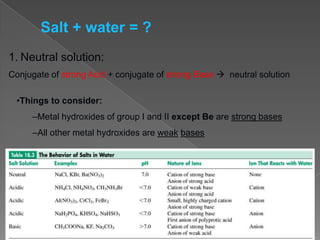
This document discusses salt hydrolysis, which is the reaction of salt ions with water that can result in an acidic, basic, or neutral solution. Salts formed from a weak acid and strong base produce a basic solution, as the conjugate base of the weak acid will accept protons from water. Salts formed from a weak base and strong acid produce an acidic solution, as the conjugate acid of the weak base will donate protons to water. Salts formed from a strong acid and strong base produce a neutral solution. Examples of sodium ethanoate and ammonium chloride are provided to illustrate basic and acidic salt hydrolysis.