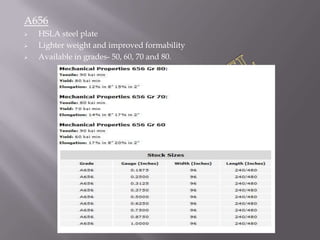
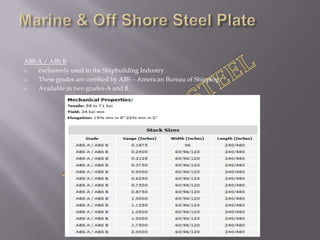
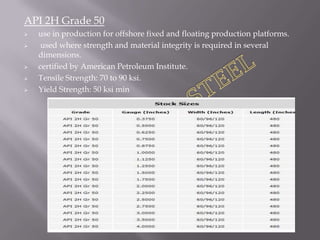
Steel plates are often used to make a variety of products through cutting and welding processes. Common applications include ships, bridges, buildings, pressure vessels, machinery, and military equipment. The document discusses the manufacturing process for steel plates including rolling, accelerated cooling, hot leveling, and ultrasonic testing to ensure quality. It then provides an overview of various international specifications for steel plates, outlining grades and their intended uses.