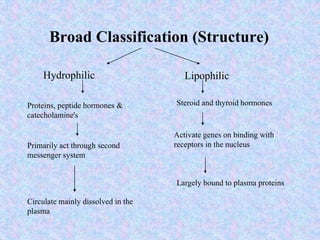
The document discusses the mechanisms and actions of hormones, defining them as biochemical messengers produced by glands that regulate various bodily functions. It classifies hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic categories based on their water solubility, detailing their interaction with cell receptors and how they influence gene activation and cellular responses. The document outlines the processes of action for both water-soluble and lipid-soluble hormones, emphasizing their unique pathways and roles in physiological effects.










![ Binding to specific cell receptor in the cell membrane and
form hormone-cell receptor complex, which diffuses to
nucleus
The receptor is eventually released for re-use
Steroid activates a specific gene to produce mRNA
mRNA pass out into the cytoplasm and initiates protein
[enzyme] synthesis
The whole process is called mobile-receptor hypothesis in
which a steroid hormone is not attached to the plasma
membrane, but seem to move freely in the nucleoplasm
HOW LIPID-SOLUBLE HORMONES
WORK?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hormoneaction-160501070511/85/Hormone-action-12-320.jpg)





