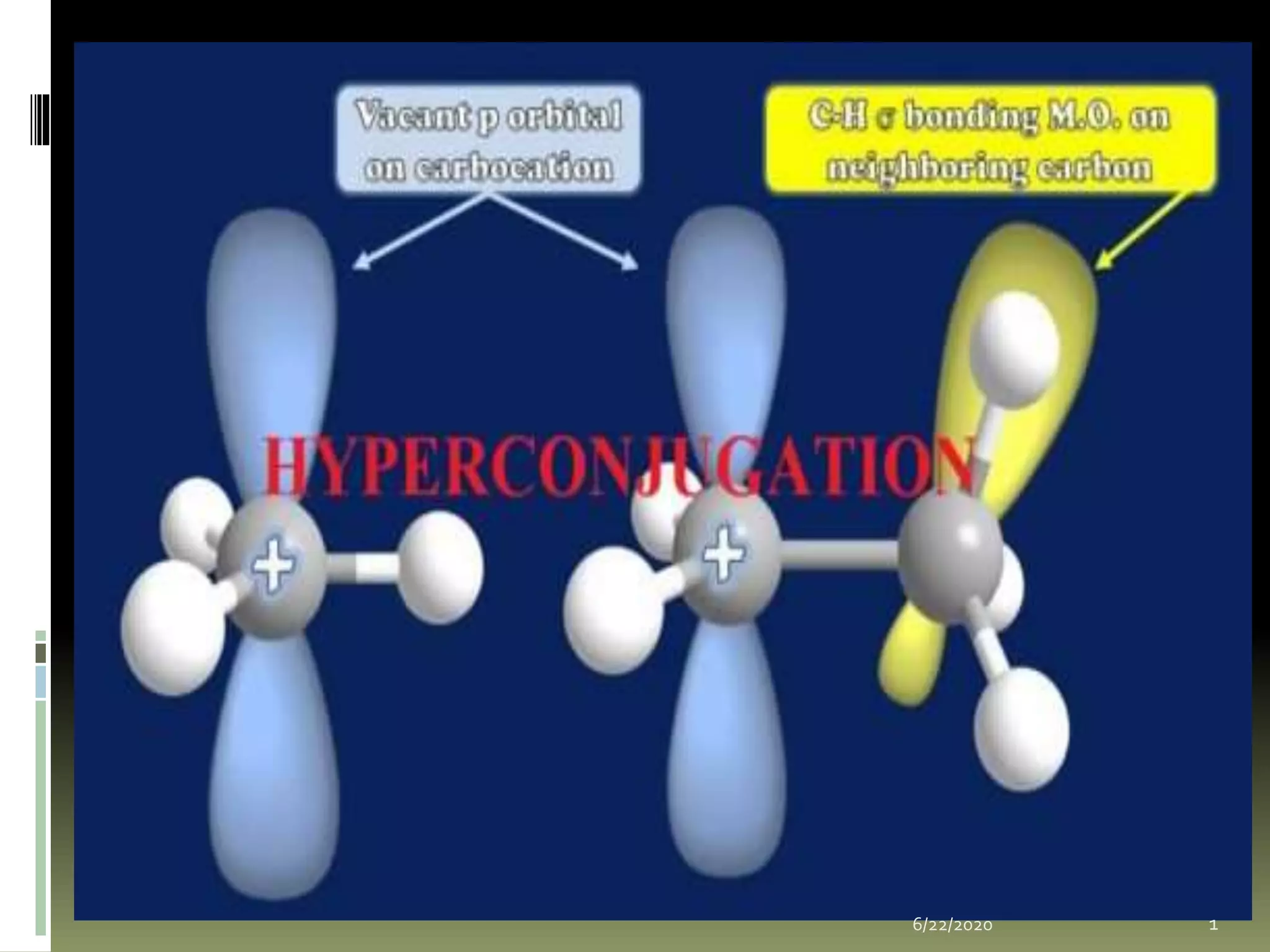
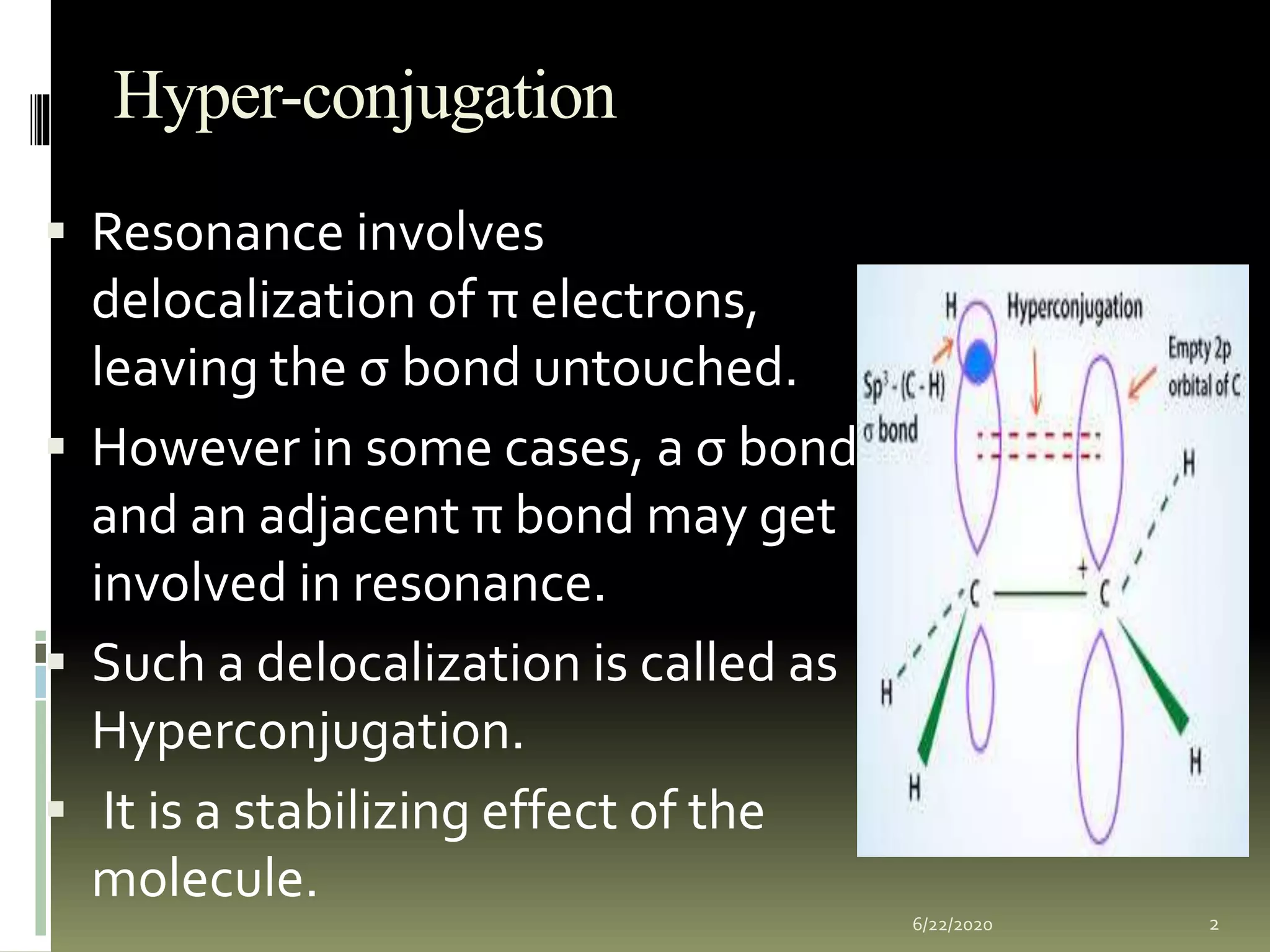
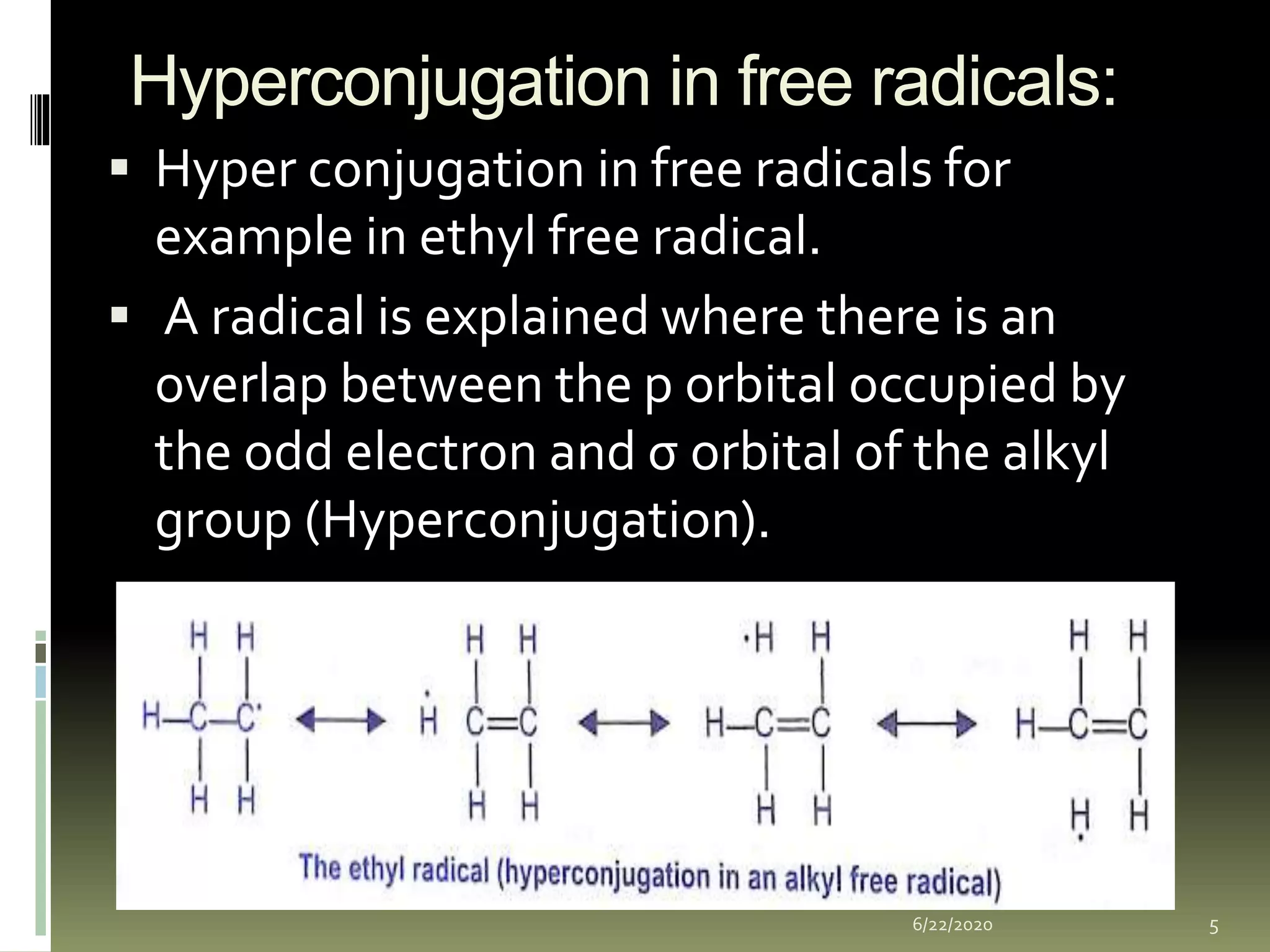
Hyperconjugation occurs when a σ bond and adjacent π bond become involved in resonance. This delocalization stabilizes molecules like carbocations, free radicals, alkenes, and alkynes. Specifically, hyperconjugation in carbocations involves overlap between the carbocation's empty p-orbital and the σ orbitals of alpha hydrogens. In free radicals, it is the overlap between the odd electron's p-orbital and the σ orbital of an alkyl group. For alkenes and alkynes, stability arises from partial overlap between sp3 σ orbitals and the π orbitals of the multiple bonds. This document discusses the hyperconjugation resonance structure effects in different organic molecules.