1. Hot rolling is a process where large metal pieces are heated and rolled into thinner cross sections between rollers.
2. The hot rolling process involves reheating slabs, descaling, roughing and finishing rolls to produce hot rolled coils.
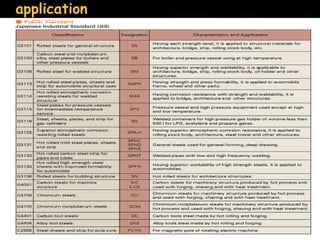
3. Hot rolled coils have a wide variety of applications including tubes, pipes, automotive parts, general structures, and are used to make cold rolled coils and sheets.