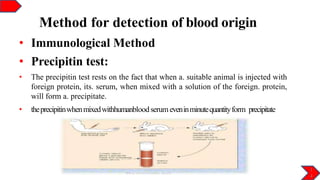
This document discusses various methods for examining blood stains, determining if they are human or animal, and identifying their blood group. Physical examination of the stain provides initial clues. Chemical tests like benzidine and phenolphthalein can detect the presence of blood. Additional confirmation is done through physicochemical tests like thin layer chromatography and electrophoresis. Microscopic analysis of crystals formed by reagents helps identify hemoglobin and confirm human blood. Spectroscopy examines the absorption bands of oxyhemoglobin, methaemoglobin, and carboxyhemoglobin. Immunological tests like precipitin and latex agglutination inhibit reactions between human blood extract and antibodies. The enzymatic method analyzes isoenzyme patterns through electrophoresis to differentiate human from