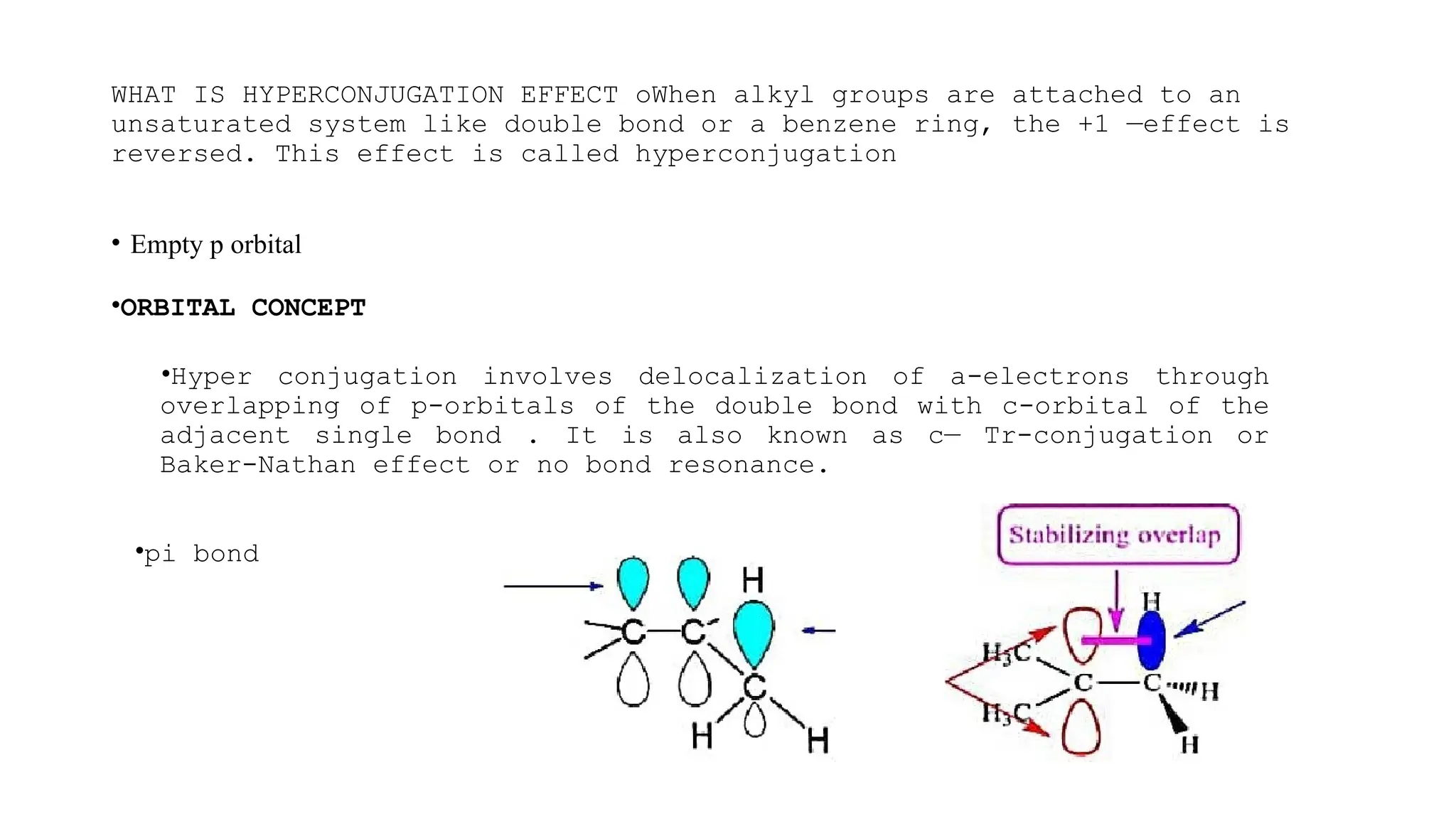
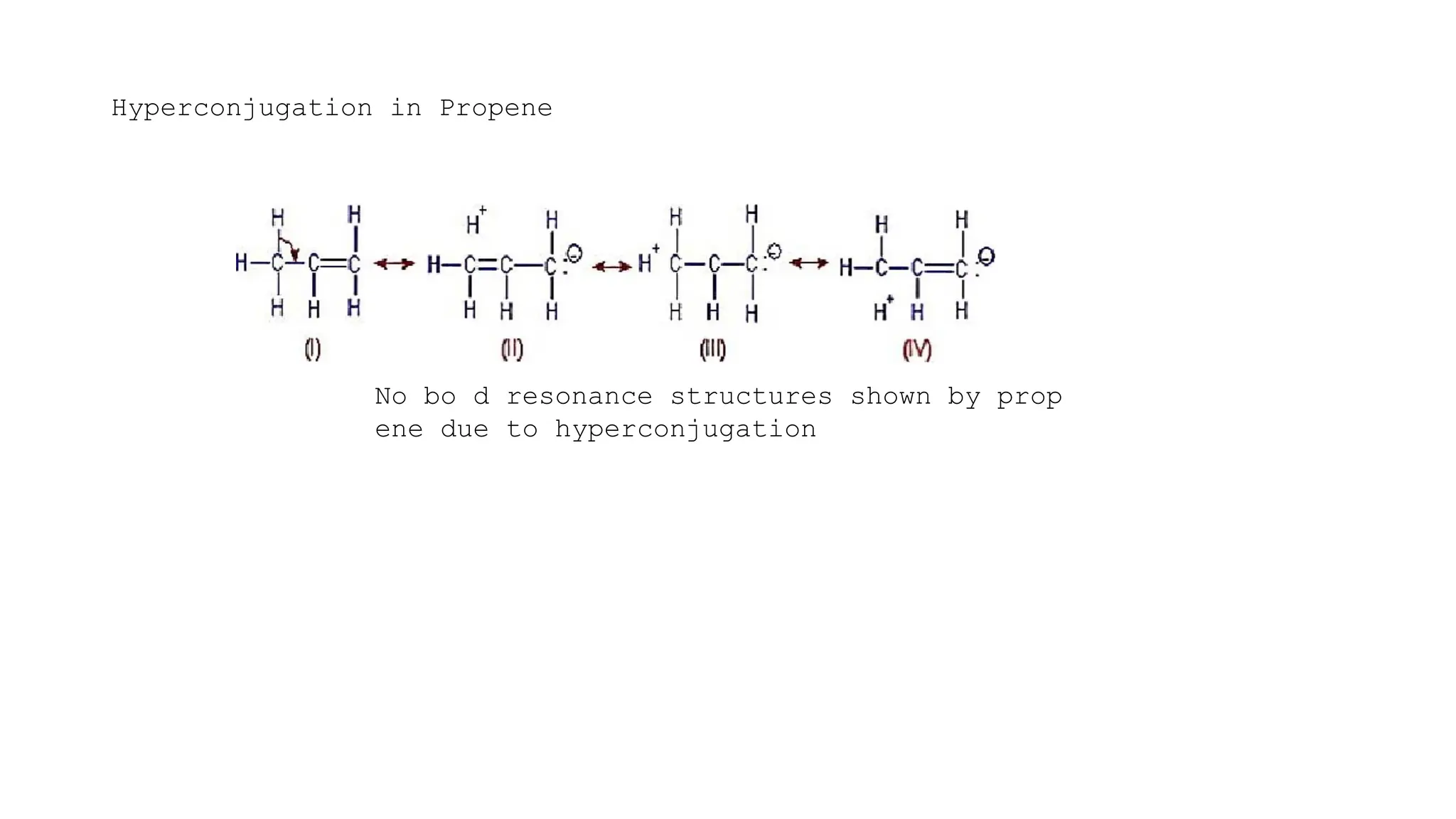
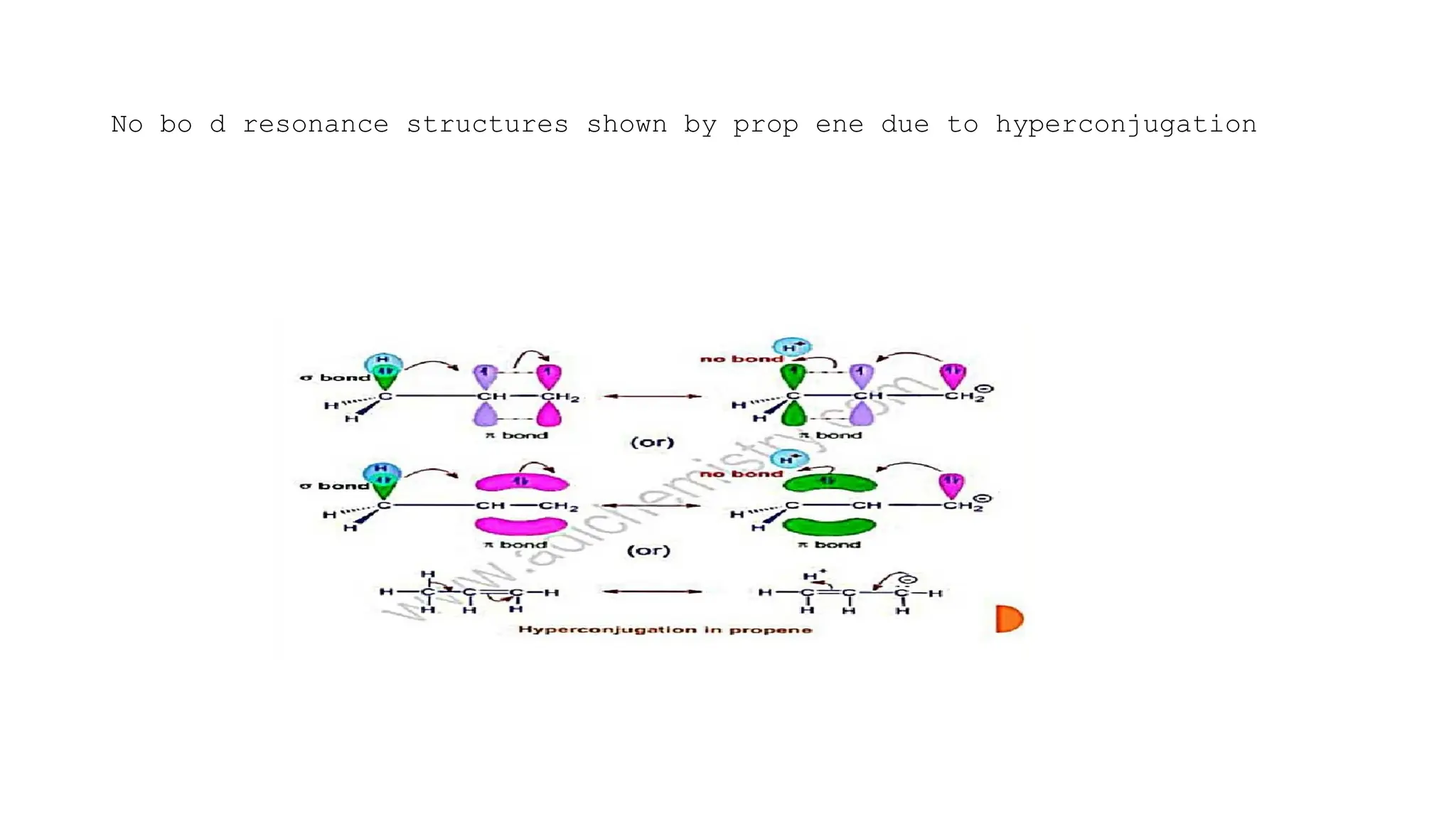
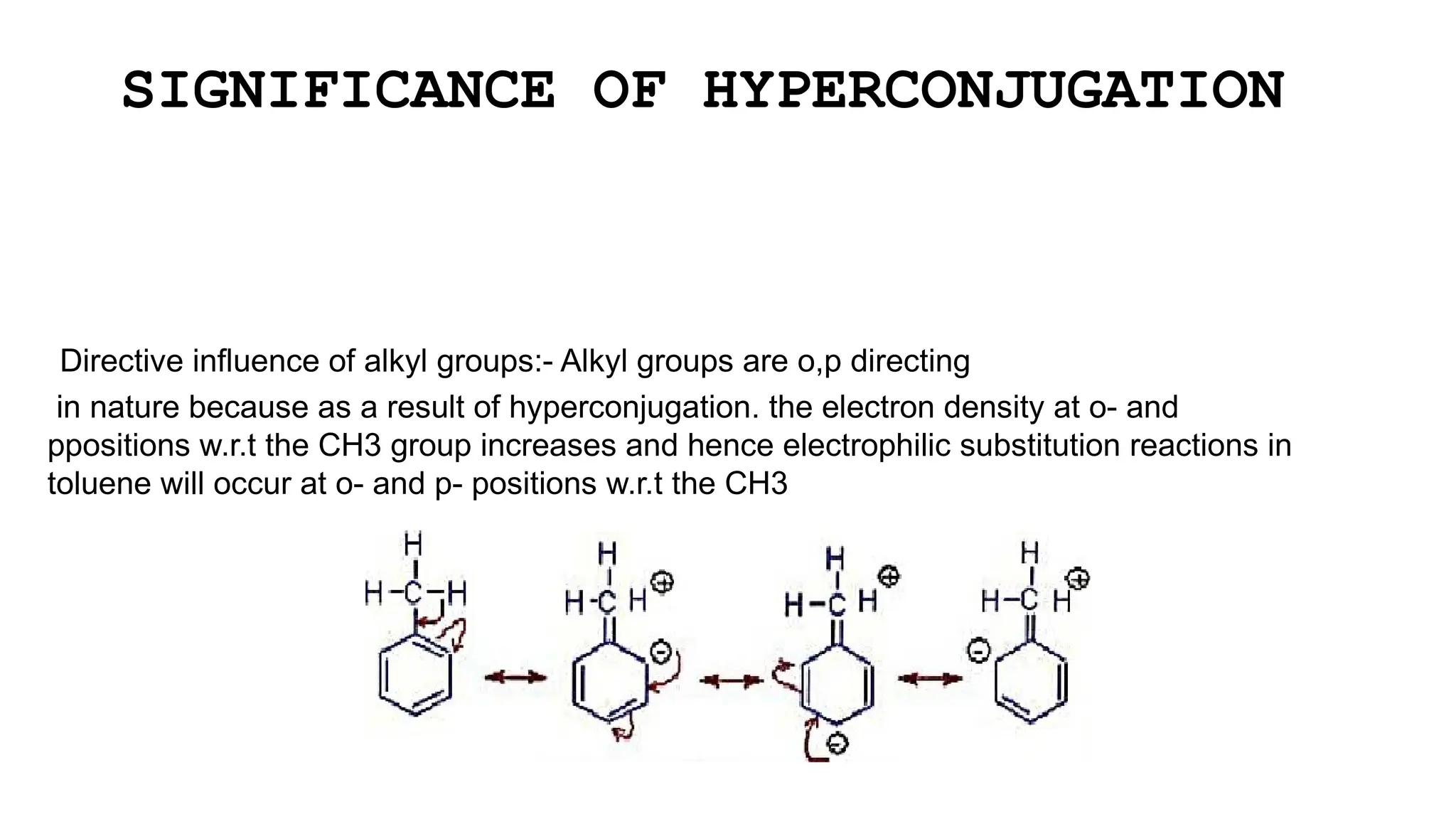
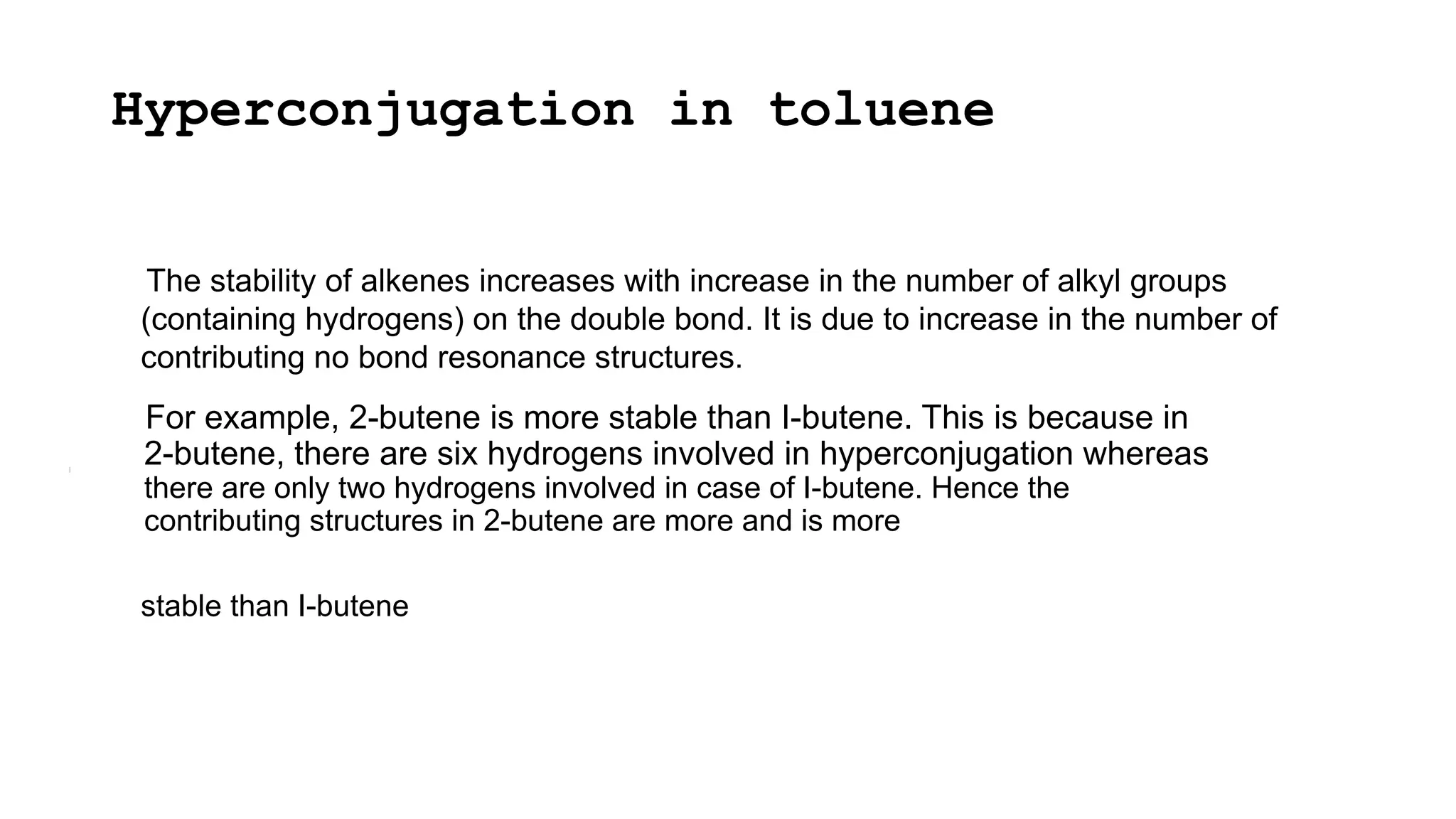
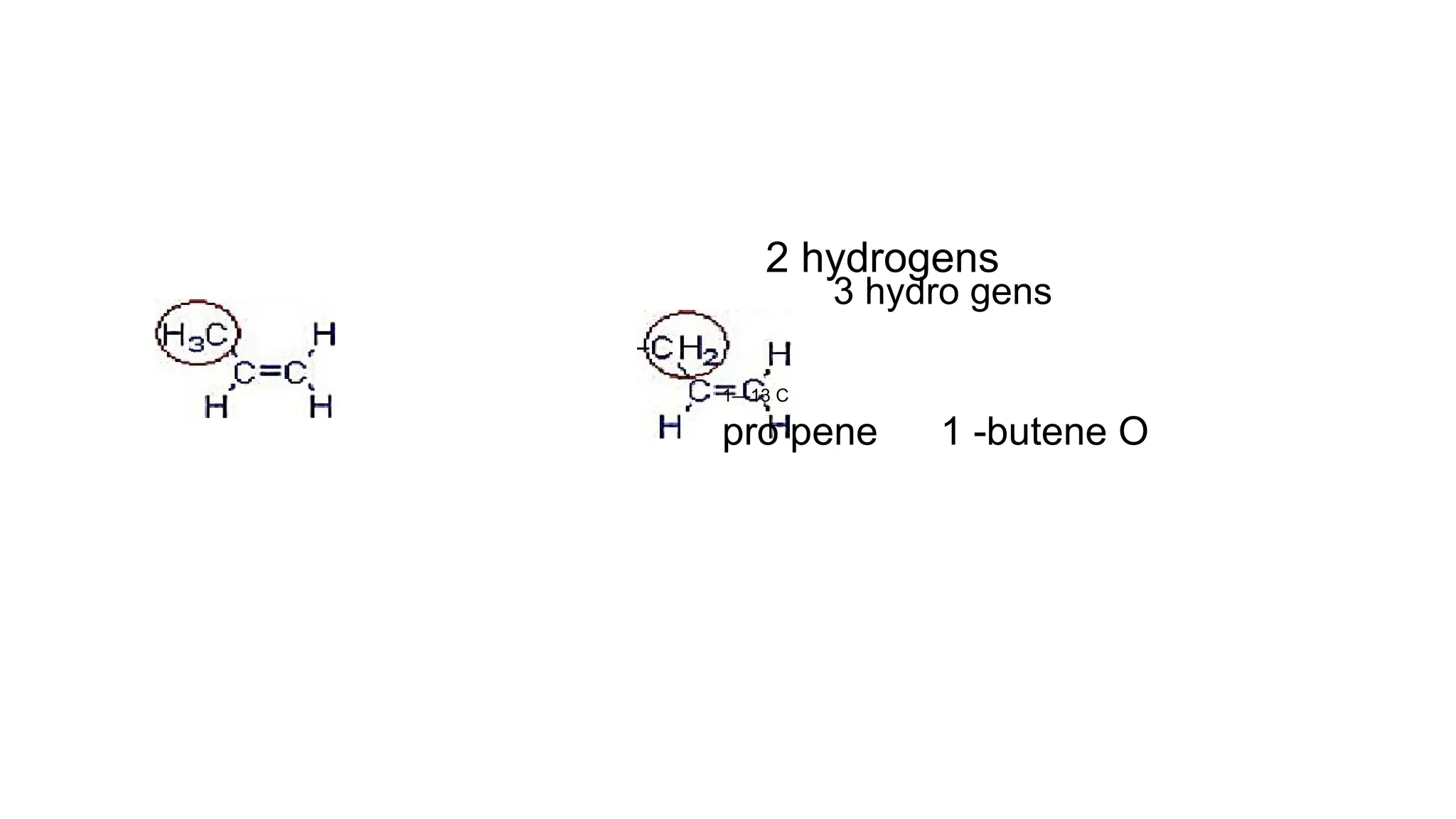
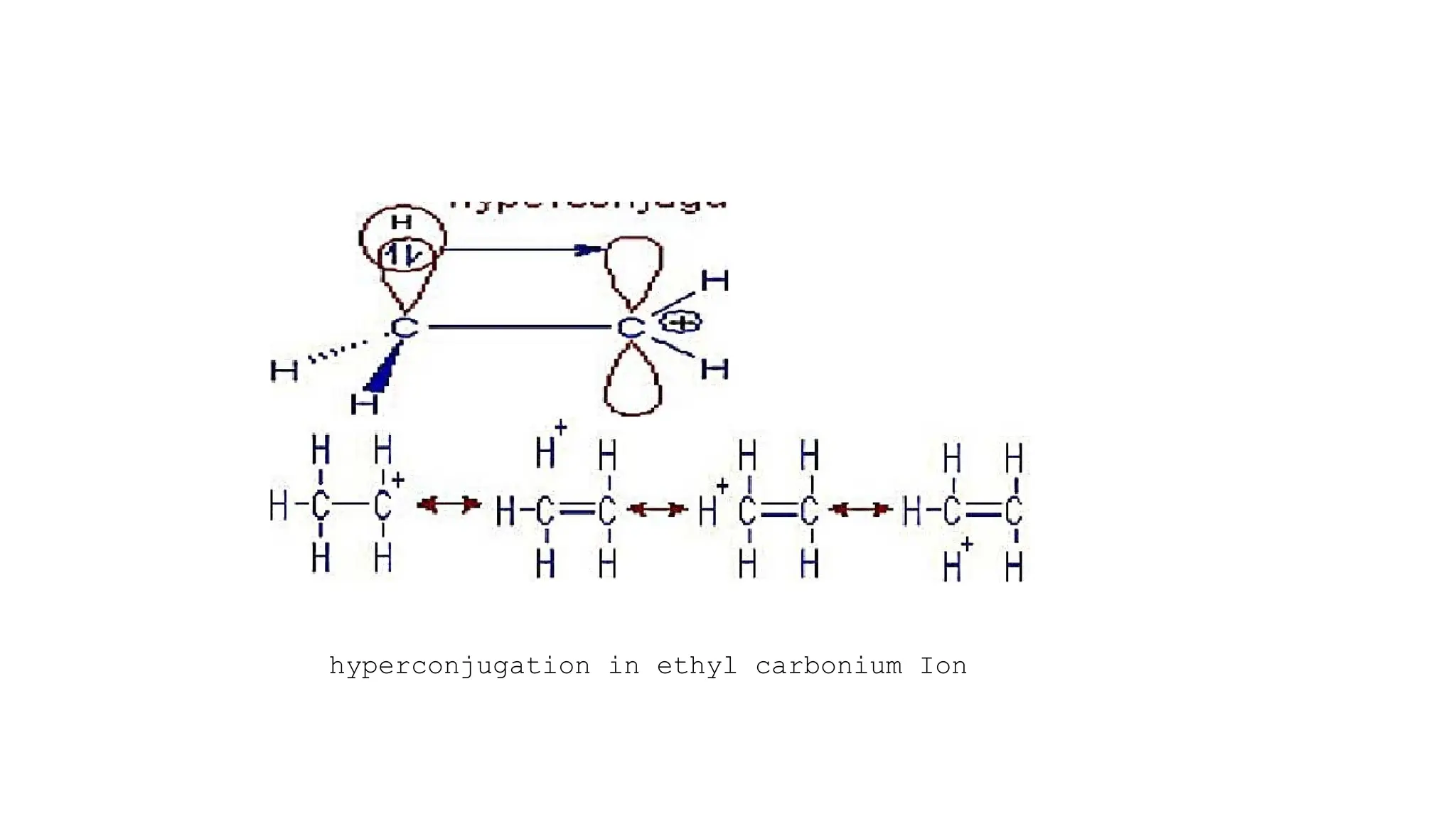
The document discusses hyperconjugation, detailing its definition, significance, and effects in organic chemistry, particularly regarding the stability of alkenes and carbocations. It explains how the presence of alkyl groups affects the electron density and stability of these compounds, using examples like propene and butenes. The stability of carbocations is also addressed, emphasizing that hyperconjugation leads to increased stability with more alkyl groups.