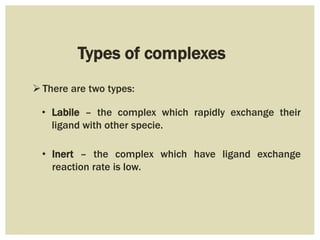
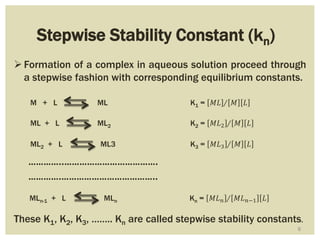
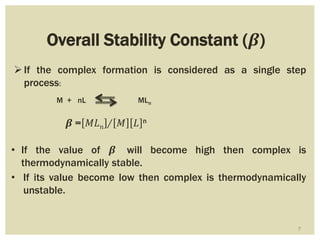
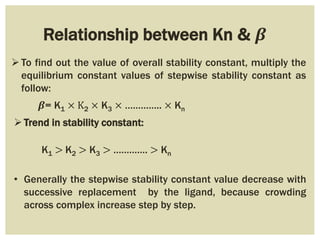
This document discusses the stability of metal complexes. There are two types of stability: thermodynamic stability and kinetic stability. Thermodynamic stability is determined by equilibrium constants and Gibbs free energy, while kinetic stability refers to the reactivity of ligand substitution reactions and is determined by reaction rates and activation energies. The factors that influence the stability include the nature of the metal and ligand, such as their size, charge, and electronegativity. The stability tends to increase with higher charges, smaller sizes, and more basic ligands. Chelates are generally more stable than open structures.