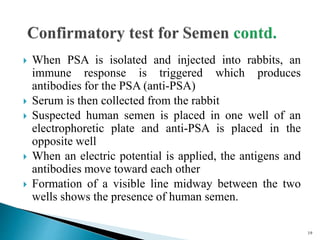
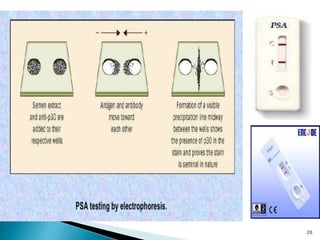
The document discusses the identification and analysis of bodily fluids in forensic investigations. It explains that serology, the analysis of bodily fluids, precedes DNA analysis and involves visual examination of stains as well as presumptive and confirmatory tests to identify fluids like blood, semen, and saliva. A variety of chemical tests are used to detect enzymes or proteins in different bodily fluids that can identify the fluid and potentially link it to a individual.