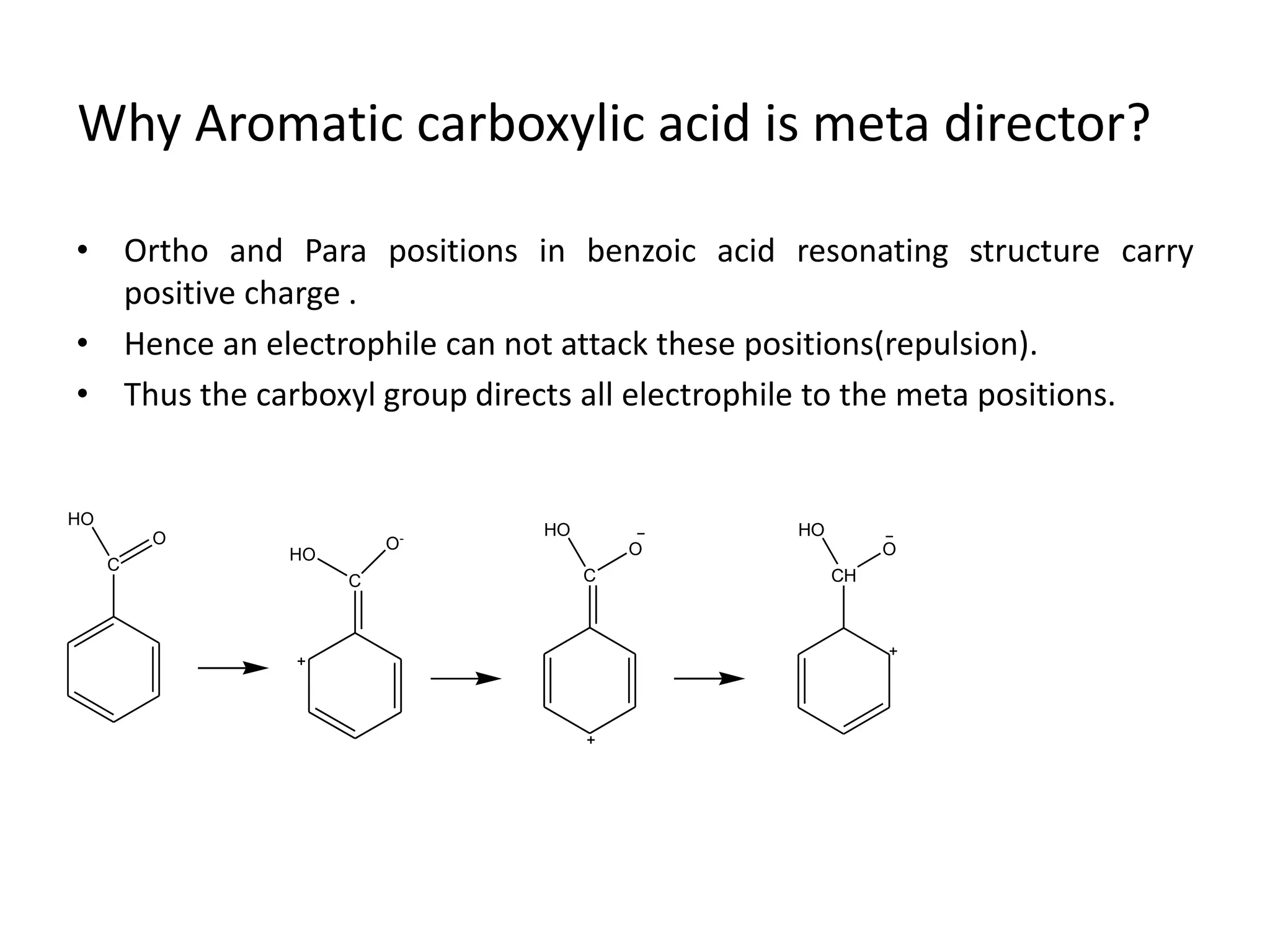
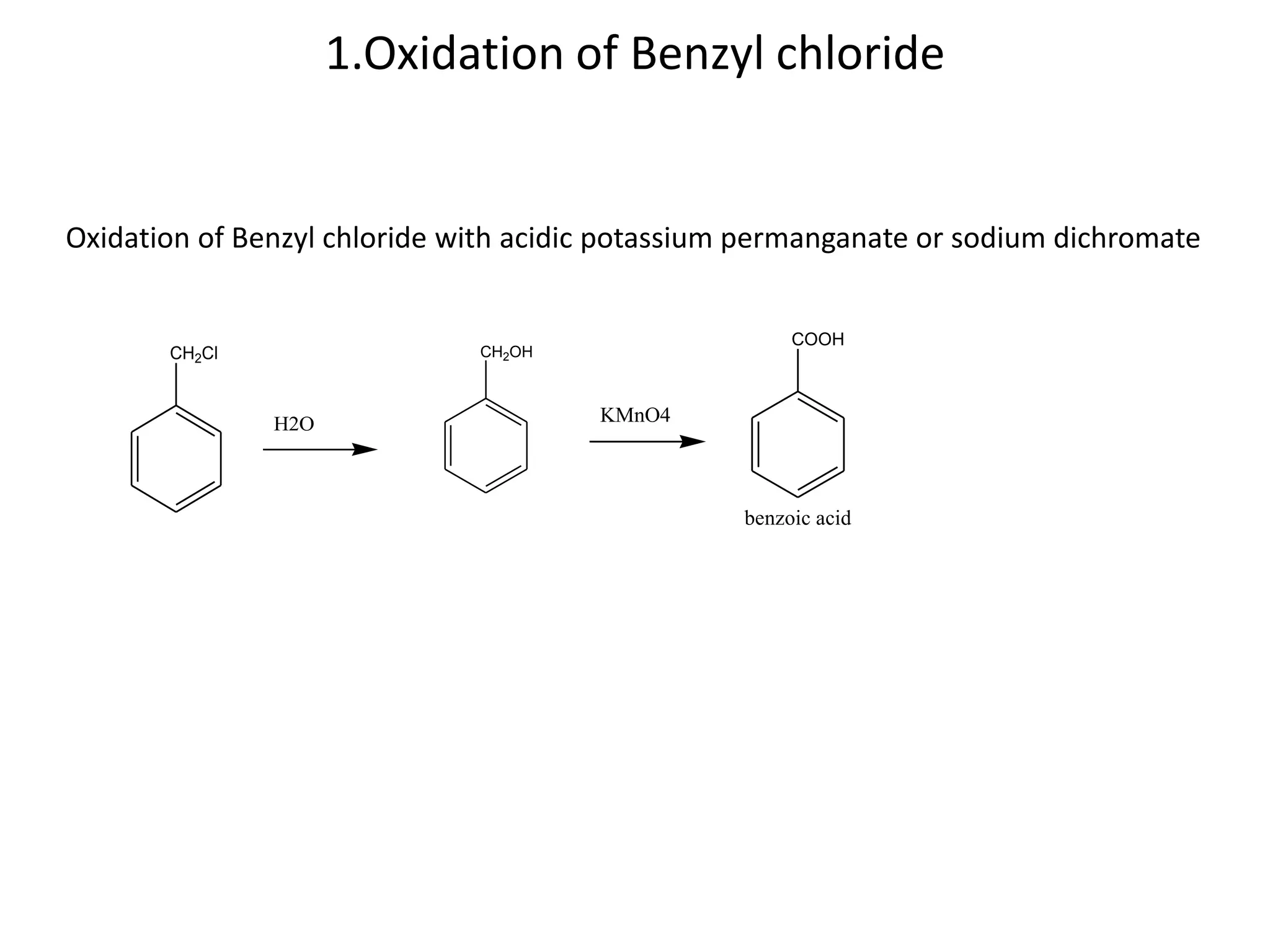
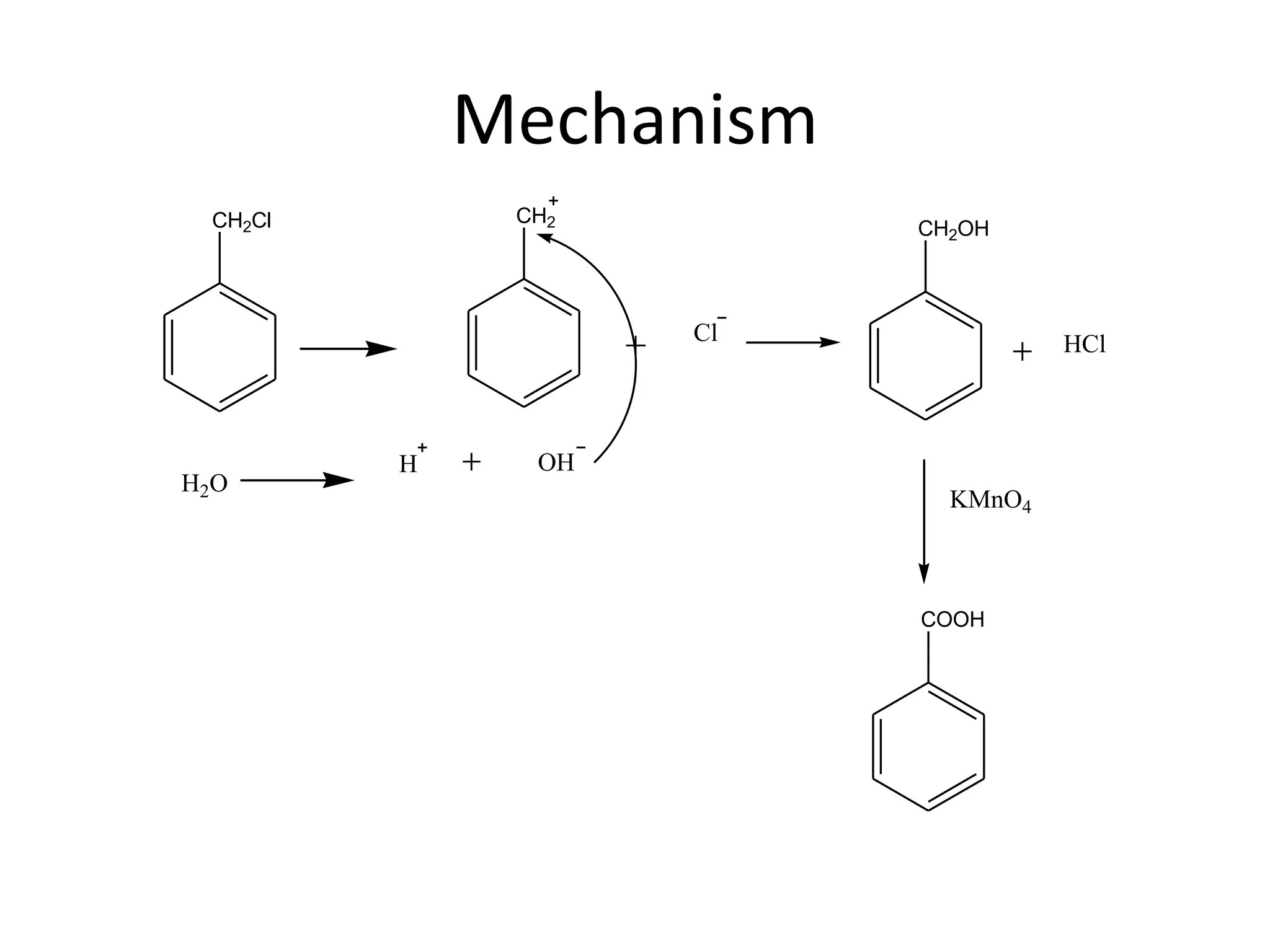
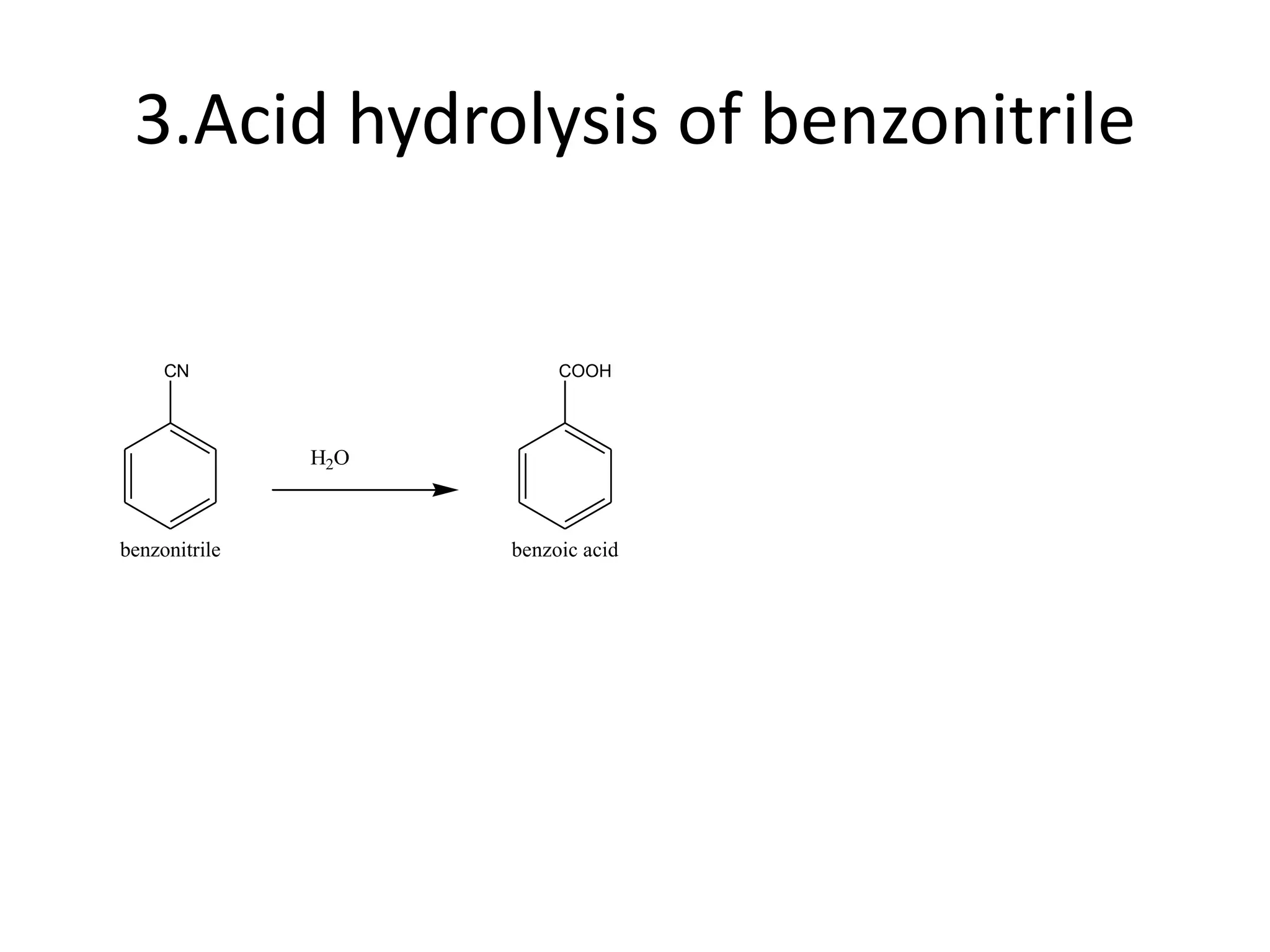
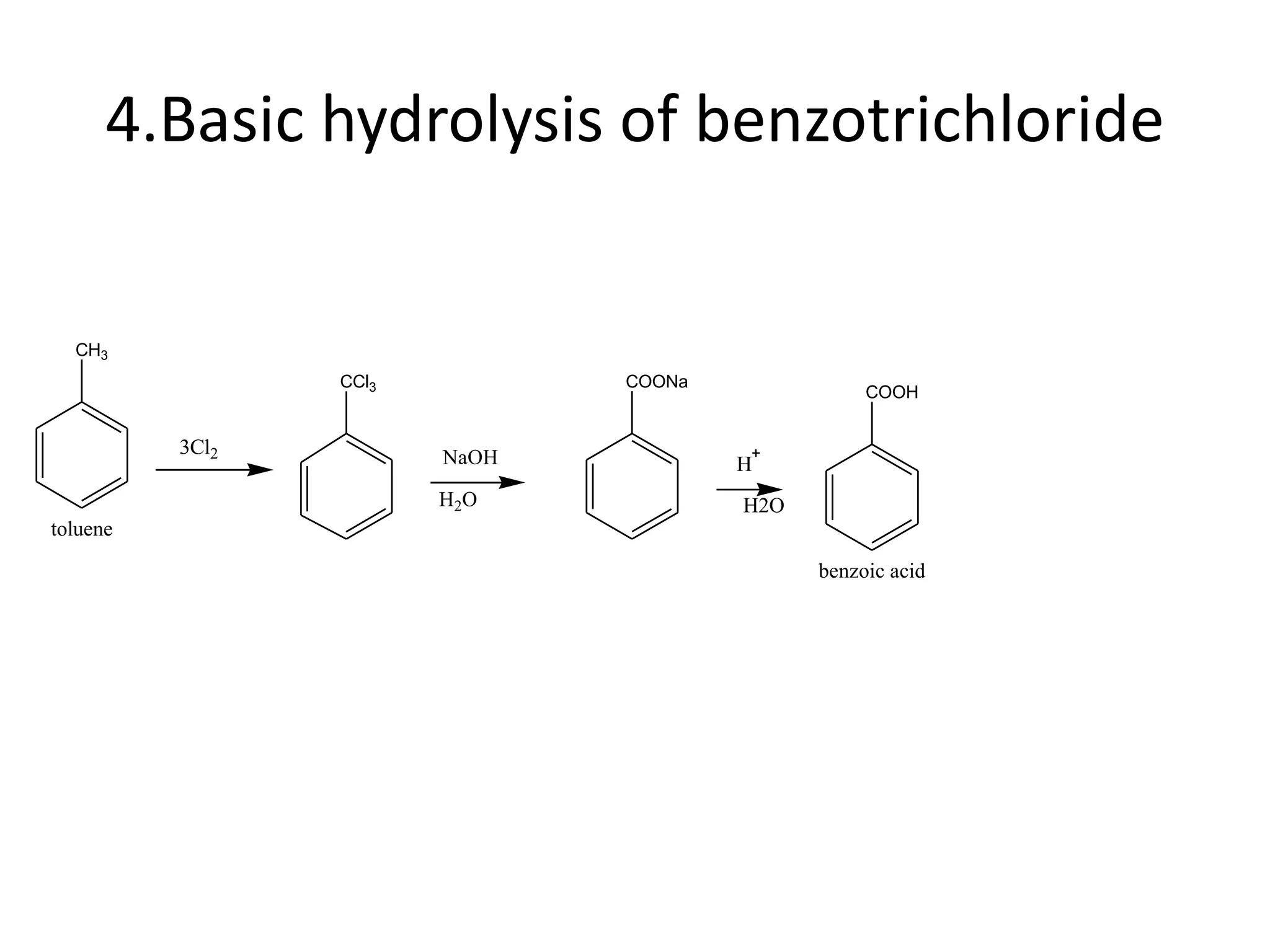
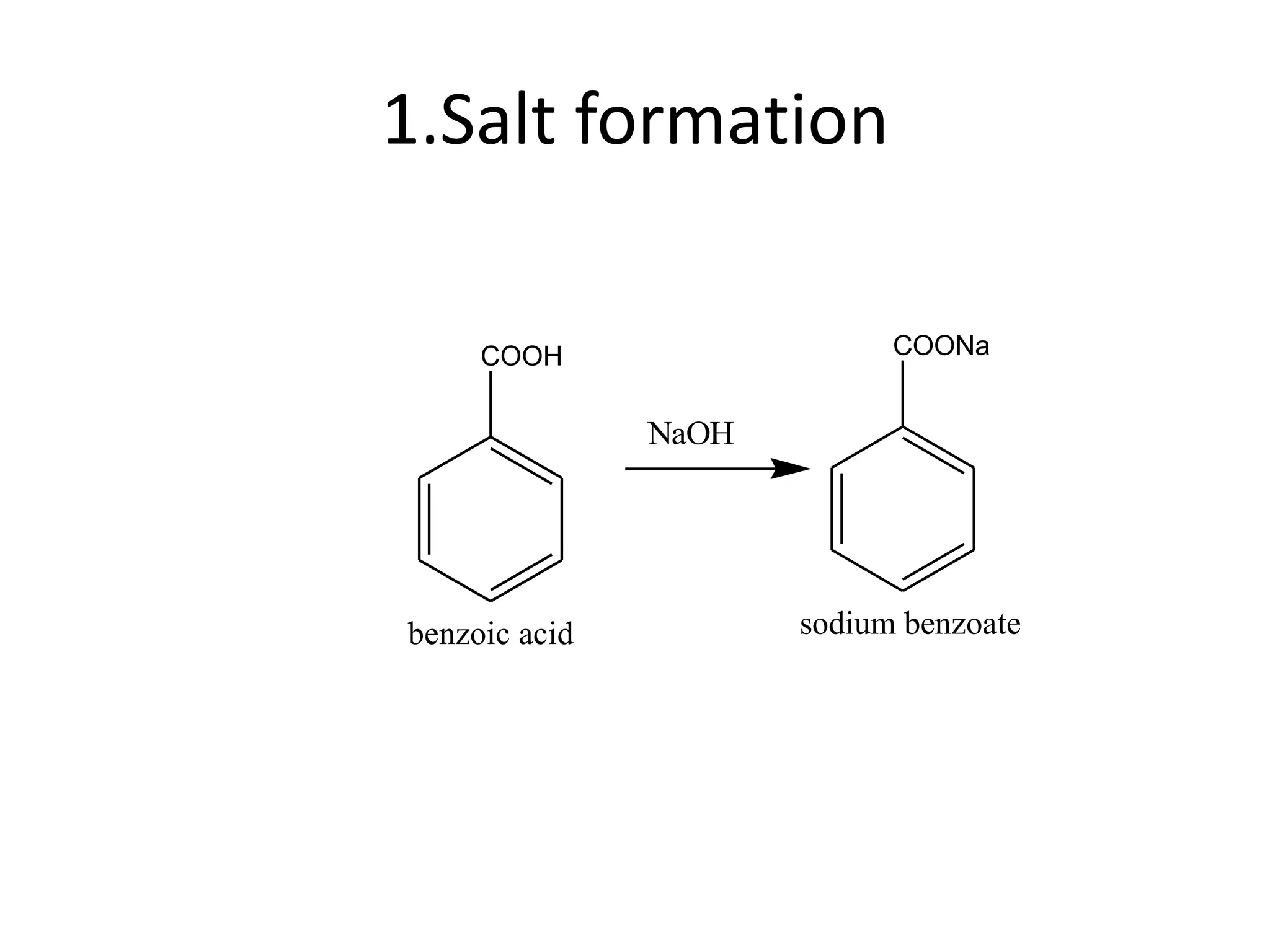
The document discusses aromatic acids, particularly their structure, acidity, and preparation methods, highlighting the role of electron withdrawing and releasing groups on acidity. It outlines several methods for preparing aromatic acids and their derivatives and describes various reactions involving these compounds. Additionally, it mentions uses for aromatic acids, such as in germicides and food preservatives.