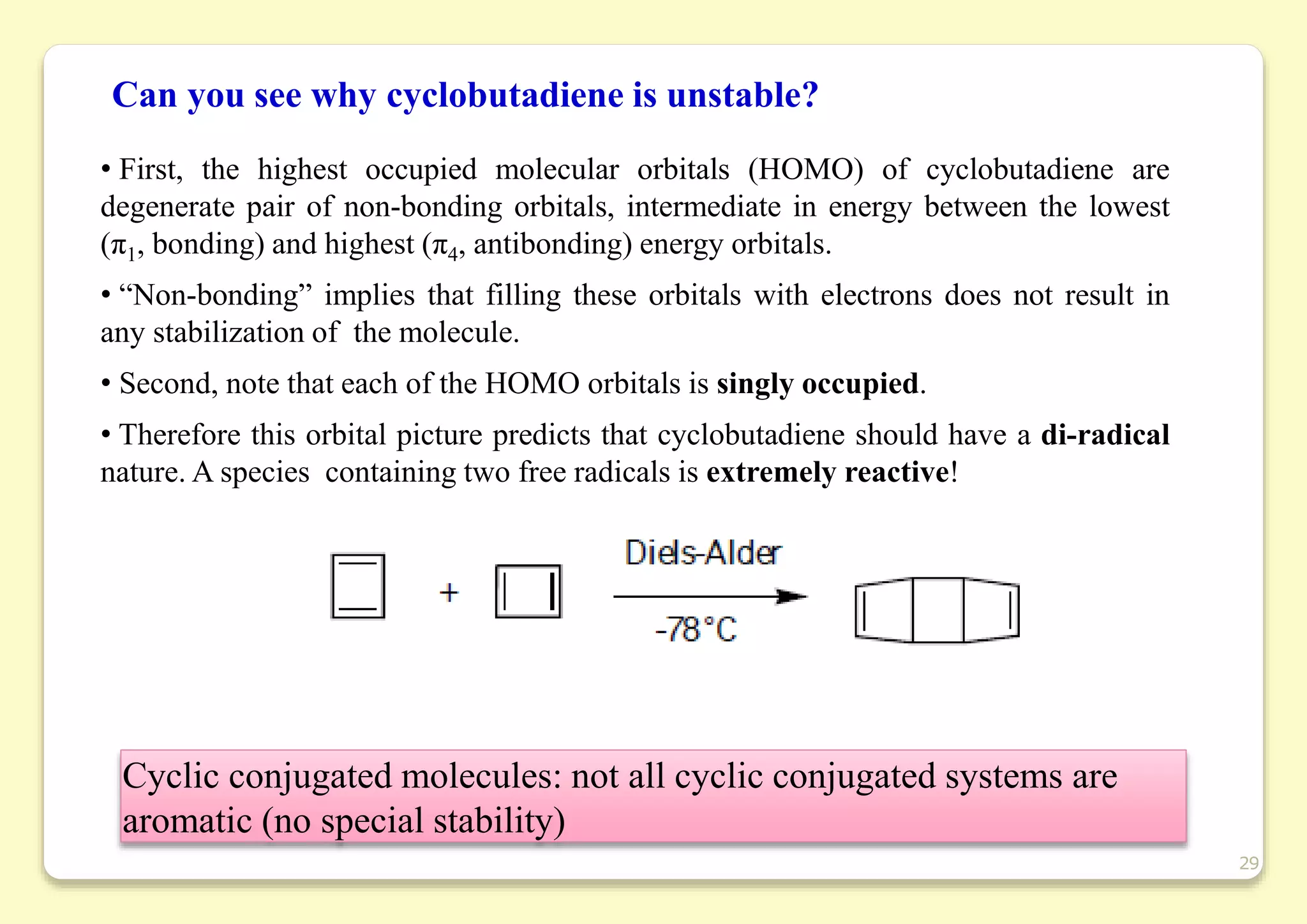
• [4]Annulene (cyclobutadiene) is antiaromatic : 4 e-
’s
• [6]Annulene (benzene) is aromatic : 6 e-
’s
32
Larger 4n annulenes are not antiaromatic because they are flexible
enough to become nonplanar. Such cyclic systems show non
aromatic behavior.
Non-aromatic
Nonaromatic compounds do not have a continuous ring of
overlapping p orbitals and may be nonplanar.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheoryconjugatedmolecules-210507092815/75/Molecular-orbital-theory-conjugated-molecules-32-2048.jpg)
![[8]Annulene (cyclooctatetraene), a conjugated 8 pi electron cyclic system –
would be antiaromatic, but it’s nonaromatic.
The molecule is not planar, it typically adopts a "tub" conformation.
The lack of conjugation allows the 8 π electron molecule to avoid antiaromaticity.
33
[10]Annulene or cyclodecapentaene, a conjugated 10 pi electron cyclic system –
should display aromaticity, but it is non-aromatic
It is not aromatic because various types of ring strain destabilize an all-planar geometry.
Cis isomer (2): angle strain. Trans isomer (3): steric strain.
The nonplanar structure (4) is the most stable of all the possible isomers.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/molecularorbitaltheoryconjugatedmolecules-210507092815/75/Molecular-orbital-theory-conjugated-molecules-33-2048.jpg)