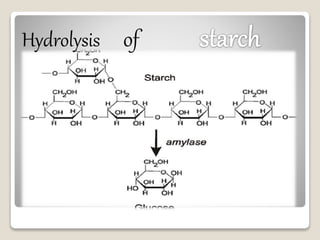
This document discusses hydrolysis, beginning with its definition as the reaction of water with another chemical compound to form two or more products by ionizing the water molecule and splitting the other compound. It then provides examples of hydrolysis including the conversion of starch to glucose and saponification. The document goes on to explain the mechanism of hydrolysis where a molecule is cleaved into two parts by the addition of a water molecule, with one fragment gaining a hydrogen ion and the other a hydroxyl group. It also discusses different types of hydrolysis reactions and some common uses of hydrolysis like breaking down food, producing soap, and generating energy through the hydrolysis of ATP.