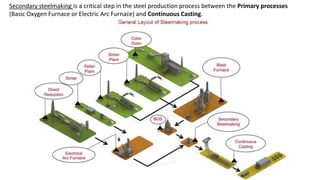
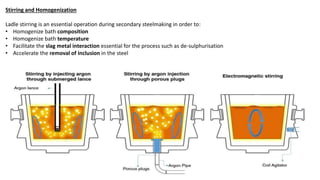
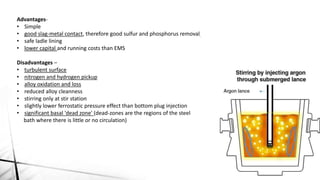
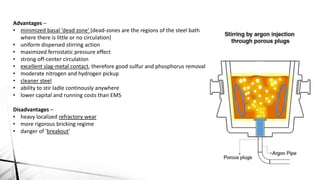
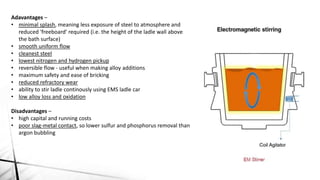
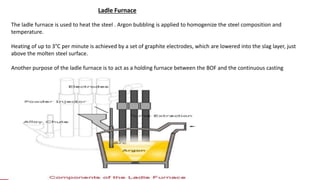
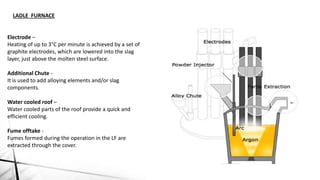
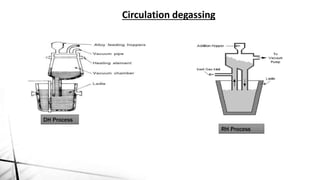
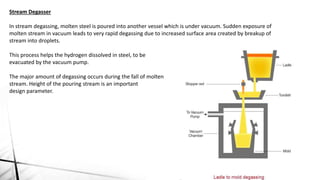
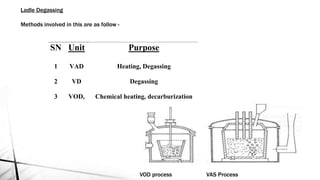
The document summarizes key aspects of secondary steelmaking processes. It discusses homogenization through ladle stirring using argon bubbling or electromagnetic stirring. Degassing processes like ladle degassing and circulation degassing are also covered, which are used to remove gases from steel. Other secondary steelmaking stages discussed include heating in the ladle furnace, deoxidation using aluminum, decarburization in vacuum degassing, and desulphurization in the ladle through slag-metal reactions. Injection metallurgy techniques like powder injection and wire feeding are also summarized for adding alloying elements to molten steel.






![Deoxidation
Deoxidation is the process to eliminate oxygen, which may be free
dissolved in steel or may have reacted to form various oxides.
Aluminum is a very powerful deoxidizing agent and controls the
oxygen activity in the liquid steel [1] .
Using the equilibrium constant K to determine the composition of
the Al-O system at equilibrium, the Al-O equilibrium curves are
plotted. As can be seen in the graph below, deoxidation with
aluminum is more efficient at lower temperatures.
De-oxidation hierarchy: Ca > Al > Si > Mn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondarysteelmaking-150413214255-conversion-gate01/85/Secondary-steel-making-19-320.jpg)

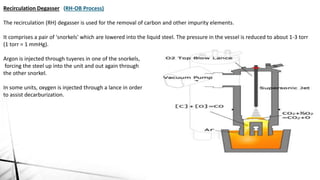
![Decarburization
The removal of dissolved carbon from the steel during vacuum degassing arises from the following reaction:
[C] + [O]→CO (g)
Using the equilibrium constant K to determine the composition of the C-O system at equilibrium, the C-O
equilibrium curves are plotted.
For RH degassers the rate constant for the carburization is given by the relationship [1] while the time needed to
decarburize is given by relationship [2]:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondarysteelmaking-150413214255-conversion-gate01/85/Secondary-steel-making-21-320.jpg)
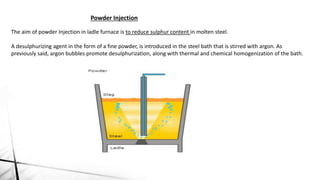
![Desulpurisation
Desulfurization in the ladle is achieved by:
Adding a synthetic CaO based desulfurizing slag at vessel tapping;
Aluminum deoxidizing the steel to very low oxygen activity (otherwise the Al will react preferentially with O);
Vigorously stirring the steel in the tank degasser in order to thoroughly mix the metal and slag.
The chemical reaction of the desulphurization process in the ladle is: - 3(CaO)+2[Al]+3[S] ---- 3(CaS)+(Al2O3)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/secondarysteelmaking-150413214255-conversion-gate01/85/Secondary-steel-making-22-320.jpg)