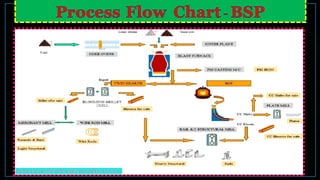
The blast furnace is a counter-current heat exchanger used to smelt iron from iron ore for steel production. Reactions inside reduce iron oxides to molten iron and separate impurities into a slag. The furnace operates at over 1500°C, using coke as the reducing agent and limestone as a flux. Key reactions include the reduction of iron oxides to iron and carbon monoxide, and the removal of impurities like sulfur. The process produces molten iron, known as pig iron, and a slag byproduct. The composition of the pig iron depends on the burden chemistry and furnace operating temperature.








![• Temperature of hearth zone is about 1500 – 1550 C.⁰
• The reactions occuring in this zone are electrochemical in nature :
1. [Mn ] = (Mn2+
) + 2 e-
[ anodic reaction ]
2.( Fe 2+
) + 2e-
= [ Fe] [cathodic reaction ]
Hence,
[Mn ] +( FeO ) = ( MnO) + [Fe ]
[Mn] +( Fe 2+
) = ( Mn2+
) + [ Fe ] .](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/blastfurnacepresentation2-160420113757/85/Blast-furnace-presentation-12-320.jpg)