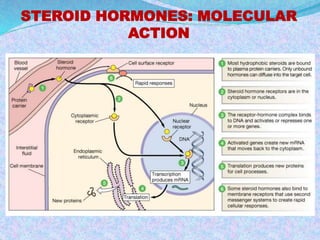
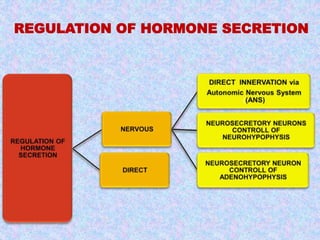
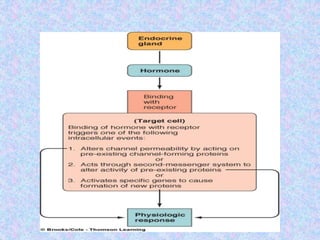
1) Hormones are organic substances that regulate growth, metabolism and other functions by acting as biochemical messengers. They can be classified based on their chemical composition and target organs.
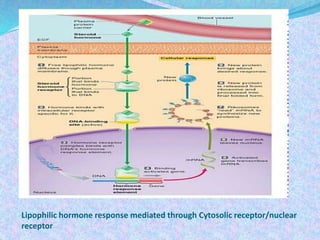
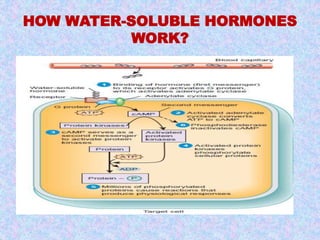
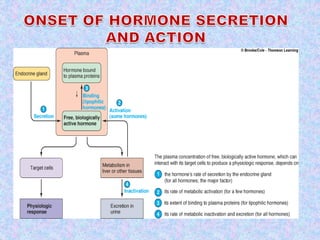
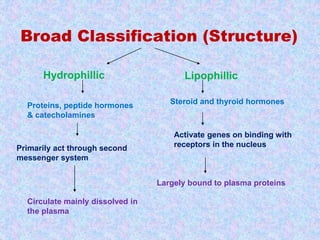
2) Hormone action involves processes like synergism, permissiveness, antagonism and feedback loops. Lipid-soluble hormones like steroids directly enter cells and activate genes, while water-soluble hormones trigger intracellular signaling cascades.
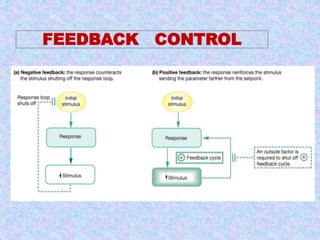
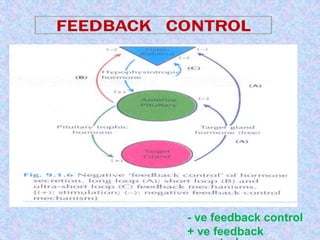
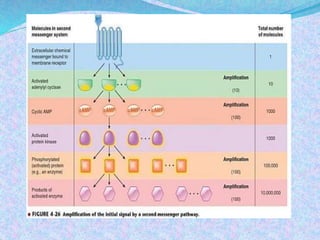
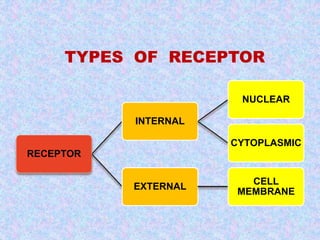
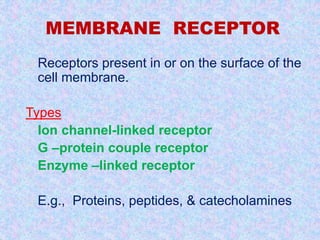
3) The document discusses the mechanisms and characteristics of hormone action, including the different classes of receptors, signal amplification pathways, and how lipid-soluble and water-soluble hormones elicit their effects on target cells and tissues. Negative and positive feedback loops help regulate hormone secretion.









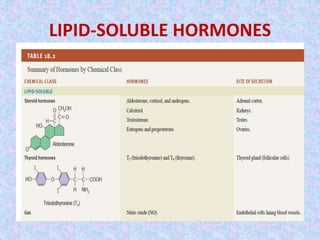
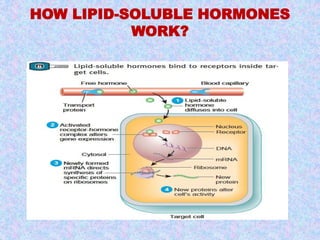
![HOW LIPID-SOLUBLE HORMONES
WORK?
• Binding to specific cell receptor in the cell membrane
and form hormone-cell receptor complex, which
diffuses to nucleus
• The receptor is eventually released for re-use
• Steroid activates a specific gene to produce mRNA
• mRNA pass out into the cytoplasm and initiates
protein [enzyme] synthesis
why do they penetrate the cell?
the whole process is called mobile-receptor
hypothesis in which a steroid hormone is not attached
to the plasma membrane, but seem to move freely in
the nucleoplasm](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mechanismactionhormone-141105010053-conversion-gate02/85/Mechanism-action-hormone-17-320.jpg)